
- The Liner Shipping Industry
and
Carbon Emissions Policy-
- September
2009-
- The Liner Shipping Industry and Carbon Emissions Policy
-
- Dear Reader: Governments, industries, and consumers around the
world are responding to concerns about the effect of carbon dioxide
(CO2 ) emissions on climate change by determining how to design more
efficient energy and environmental practices and regulatory regimes.
We have prepared this paper to inform you about the work of the
liner shipping industry on this issue.
-
- Maritime shipping produces an estimated 2.7% of the world's CO2
emissions, while at the same time it provides an essential service
to all nations' economies and consumers. The World Shipping Council
and its Member liner shipping companies are supporting the efforts
of governments at the International Maritime Organization (IMO) to
develop a new regulatory regime addressing CO2 emissions from ships.
This work on carbon emissions follows last year's successful IMO
agreement on new regulations to reduce ships' NOx, SOx, and
particulate matter (PM) emissions. CO2 emissions are now the focus
of debate at the IMO, at the United Nations Framework Convention on
Climate Change (UNFCCC), and within the capitals of numerous
governments.
-
- In this paper you will read about many of the issues, important
principles, and challenges in constructing an effective and
efficient international carbon emission regime for shipping.
Developing that regime is difficult. It is not difficult because the
industry opposes it. It is difficult for a variety of reasons,
including: political differences between governments on how the
resulting economic burdens should be allocated; the fact that the
vast majority of ships' emissions occur outside the territory of any
government; the absence of effective precedent no transportation
mode has a comprehensive carbon emission regime that can simply be
borrowed and applied; and it is difficult because there are very
different approaches under discussion with additional proposals
likely to emerge.
-
- The task is also complicated by the fact that maritime shipping
is by far the most carbon efficient mode of transporting goods.
Despite the very significant efficiencies of marine transportation
today, further improvements in efficiency are being regularly made,
and even greater improvements will be possible in the future.
Consequently, a central challenge lies in developing a regime that
not only stimulates even greater improvements in the energy
efficiency of the world's fleet, but a regime that does not produce
an unintended consequence of shifting the transportation of goods to
other transport modes (and their consequent increase in emissions)
or otherwise discouraging maritime transportation. In fact, total
global CO2 emissions would be reduced if more goods were transported
by maritime commerce instead of the other less energy efficient
transportation modes.
-
- This paper has been organized into three sections. Part I
provides a brief description of the liner shipping portion of the
maritime shipping industry. Part II addresses common questions about
the generation of CO2 emissions from ships. Part III describes the
international process for developing new ship emission regulations,
the current status of the international discussions, and some of the
main issues that make these negotiations challenging.
-
- The liner shipping industry is committed to working with
governments and other interested organizations to develop a sound
carbon emissions regulatory regime for shipping. We hope this paper
will inform interested readers about some of the issues that we will
need to address on the road to accomplishing that objective. Please
contact us if you have any questions regarding its content.
-
- Thank you for your interest.
-
- Sincerely,
Christopher L. Koch
President and CEO-
- I. The Liner Shipping Industry
-
- What is liner shipping?
-
- Liner shipping is the service of transporting goods by means of
high capacity, ocean going ships that transit regular routes on
fixed schedules. Liner vessels, primarily in the form of container
ships and roll on/roll off ships, carry more than 581
percent of the goods by value moved internationally by sea each
year. The 29 liner shipping companies represented by the World
Shipping Council (WSC) carry approximately 90 percent of the world's
containerized ocean traffic. WSC members also serve as the principal
ocean transporters of cars, trucks and other heavy equipment around
the world.2
-
- In addition to the liner shipping sector that moves mostly
containerized goods and vehicles, the maritime industry at large
encompasses a wider set of ship operations, including tankers for
transporting liquids, bulk carriers that haul commodities such as
grain, coal and iron ore, passenger ships, cruise ships, tugs and
barges, ferries, fishing fleets, and offshore drilling and supply
vessels.
-
- The world's seaborne cargo shipping fleet consists of more than
75,000 ships3 that fly the flags of many nations and
operate regularly between ports in over 200 countries.4
-
- What is the role of the World Shipping Council?
-
- The World Shipping Council's mission is to provide a coordinated
voice for the international liner shipping industry in its work with
policymakers and industry groups on international transportation
issues. WSC works with a broad range of public and private sector
stakeholders in support of policies and programs to advance the
development of an efficient, secure, and sustainable global
transportation network. The WSC and its member companies partner
with governments and collaborate with a wide range of government and
non government organizations to formulate solutions to some of the
world's most challenging transportation problems. In 2009, the World
Shipping Council was granted consultative status at the United
Nation's International Maritime Organization (IMO), which allows WSC
to participate in the process of setting new international
regulations that will affect the liner shipping industry.
-
- Why is the liner shipping industry so important economically?
-
- It is the conduit of world trade.
Ocean shipping is
the primary conduit of world trade, a key element of international
economic development, and a central reason why the world enjoys
ready access to a diverse spectrum of low cost products. Seventy
five percent of internationally traded goods are transported via
ocean going vessels.5 In 2008, world container ship
traffic carried an estimated 1.3 billion metric tons of cargo.6
Products shipped via container include a broad spectrum of consumer
goods ranging from clothing and shoes to electronics and furniture,
as well as perishable goods like produce and seafood. Containers
also bring materials like plastic, paper and machinery to
manufacturing facilities around the world.
- It is the most efficient mode of transport for goods.
In
one year, a single large containership could carry over 200,000
containers. While vessels vary in size and carrying capacity, many
liner ships can transport up to 8,000 containers7 of
finished goods and products. Some ships are capable of carrying as
many as 14,000 TEUs (twenty foot equivalent units). It would require
hundreds of freight aircraft, many miles of rail cars, and fleets of
trucks to carry the goods that can fit on one large container ship.
In fact, if all the containers from an 11,000 TEU ship were loaded
onto a train, it would need to be 44 miles or 77 kilometers long.
- It is comparatively low cost.
Ocean shipping's
economies of scale, the mode's comparatively low cost, and its
environmental efficiencies enable long distance trade that would not
be feasible with costlier, less efficient means of transport. For
example, the cost to transport a 20 foot container of medical
equipment between Melbourne, Australia and Long Beach, California
via container ship is approximately $2,700. The cost to move the
same shipment using airfreight is more than $20,000.
- It is a global economic engine.
As a major global
enterprise, the international shipping industry directly employs
hundreds of thousands of people and plays a crucial role in
stimulating job creation and increasing gross domestic product in
countries throughout the world. Moreover, as the lifeblood of global
economic vitality, ocean shipping contributes significantly to
international stability and security.
|
5 |
Lloyd's
Maritime Intelligence Unit. See :
http://www.imsf.info/papers/NewOrleans2009/Wally_Mandryk_LMIU_IMSF09.pdf |
|
6 |
Clarkson's Research - World Seaborne
Trade - March 2009 |
|
7 |
Containers are intermodal boxes built to
international standards and specifications. The same container can
be moved by truck, on rail and via ship. The most common sizes are
20-foot containers, which are 20 feet in length and 40-foot
containers, which are 40 feet in length. The standard unit measure
for all containers is in Twenty-Foot Equivalents (TEU). A 40-foot
container equals two TEUs. |
- Why is the shipping industry so important environmentally?
-
- It is the most carbon efficient mode of transportation.
As
illustrated by the graph below, ocean shipping is by far the most
carbon efficient mode of transportation. Because of its inherent
advantages, including much greater payloads per trip than ground or
air, the industry emits far less carbon dioxide (CO2 ) per ton/mile
of cargo than any other transportation mode.-
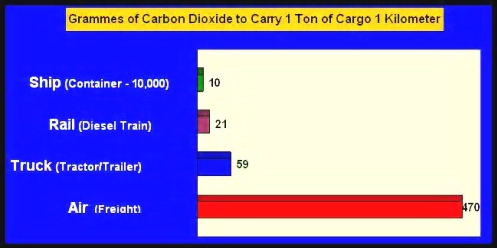
- Source: Data provided by Network for
Transport and the Environment
-
- According to the figures in this graph, transporting the 2008
volume of 1.3 billion metric tons of cargo via containership
generated approximately 13 billion grams of CO2 per kilometer . If
that same volume had been transported by airfreight instead, carbon
dioxide emissions would have increased by 4,700% to some 611 billion
grams of CO2 per kilometer.
-
- II. Carbon Dioxide Emissions (CO2 )
from Ships
-
- Ships, like all other mobile sources such as cars, trucks,
trains, and planes that are powered by fossil fuels, emit carbon
dioxide in their engine exhaust.
-
- How much carbon dioxide does the international shipping
industry emit per year?
-
- International maritime shipping accounts for approximately 2.7
percent of annual global greenhouse gas emissions.8
Container ships account for approximately 25% of that amount, while
moving roughly 52%9 of maritime commerce by value.
-
- Does international maritime shipping of goods produce more
CO2 emissions than transporting locally produced goods because of
the long transportation distances involved?
-
- Generally, the answer is no. Because maritime shipping is the
most carbon efficient form of transportation, shipping goods across
the ocean often results in fewer carbon emissions than transporting
such goods domestically.
-
- For example, a ton of goods can be shipped from the Port of
Melbourne in Australia to the Port of Long Beach in California, a
distance of 12,770 kilometers (7,935 miles), while generating fewer
CO2 emissions than are generated when transporting the same cargo in
the U.S. by truck from Dallas to Long Beach, a distance of 2,307
kilometers (1,442 miles). Similarly, a ton of goods can be moved
from the port of Ho Chi Minh City in Vietnam to Tianjin, China, a
distance of 3,327 kilometers (2,067 miles) generating fewer CO2
emissions than would be generated if the same goods were trucked
from Wuhan in Central China to Tianjin, a distance of 988 kilometers
(614 miles.)10 The wine industry recently examined this
issue and found that a bottle of French wine served in a New York
restaurant will have a lower carbon transportation footprint than a
bottle of California wine served in that restaurant.11 A
whitepaper released for the Transport Intelligence Europe Conference
states that researchers evaluating this issue for the World Economic
Forum “found that the entire container voyage from China to
Europe is equaled in CO2 emissions by about 200 kilometers of long
haul trucking in Europe. So, for most freight, which is slow moving,
there is not really a green benefit to moving production to
Europe.”12
-
- In fact, shipping goods by sea to ports adjacent to major retail
markets is the most carbon efficient means of moving most products
to market in a global economy.
-
- What efforts are being made by the industry to reduce its
carbon footprint?
-
- The liner shipping industry continues its significant efforts to
reduce its carbon emissions, through a wide variety of measures.
-
- Increasing Efficiency
A recent study by Lloyd's
Register found that the fuel efficiency of container ships (4500 TEU
capacity) has improved 35% between 1985 and 2008.13 If
one compares today's largest ships with container vessels of the
1970s, the results are even more pronounced. A 1500 TEU container
ship built in 1976 consumed 178 grams of fuel per TEU per mile (or
96 grams per TEU per kilometer) at a speed of 25 knots.
The
fuel consumption per TEU per mile for a modern 12,000 TEU vessel,
built in 2007, is only 44 grams (or 24 grams per TEU per kilometer).
Looking at this example, carbon efficiency on a per mile per cargo
volume basis has improved 75% in 30 years as a result of
technological improvements and the utilization of larger vessels.
This improvement is even greater if one considers that today's ships
are operating at slower speeds that produce even greater reductions
in fuel consumption.
- Advancing Technology
The industry continues to seek
engineering and technological solutions to increase its energy and
carbon efficiency. Efforts are underway to engineer better hull and
propeller designs, implement waste heat recovery, and reduce onboard
power usage to minimize emissions. Moreover, the industry is
studying opportunities to switch to lower carbon energy sources such
as Liquid Natural Gas (LNG) and bio fuels.
- Improving Operations
Industry members are implementing
a wide range of operational strategies to reduce energy use. This
includes employing advanced information technology to aid in
operational decision making to improve efficiency, including vessel
routes, speeds, load factors, and other fleet management strategies
that promote conservation.
- Partnering for Progress
Many liner shipping companies
are members of the Clean Cargo Working Group, and adhere to
environmental stewardship guidelines established by Business for
Social Responsibility.14 Members voluntarily track
emissions, set efficiency targets, and examine ways to offset
emissions through certified international programs. In addition to
the wide range of steps the industry is taking on its own accord,
the WSC and its members are working through the International
Maritime Organization to develop uniform standards for improving the
energy efficiency of ship designs and exploring what global legal
structure would best serve to reduce carbon emissions from maritime
shipping.15
|
8 |
Second International Maritime
Organization Green House Gases Study 2009 |
|
9 |
http://www.imsf.info/papers/NewOrleans2009/Wally_Mandryk_LMIU_IMSF09.pdf |
|
10 |
Comparison is based on the CO2 emissions
by transport mode provided by The Network for Transport and the
Environment. |
|
11 |
American Association of Wine Economists,
“ Red, White, and Green: The Cost of Carbon in the Global
Wine Trade, ” AAWE Working Paper #9, Victor Ginsburgh, Oct.
2007. Available at:
http://www.wine-economics.org/workingpapers/AAWE_WP09.pdf |
|
12 |
http://www.ticonferences.com/gds_europe/whitepapers/Nearshoring_Beat_Simon.pdf |
|
13 |
Ship Efficiency Trend Analysis, Report
2008/MCS/ENV/SES/SES08-008, Marine Consultancy Services, Lloyd's
Register, London, October 2008. |
|
14 |
See:
http://www.bsr.org/consulting/working-groups/clean-cargo.cfm |
|
15 |
See
http://www.unctad.org/sections/wcmu/docs/cimem1p09_en.pdf
See: IMO Energy Efficiency Design Index and the Energy Efficiency
Operational Index, and the Shipboard Efficiency Management Plan. |
- Why is the shipping industry participating in the effort
to reduce carbon emissions and address global warming?
-
- To be responsible environmental stewards.
The liner
shipping industry and its customers recognize that environmental
stewardship requires their participation in developing an effective
way to address their carbon dioxide emissions.
- To inform the process.
The process of setting
international carbon management policy must be guided by scientific,
technical, economic and operational knowledge. Policy solutions must
be environmentally effective, realistic, and sustainable. The
resulting carbon regime must be global in scale, legally binding,
and applicable to all ships. It would also be counter productive to
prejudice ocean transportation vis à vis other forms of
transportation that are actually more carbon intensive.
- To ensure an effective international standard is
achieved.
The industry recognizes that an international,
environmentally effective regulatory regime is the best way to avoid
a confusing and inefficient tangle of carbon emission regimes
established by different regional, national or local governments.
- To achieve lower fuel costs through improved
efficiency.
Reducing carbon emissions by improving ships'
energy efficiency will lower fuel consumption while ensuring that
the movement of goods by sea remains the most carbon efficient means
of moving goods from their point of production to the marketplace.
- What is the expected trend in carbon dioxide emissions
from the shipping industry?
-
- Because of its economic and environmental advantages over other
transportation modes, the reliance on ocean shipping to transport
raw materials and manufactured goods internationally is expected to
rise. The U.N.'s International Maritime Organization (IMO) has
estimated that without changes in current operating efficiencies and
with increasing trade volumes, total ship emissions of CO2 will
increase. However, introduction of new technology, changes to ship
and engine design and improvements to operating procedures will
ensure a much slower rate of growth for CO2 emissions. Forecasting
exactly how much CO2 emissions will be attributable to liner
shipping in future years is subject to considerable uncertainty due
in part to variations in international trade volumes, but more
importantly due to continuing improvements in vessel efficiency that
have not yet been quantified, and the effect of expected global CO2
rules to be developed under the IMO.16
-
- What are the potential methods of reducing carbon
emissions from marine shipping?
-
- There are a wide range of efforts underway to increase energy
efficiency in the shipping industry and thereby reduce CO2
emissions. Technical methods include improved ship/hull
design to reduce drag, and more efficient propulsion systems,
including engines that use low carbon fuel. Operational methods
include employing advanced information technology to manage vessel
weight, reducing speed, and improved weather routing to maximize
fuel efficiency.17
-
- What incentives currently exist for the industry to lower
fuel use and carbon emissions?
-
- Fuel costs are a dominant factor in the bottom line
profitability of shipping companies. Fuel costs account for as much
as half of a container ship's operating expenses. Accordingly,
market forces already provide a significant incentive for the
industry to minimize energy use (and therefore emissions). This
incentive will continue to intensify as energy prices resume their
expected upward climb due to market conditions, even in the absence
of new climate change policies that may or may not increase fuel
prices further.18
-
|
16 |
See IMO, “ Prevention of Air
Pollution from Ships, ” MEPC 59, INFO. 10, April 9, 2009.
available at:
http://www.imo.org/includes/blastDataOnly.asp/data_id%3D26047/INF-10.pdf |
|
17 |
See: OECD, Joint Transport Research
Center, Discussion paper No. 2009-11, “ Greenhouse Gas
Emission Reduction Potential from International Shipping, ”
May 2009, at
http://www.internationaltransportforum.org/jtrc/DiscussionPapers/jrtcpapers.html |
|
18 |
See:
http://money.cnn.com/2008/12/17/news/economy/oil_eia_outlook/?postversion=2008121716 |
- III. Air Emission Regulation and the
Shipping Industry
-
- Currently, what is the international process for
regulating greenhouse gas emissions from ocean going vessels and
what are the next steps?
-
- Governments across the globe establish legally binding
international standards through the United Nation's International
Maritime Organization (IMO). The IMO is the appropriate forum to
create a comprehensive legal regime to address vessel carbon
emissions, because ships are mobile assets that are registered in
many different flag states and call at many different ports around
the world. Ships need a predictable and uniform set of regulations.
-
- Effective carbon emission reduction policy also favors an
international regime that applies to ships wherever they may be
operating, because that is the approach that truly reduces CO2 from
the shipping sector world wide. More limited national or regional
schemes would only address emissions associated with certain voyages
or within certain jurisdictions. Development of an effective climate
regime applicable to international shipping should apply to all
international ship movements across the globe.
-
- The IMO also possesses unique technological, operational, and
legal expertise in the ocean shipping sector. Through the
establishment of binding international regulations, the IMO provides
for a consistent and uniform set of standards for ships operating
throughout the world, greatly enhancing predictability, compliance,
enforcement, and the achievement of shared environmental objectives.
-
- In 2008, the IMO successfully created a rigorous, new regulatory
regime for those ship emissions that can adversely affect human
health, namely nitrous oxides (NOx), sulfur oxides (SOx) and
particulate matter (PM). Those rules were established as part of
Annex VI to the International Convention for the Prevention of
Pollution from Ships (MARPOL) and are being implemented around the
world. Annex VI, however, did not directly address carbon emissions.
-
- Governments at the IMO are now engaged in negotiations to
develop a global carbon emissions regime applicable to shipping. The
organization is also drafting specific standards concerning ship
design and other technical issues aimed at reducing CO2 emissions.19
Most stakeholders expect the current negotiations to lead to a final
agreement sometime in 2011.
-
- At the same time, governments participating in the United
Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) are focused
on developing a successor to the “Kyoto Protocol”, whose
provisions are effective through 2012. The Kyoto Protocol does not
address greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions associated with international
aviation or shipping. Instead, GHG emissions associated with
international aviation and marine shipping are expected to be
addressed through negotiations at the International Civil Aviation
Organization (ICAO) and the International Maritime Organization
(IMO). Both of these organizations were created to facilitate
international agreement on standards applicable to these sectors,
which routinely operate across numerous national borders and are
subject to unique technology considerations. Nevertheless, some
countries have called for maritime and aviation activities to be
regulated under the UNFCCC, while other governments have strongly
argued that international maritime emissions should be addressed
through the IMO and international aviation emissions should be
addressed through the ICAO. The next round of comprehensive
international talks pursuant to the UNFCCC is scheduled to take
place in Copenhagen in December, 2009.
-
- The outcome of these UNFCCC negotiations should help better
define the overall direction of climate policy. Developments at the
UNFCCC in December will further shape the debate at the IMO as those
negotiations continue in the spring of 2010. The next meeting of the
IMO Marine Environment Protection Committee to address carbon
emissions is scheduled for March 2010.
-
|
19 |
See: IMO Energy Efficiency Design Index
and the Energy Efficiency Operational Index, and the Shipboard
Efficiency Management Plan. |
- What are the issues that make reaching agreement
challenging? Why is implementation difficult if everyone agrees on
the need to reduce CO2 emissions?
-
- CO2 regulatory regimes do not yet exist in most countries. It is
both technically and politically difficult to create such systems
for fixed emission sources (like power plants) in domestic
economies. It is even more challenging to address mobile
transportation sources, like automobiles, rail, aviation and
shipping. The challenge of addressing these mobile sources becomes
even more complex when those sources operate under the registries of
different nations, call at ports in multiple nations, and generate
emissions on the high seas outside any nation's jurisdiction.
-
- The IMO has in fact made substantial progress on developing an
energy efficiency design index for new ships to reduce carbon
emissions. It is generally accepted, however, that such a design
index, if only applied to new ships, is unlikely, by itself, to
sufficiently address the issue. Accordingly, the IMO is considering
several proposals characterized as “market based instruments”
(MBIs) and other hybrid proposals to create a more comprehensive
regime. These proposals are novel, and there is little precedent or
experience to guide governments. While it appears probable that the
IMO will develop a new convention in the foreseeable future, one
should recognize that the issues being considered present unique
challenges. The following provides a short description of some of
those challenges.
-
| |
- Macro Political Questions in the Climate Debate
The
IMO's regulatory regimes are based on the principle that all
ships, regardless of who owns them or where they are registered,
should comply with the same rules. The World Shipping Council and
other industry organizations strongly support this principle.
Furthermore, a carbon emission reduction regime would have little
positive effect on climate change concerns if a ship operator
could avoid it by changing the registration of its ship.-
- At the same time, however, there is a macro political
disagreement between developed and developing nations about
appropriate restrictions on carbon emissions. The United Nations
Framework Climate Change Convention (UNFCCC) and “Kyoto
Protocol” distinguished between Annex I countries with one
set of carbon emission reduction obligations and lesser developed
non Annex I countries that did not have such obligations.20
-
- Additionally, only a little more than one third of the world
cargo fleet is registered in Annex I countries. Many non Annex I
countries under the existing Kyoto Protocols insist that a new
global carbon regime must not impose burdens on their developing
economies. Other governments insist that the carbon emissions
from non Annex I countries now and projected in the foreseeable
future are so substantial that there can be no meaningful impact
on CO2 emissions or their effect on climate without the
participation of these governments and their economies.
-
- This set of political disagreements between governments is
beyond the capacity of the shipping industry to resolve, but
these issues will need to be addressed before the content of a
new regime can be developed.
-
- Market Based Instrument Options
Market based
instruments (MBI) include a variety of economic or market
oriented incentives and disincentives, such as taxes or tax
credits, new fees, or tradable emissions limitations, often
referred to as “Cap and Trade”.-
- Marine Fuel Levy: One MBI concept being given
consideration at the IMO is the establishment of an international
“levy” on marine fuel, with the revenues being
dedicated to a new United Nation's climate fund. Proponents
advocate that the levy approach would be easier to implement and
operate than other MBI approaches being considered. This proposal
has been made by Denmark, and has been set forth in more
detail and with more specifics than other MBI proposals.21
Issues surrounding it include the following:
-
- Will governments be willing to adopt a UN administered
international levy on the sales of fuel?
- What would be the mechanism for collection and
enforcement?
- What entity should be responsible and accountable
for the collection of the revenues associated with the fund? What
is the enforcement scheme to ensure the payment of the levy?
- What
is the role of port states in that enforcement scheme? What are
the penalties and consequences to buyers and/or sellers who try
to evade payment of the fee?
- What would be the level of the levy to be applied? How would
it be set, raised, lowered or suspended?
- Assessing fees to a product will make it more expensive and
will thus cause users to consume less of it, but predicting
precise emission reduction results from a levy is problematic.
For that reason, advocates of the concept argue that carbon
emissions reductions would also be accomplished from this
proposal via the use of the revenues generated from the levy for
carbon mitigation projects. Questions about the control and
management of such a fund are many, including:
- Who would
control the disbursement of the revenues collected?
- Is the
Clean Development Mechanism of the UNFCCC the most appropriate
and efficient vehicle for ensuring the funds are productively
used for CO2 reduction?
- Should the funds, or a portion of the
funds, be devoted to research and development that is specific to
improving fuel economy in the world's shipping fleet, alternative
propulsion systems, and other measures to reduce CO2 emissions -
both in the short term and long term? If yes, what entity would
be responsible for determining which research institutions and
other stakeholders receive the funds and that the work is
completed and disseminated?
- If the funds are to be split
between non maritime CO2 reduction projects and research and
development projects specific to the maritime sector, what should
be the relative split in funding?
- What mechanism should be
used to ensure that projects actually result in CO2 emission
reductions as opposed to theoretical or paper reductions?
- Is the levy a flat, uniform assessment per ton of fuel, or
does the amount of the tax vary depending on the efficiency of
the vessel in order to create an additional economic incentive
for the construction and operation of more efficient vessels?
Japan, for example, has proposed that a vessel operator should
get a rebate under the levy system if it improves vessel
efficiency.22
- This concept has been proposed as an alternative market based
instrument to emission “cap and trade” type concepts.
If this course were pursued, industry would need assurance that
other measures are not also adopted so that it faces both a fuel
levy plus other market based instruments.
- Cap and Trade or Emissions Trading: The
European Commission, some European governments, and some industry
groups have expressed support for the idea of developing an
alternative carbon emissions trading system as the most
appropriate MBI. Unlike the Danish levy proposal, however, there
has been no proposal made that specifically describes how such an
emissions trading system would function at an operational level.
The absence of a clear proposal has made discussion and
assessment of the concept difficult. If this avenue were to be
pursued, a significant number of questions would need to be
addressed, as the design and operation of an emission trading
proposal is likely to be more complicated than a levy on marine
fuels. The unresolved issues include:
-
- How is a “cap” on emissions from shipping
established?
- What is the level of the cap and how much is it
lowered over what period of time?
- What is the baseline year
for establishing the cap?
- Will allowances be allocated in a
manner that gives credit to those vessel operators that have
implemented fuel efficiency efforts to date?
- How are the allocations of the emission allowances within the
cap distributed amongst the various sectors of the industry?
- Are
they auctioned? If so, by whom?
- Are they sold at a fixed
price, and if so, who sets that price?
- If sold or auctioned,
who receives the revenues?
- What are the permissible uses of
the revenues raised? (Additional questions similar to those that
exist for the marine fuel levy proposal discussed above must also
be addressed.)
- Are the emission allowances allocated at no
charge? If so, by whom? According to what criteria?
- Who is covered by the cap? What vessels? Are there vessels
that are not covered?
- Who must hold the emission allowances? The ship owner? The
ship operator?
- What are the trading characteristics of the allowances? For
example:
- Once allocated, are the emission allowances freely
tradable? Are the allowances issued and sold on an annual basis
or a multi year basis?
- Is there a limit on how many allowances
may be purchased or acquired by a particular vessel or
company?
- Is there a restriction on who may purchase
allowances?
- Is there any expiration or “use-by”
date on an emission allowance or can they be “banked”
indefinitely?
- Does an emission allowance shrink in size over
time at the same rate as the total emission cap is reduced over
time?
- May ship operators purchase and use carbon emission
allowances from other industrial sectors?
- Most stakeholders
supporting development of a cap and trade system for maritime
emissions have argued that such a system must be “open”.
An open system would allow trading of allowances across
industrial sectors, but also requires, by definition,
establishment of an economy wide cap and trade system.
- If the
countries that have established such cap and trade systems are
limited to certain developed countries, how does the system
function in the shipping sector, which constantly crosses borders
and operates on a global scale?
- If governments do establish a
cap for the economy as a whole, what criteria must govern the
regimes establishing such allowances in other sectors to be
acceptable for use by the maritime industry under its regime? 23
Who establishes and enforces such criteria?
- Can such an
emission trading system exist in the absence of a comprehensive,
international UN agreement and regime coming out of the
Copenhagen UNFCCC meetings?
- How could the IMO, as a
specialized maritime regulatory entity, monitor and administer a
cross sectorial trading process?
- If the emission trading
system is not an open system allowing for cross sectorial
trading, but instead the cap and trade regime is a closed system
governing only shipping, what would realistic carbon emission
caps be and how would the system allow maritime shipping to
service the expected increase in global commerce over time?
- How is the system enforced? (Similar questions may exist for
the fuel levy proposal.)
- For example, must emission allowances
be surrendered in order to purchase fuel? If so, the similarities
to a levy system are significantly increased, although
enforcement against fraudulent allowances and allowances
generated by non maritime sources may be more difficult than
simply collecting a tax.
- Does one require that all fuel oil
suppliers, whether they are located in a State party to the
Treaty or in a non party State, be registered as proposed in the
global levy system?
- Is a reporting scheme from vessels and/or
fuel suppliers necessary? What would that be?
- Such allowances
would need to be registered and monitored in some manner to
protect against cheating and counterfeiting. How does the
maritime sector administer such a system when allowances are
generated from a multitude of sectors and countries where many of
the countries are not party to or otherwise part of the system?
What is the responsibility of the flag state with respect to
enforcement?
- How would an arriving ship to a given port state
demonstrate compliance?
- What are the consequences of non
compliance?
- If a ship or ship operator does not possess enough allowances
to cover its emissions, what happens? Does it pay a tax or
penalty in order to continue to operate? If so, how is the level
of the penalty established? If not, must it cease operation until
it obtains sufficient emission allowances?
- Do all transportation modes have a similar carbon regime
applied to them so that maritime commerce is not disadvantaged
vis à vis other transport modes?
- Hybrid Proposals: Other governments at the IMO
have made hybrid MBI proposals that offer a variation on the
Danish levy concept or that are different from either the marine
fuel levy or emission trading systems. More such proposals are
likely to emanate from governments after the UNFCCC Copenhagen
meeting in December 2009 and prior to the next IMO Marine
Environment Protection Committee meeting in March of 2010.
-
- As previously mentioned, Japan has proposed that the
Danish levy concept be modified to provide a rebate of the levy
if a vessel operator improves the efficiency of its vessel. 24
Some have noted with favor that this idea seeks to incentivize
improved vessel efficiency and thus reduced carbon emissions.
Some have noted with disfavor that this idea would provide a
greater reward to an operator of an existing, inefficient vessel
for marginal improvement than a new, more efficient vessel that
has built improved efficiency into it.
-
- Additionally, the United States has proposed that all
vessels, both existing and new builds, be subjected to the new
energy efficiency design index. In essence, this proposal would
establish mandatory efficiency standards for all ships (new and
existing) that increase in stringency over time. This system
would also facilitate trading of efficiency credits so that ships
that operate below the standards may trade credits with less
efficient ships in the existing fleet. This would constitute a
type of “cap and trade” of ship energy efficiency
rather than a cap and trade of carbon emissions.25 If
a ship fell below the energy efficiency standards, it would need
to purchase energy efficiency credits from other ship operators
that perform above the standards or otherwise face punitive
measures. Some stakeholders have noted favorably that such a
system would effectively require the world's vessel fleet to
significantly improve its energy efficiency, thereby reducing
emissions yet avoid the political and practical complications
associated with both an emissions cap and trade system and an
international levy on marine fuels. Others have noted that the
proposal does not yet provide sufficient detail, particularly
with respect to existing ships that fall below the required
efficiency standard and cannot find design index credits to
purchase from those who operate more efficient ships.
|
|
20 |
http://unfccc.int/kyoto_protocol/items/2830.php |
|
21 |
Submittal by Denmark to the 59 th Session
of the International Maritime Organization's Marine Environment
Committee, MEPC 59/4/5, April 2009 |
|
22 |
Japanese submittal to the 59 th Session
of IMO's Marine Environment Protection Committee, MEPC 59/4/34,
Consideration of a Market-Based Mechanism to Improve the Energy
Efficiency of Ships Based on the International GHG Fund] |
|
23 |
For example: Assume a particular country
gives landholders emission allowances for not developing forested
property. Can a vessel operator purchase those allowances for use
in a maritime emission trading system? If after purchased by the
vessel operator the landowner develops the property, what happens
to the vessel operator's emission allowances? For example, could a
vessel that needs emission allowances to operate a service between
Morocco and Germany, purchase and use allowances issued in China? |
|
24 |
Japanese submittal to the 59 th Session
of IMO's Marine Environment Protection Committee, MEPC 59/4/34,
Consideration of a Market-Based Mechanism to Improve the Energy
Efficiency of Ships Based on the International GHG Fund] |
|
25 |
Submittal by the United States of America
to the 59 th Session of IMO's Marine Environment Protection
Committee, MEPC 59/4/48, Comments on MEPC 59/4/2 and an Additional
Approach to Addressing Maritime GHG Emissions.] |
- What challenges does the unique and complex nature of the
shipping industry pose in crafting effective and responsible climate
policy?
-
- Global complexity.
The global nature of ocean shipping
poses a challenge for the effort to craft coherent and practicable
carbon emissions policy. The international fleet is owned,
registered, and operated in many different parts of the world. The
industry's mobile, trans boundary operations pose a much more
complex range of political, practical, and administrative
difficulties than economic sectors characterized by fixed operations
and stationary sources of greenhouse gases. Significant challenges
include how to properly account for international emissions, how to
enforce rules equitably among diverse jurisdictions, and how to
maintain competitive fairness and balance in an inherently global
business.26
- Duplicative Jurisdiction
While complex and
challenging, an international IMO regime would avoid many of the
problems that would arise if various nations, regional blocs, and
localities were to try to impose their own carbon emission rules,
regulations, and regimes. The potential for a multi jurisdictional
patchwork of rules would raise significant concerns about regulatory
duplication, inefficiency, and incompatibility. Ocean shipping is a
global enterprise with operations that span many different
geographic, national, and regulatory jurisdictions. Some container
ships call on 20 different ports in 8 different countries per year.
- Integrated Supply Chain
Another critical factor that
must be considered is that maritime shipping is part of a large,
complex, and inter connected global supply chain. Changes in
shipping services can produce effects up and down the chain with
significant economic and environmental consequences. For example,
carbon rules that raise the cost or limit the availability of
certain traded goods may cause consumers to buy alternative products
with a greater carbon footprint, in part from increased dependence
on carbon intensive ground transportation. Moreover, irregular or
reduced liner services may affect the inventory management practices
of producers raising demand for carbon intensive infrastructure and
services such as storage, utilities, and ground transportation. A
recent study found that the carbon footprint of the seaborne
importation of wine to the eastern U.S. is significantly less than
the emissions from transporting domestic product by ground, rail, or
air. In this instance, economic or regulatory restrictions on ocean
shipping could have adverse, unintended consequences resulting in
higher net carbon emissions.27
- Long Lead time Requirements
The high cost and long
life of cargo ships present challenges that must be factored into
climate solutions. A single container ship capable of carrying 8,500
TEU's costs approximately $100 million and must be ordered three or
more years in advance of delivery. It will operate for 20 to 25
years. Additionally, ships are often ordered in a set of four to
ten, since multiple ships of a similar size are needed to operate a
single liner service. For these reasons, changes in design
specifications require ample planning and sufficient lead time to be
smoothly implemented.28
|
26 |
To illustrate, consider the example of a
liner shipping service comprised of nine liner shipping vessels,
registered in four different nations, operating in a four carrier
Vessel Sharing Agreement, that provides regular weekly service
between ports in four different Asian nations and four different
European nations, with an intermediate port call in North Africa,
and therefore providing 20 different cargo port pair combinations. |
|
27 |
American Association of Wine Economists,
“ Red, White, and Green: The Cost of Carbon in the Global
Wine Trade, ” AAWE Working Paper #9, Victor Ginsburgh, Oct.
2007, available at
http://www.wine-economics.org/workingpapers/AAWE_WP09.pdf |
|
28 |
Daniel Machalaba and Bruce Stanley, Wall
Street Journal published by Pittsburgh Post-Gazette. See:
http://www.post-gazette.com/pg/06283/728846-28.stm |
What do these complexities and challenges mean for the
likelihood of a carbon emission regime applicable to shipping?-
- The objective of an environmentally effective agreement to
reduce carbon emissions from shipping and the industry's objective
of a single, predictable international regulatory regime are highly
compatible. Indeed, improved energy efficiency, reduced fuel
consumption, and fewer emissions are outcomes that should be
strongly supported by all the relevant stakeholders. Many of the
stakeholders, including the World Shipping Council and its member
companies, are optimistic that a global solution is feasible in the
2011 timeframe. It is too early to predict the precise nature of
that regime, as governments and nongovernmental organizations are
still in the formative process of developing proposals. The pace of
such developments is expected to accelerate in 2010 after the
Copenhagen UNFCCC discussions have concluded.
-
- The World Shipping Council and its member companies strive to
improve the climate performance of shipping and will continue to
strongly support the creation of an effective and practical IMO
regime to address these issues. Even in the absence of a new
international regime, these companies will continue to pursue
reduced carbon emissions through changes in ship design, fuel
consumption and ship operations.
-
- IV. Summary
-
- Developing an effective international regulatory regime to
reduce carbon emissions from shipping requires governments and
industry to address a host of complicated political and technical
questions. There is limited precedent to build upon. There is no
viable CO2 emission regulatory system (other than engine or mileage
standards) functioning anywhere in the world that is applicable to
mobile transportation sources, whether that be automobiles (which
emit more CO2 than ships29), trucks, trains, planes,
tugboats, ferries, and other mobile sources. Most nations have not
established such regimes for their own domestic economies. There is
no functioning regime in place for other transnational industries,
such as international aviation.
-
- The IMO is the most appropriate forum to develop this regime for
shipping, and the success of the IMO in developing the MARPOL Annex
VI regulatory regime for NOx, SOx and particulate matter (PM)
emissions from ships demonstrates that it is an environmentally and
globally effective regulatory body. The World Shipping Council and
its member companies are actively engaged in efforts at the IMO to
develop an effective global agreement. While the challenges to
negotiating a global agreement are significant, the World Shipping
Council and numerous other organizations are strongly committed to
helping forge agreement of an effective global regime. More specific
proposals from participating governments and organizations on both
the political and technical aspects of this effort are expected, and
many observers are hopeful that significant progress can be made
following the UNFCCC climate negotiations scheduled for December
2009 in Copenhagen.
-
|
29 |
International Council on Clean Transport
from data supplied by the International Energy Agency, 2008. |
- In the interim, governments at the IMO have agreed to key
principles that must apply to the new regulatory regime for carbon
emissions from ships. They require that regulations:
-
- Effectively reduce CO2 emissions.
- Be binding and include all flag states.
- Be cost effective.
- Not distort competition.
- Be based on sustainable development without restricting trade
and growth.
- Be goal based and not prescribe particular methods.
- Stimulate technical research and development in the entire
maritime sector.
- Take into account new technology.
- Be practical, transparent, free of fraud and easy to administer.
- The World Shipping Council and its member companies endorse
these principles and will work with governments at the IMO to ensure
that these principles are appropriately addressed in new regulations
for carbon emissions from ships.
-
- For additional information about the liner shipping industry,
please contact the World Shipping Council.
-
|
In Washington, D.C.
1156 15 th
Street N.W.
Suite 300
Washington, D. C. 20005
U.S.A.
+1
202 589 1230 |
|
In Brussels
Avenue des Gaulois
34
B 1040
Brussels
Belgium
+32 2 734 2267 |
|
Email the Council at: |
info@worldshipping.org |
|
|
Visit the Council's website at: |
www.worldshipping.org |
|
|