
Special Interest Group on Maritime Transport and Ports
a member of the WCTR Society
INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP
Genoa - June 8-10, 2000
STRATEGIC CHOICES
FOR SMALL BULK SHIPPING COMPANIES
IN THE POST ISM
CODE PERIOD
Ioannis N. Theotokas
Department of Shipping Trade and Transport
University of the Aegean
2a Korai Str., 82100 Greece
Email: gtheotokas@stt.aegean.gr
| |
Eleftherios D. Katarelos
Department of Shipping Trade and Transport
University of the Aegean
2a Korai Str., 82100 Greece
Email: e.katarelos@stt.aegean.gr
|
1. INTRODUCTION
The new regulatory framework
that has been imposed mainly by IMO in world shipping in the
last few years has created a new environment for shipping companies.
The complete implementation of these regulations will further
differentiate companies' external environment. Shipping companies
wishing to remain competitive in the market must be prone to adapting
to this change. For a certain number of companies adaptation will
be easily achieved either because they have already moved towards
this, applying safety & quality systems or because their structural
characteristics allow this. This does not apply, however, to a
large proportion of shipping companies, whose structural characteristics
might impose hindrances to the adaptation process. This article
is aimed at defining the influence of the new environment to the
latter group that is for small sized companies.
The trend towards consolidation
also apparent in bulk shipping over recent years (Chorinou, 1999),
did not differentiate proportionately the structure of all markets
or segments of the industry. This is especially true for dry bulk
shipping markets, as liquid and other specialized markets like
chemicals, have already lived the consolidation effects. However,
this is an ongoing process whose termination cannot be predicted.
Nowadays, small sized companies operate a great proportion of
bulk shipping fleet. This is especially true for Greek-owned shipping.
According to the latest figures, 45% of companies operate one
or two ships (Naftemporiki, 4/5/200). Having this in mind, it
is logical to suppose that Greek-owned shipping will be affected
by this change, unless companies succeed in adapting to the requirements
of the new shipping environment. In other words, as environment
defines strategy, a large proportion of Greek-owned shipping companies
might find themselves in a dilemma regarding their strategy.
The second aim of this paper
is to produce a methodology, which will help shipowners/decision
makers to analyze and evaluate the external and internal environment
of their companies and to select and implement the proper strategy.
The basis of this methodology is the combination of Minimum Standards
and the Reliability Curves System and the Cost/Reliability and
Investment Choices/Reliability Matrices.
2. THE PRE ISM CODE ERA
In the pre-ISM Code era, companies
based their competitiveness on their ability to produce low cost
services. Sletmo and Holste identified three generic strategies
for shipping companies, that are absolute competitive advantage,
differentiation and specific adaptation to customer needs. (G.
Sletmo-S.Holste, 1993) If a company covers with its ships the
major trade routes, it could implement either the strategy of
absolute cost advantage or that of differentiation. If its market
coverage are in special niches of the market, the strategy of
specific adaptation to customer needs would be more appropriate.
The driving forces in the shipping industry have been historically
minimal charter hire and minimal operating cost (Thorstensen-Shield,
1996). This is more apparent in case of bulk shipping, which is
built around minimizing unit cost (Stopford 1997). Furthermore,
other structural characteristics of bulk shipping eliminate the
strategy selection. For a bulk shipping company that covers with
its ships the major trade routes, the only viable strategy is
that of absolute cost advantage. (Theotokas, 1997). Quality,
although present in these days, was rarely perceived as the main
source of competitive advantage, but instead as a factor that
contributed to the strengthening of the low cost advantage. Differentiation
based on the quality of the service did not allow companies to
differentiate its freight rates.
Social responsiveness was a
matter of choice for the companies of the self-regulated bulk
shipping. For a certain number of companies, quality and safety
were values as elastic as the achieved cost level(Theotokas-Alexopoulos,
1998). Since there was a lack of market mechanism for the definition
of the lowest acceptable cost level, numerous shipping companies
strove to preserve their competitiveness through lowering their
costs and consequently their safety and quality standards. However,
there were also companies that strove for competitiveness being
simultaneously socially responsible, that is, applying to self
imposed minimum safety and quality standards. In this environment
they were allowed to base their competitiveness on their core
competencies applying governance and operational systems that
served their aim, being simultaneously part of what we could call
quality shipping. Here, in our opinion, the basic environmental
change arrives. What was voluntarily applied will be strictly
enforced, depriving companies from the flexibility which was the
core of their competency.
3. THE NEW SHIPPING ENVIRONMENT
A key factor for the analysis
of competitive position of every company is the environment in
which it operates. Determination of a suitable strategy for a
company begins in identifying the opportunities and risks in its
environment (Andrew, 1998). At the same time a critical task is
the internal analysis of the company, which will allow the assessment
of its strengths and weaknesses in order to maximize the former
and minimize the latter. In other words internal analysis is
the task of identifying its resources and capabilities that contribute
to the creation of its core competencies, i.e. the critical bundle
of skills that an organization can draw on to distinguish itself
from its competitors (Miller, 1998).
The external and internal analysis
is extremely useful for shipping companies especially in nowadays,
as several changes have evolved differentiating basic structural
characteristics of bulk shipping markets. These changes are mainly
related to the imposition of a series of regulations that intend
to improve the whole performance of the industry regarding safety
and quality. The 90's were the decade of regulation for shipping.
OPA' 90, ISM Code, STWC, are just a few of the new regulations
that have been imposed during those years. However regulations
imposed either by governments or by international organizations
such is IMO can be an important factor affecting who can hold
a competitive advantage.,Also changes in this arena can alter
competitive standing of the industry (Miller, 1988). Considering
this side effect of regulations it is expected that competitive
standing in shipping will also be altered, as we will explain
shortly.
3.1 THE POST ISM CODE ERA
The changes that ISM and other
regulations will bring to bulk shipping markets are expected to
be substantial. The complete application of these regulations
is expected to create a more formal approach to what is called
social responsiveness of shipping companies. Safety and quality
will be central values and their application pre-requisition for
every shipping company in the new environment. This is of-course
a very positive evolution for the shipping industry, although
it is not without repercussions. The new environment is expected
to create opportunities for a certain number of companies whereas
it will be a threat to others. What would be the effects for a
shipping company is not necessarily related to its attitude towards
social responsiveness. Certainly for those companies that had
already embarked on the development of quality management systems
the new environment will be considered as an opportunity. For
them, new regulations are simply a way of meeting the challenge.
However, there exists a certain number of shipping companies,
mainly of small and medium sizes, with the same attitude towards
social responsiveness whose ability to respond to it, will unavoidably
affect their competitiveness. In other words, they will be obliged
to operate following specific procedures in order not to just
comply to the values of safety and quality but to also certify
their compliance and to stay in the business. For these companies
the new environment can be considered as a threat, since no compliance
could gradually lead them out of the market while imperfect compliance
could lead to decreased competitiveness. This is, in our opinion,
the change that will differentiate the shipping environment and
the factor that will alter the competitiveness in the shipping
industry.
In the post-ISM Code era the
implementation of minimum safety and quality standards will define
the way the shipping companies operate and manage their business.
A particular way of organization and management will simultaneously
affect the minimum operating cost level of companies that apply
to them. In other words, the minimum standards will redefine
the conditions of competitiveness for all companies. For companies
that were already familiar with quality management systems the
effect will not only be minimal but it will also create conditions
for further expansion. For those companies that without applying
formalized and structured quality systems, produced quality services,
the competitive standing will change. They will be enforced to
abandon cost effective practices that helped them to be competitive,
without necessarily being substandard. (Theotokas-Alexopoulos,
1998).
3.2 THE FORTHCOMING FORMAL
SAFETY ASSESSMENT
The expected introduction
of Formal Safety Assessment (FSA) (Kuo,1998)
for the evaluation of
safety standards will complete the framework through the imposition
of Reliability Standards. FSA may be seen as consisting of the
identification of hazards; the assessment of risks associated
with these hazards; ways of managing the risks identified; a cost-benefit
assessment of the options identified in managing risks; and decisions
on which options to select. All marine transportation systems
comprise of three interacting components (Ronald - Moriati, 1990):
- the ship and her equipment
(the hardware - HWR)
- the rules and regulations,
codes of practice, operating procedures and casualty records and
statistics (software SWR)
- and the personnel involved,
both afloat and ashore (humanware - HR).
In a previous paper of one
of the co-authors (Angelis-Katarelos, 2000) a System Reliability
(Spiegel, 1975)assessment method has been developed, which is
based on Reliability Curves. Reliability is expressed as a function
of three factors and hence its graph is 3-dimensional. But, to
simplify things we combined the first two factors into one, namely
HSR, expressing the reliability of both Hardware and Software
(Figure 1).
Figure 1
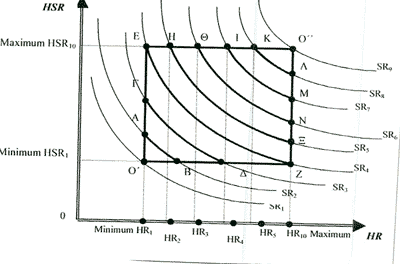
The Reliability
Curves and the Company's Options Square
All attainable reliability
levels lie on Reliability Curves restricted by a square O'O''EZ.
The square contains minimum and maximum levels. The latter of
course, although realistic seen from a cost-benefit analysis view,
cannot be easily identified. Every point in a given Reliability
Curve expresses the same reliability although resulting from different
combinations of the factors.
A shipowner may choose for
his vessel any point within the Options Square. In doing so, he
decides on the level of Reliability (and hence Safety) he wants
for his ships. Also he decides on the combination of HSR and HR
he will use in order to achieve this level, subject of course
to the constraints that minimum acceptable standards are satisfied.
Therefore shipping companies are able to define their own particular
Reliability Curve (RC). The System Of Minimum Reliability Standards
means that for a company to remain competitive in the market,
its Reliability Curve must be at least above the minimum level,
namely in Company' Options Square.
4. THE RELIABILITY MATRIX
AS DECISION MAKING TOOL
One of the uses of the developed
decision making model is to determine the control options of FSA
method. In other words, to help the decision maker in preparing
his strategic plan by taking into account the market in terms
of supply- demand (Mitropoulos, 1998), and the company's market
positioning (Karlof-Ostoblom, 1993) on one hand and safety on
the other. The decision maker is able, to know in advance the
minimum/maximum standards and therefore is able to decide where
to place his ship according to his corporate and marketing strategy,
while of course always satisfying minimum standards.
Supposing that the market compensates
for quality, then it is the company that will decide in which
quarter of the matrix of Figure 2 it will place itself. Company's
decision is of course influenced by the vulnerable character of
the freight markets. This placement helps the company to evaluate
the various alternatives of its own position against those of
its competitors. Therefore the use of that matrix allows the placement
of the company's alternatives in terms of strategy and helps in
decision making.
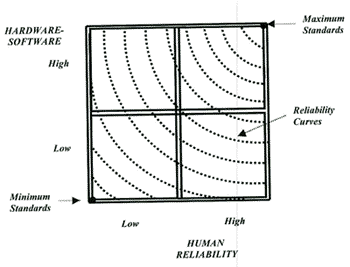
Figure 2
Safety and Quality
Matrix based on Reliability curves
The higher the achieved standards
of any of these three factors, the higher the RC of the company
will be. At the same time, the higher the RC, the higher the
cost for the company will be. At this point, however, economies
of scale emerge as the increase in reliability and cost are not
proportionate. For example, a company that operates sufficient
number of ships has the ability to employ a pool of seamen and
recruit them onboard the same ship. Furthermore, it can afford
the cost of internal training procedures thus upgrading its seamen
qualifications. This ability allows the company to achieve the
highest level of "Humanware" compared to a smaller company
which operates two ships and cannot follow the same policy. Furthermore,
this difference allows the former company to be in a higher position
in the RC than the latter, despite both facing the same manning
costs. Since higher RC leads to increased competitiveness, it
is evident that competitiveness for every shipping company will
be based on its ability to achieve a higher RC with minimum cost.
This approach is dictated by
of the market, according to which the charterers are only willing
to pay for the minimum standards. The increased quality does not
provide to shipowners increased freight rates (Goulielmos-Giziakis).
Charterers are indifferent about higher standards when they cost
more so choose the ships that combine the lowest costs while simultaneously
offering standards above the minimum. Especially in the case of
dry bulk market, the almost perfect competitive character of the
market does not seem to perceive quality as crucial for the fixing
of freights. As Thanopoulou and Tamvakis state "any indications
towards freight rate differentiation depending on quality are
still too sporadic to revolutionize our current perception of
the dry bulk carrier market". The Erica case and the dispute
that arose has also indicated that charterers in liquid bulk shiping
are not always interested in quality vessels if they cost more
(Efoplistis).
Under these circumstances smaller
companies are expected to become less competitive, especially
in periods of low demand. In those periods charterers choose vessels
that offer minimum cost combining it with higher quality, that
is companies which are able to be positioned on the upper level
of the safety matrix. Smaller companies are not able to meet these
criteria because of their inability to exploit economies of scale
in achieving high RC. This inability becomes more intense because
of the structural characteristics of these companies related to
their fleet age, that is their hardware. Of 376 small Greek-owned
shipping companies with one or two ships, 302 of them (80,3%),
operate ships whose age is above 20 years old (Neftemporiki).
They could increase their reliability by achieving higher RC through
humanware and software. These two factors, however, are definitely
dependent on the companies' size. Their present status imposes
hindrances to that aim. Certainly, even during the pre-ISM period
size was a factor that defined competitiveness for small companies
and gave to shipmanagement companies a considerable boost (Spruyt
p.43-44). In that period however, small companies were able to
apply cost effective solutions based on their flexibility. The
post-ISM period deprives them from this ability and affects their
competitiveness especially during periods of low demand.
However, they could remain
competitive in the market no matter what the level of supply and
demand will be, only if they adapt to the requirements that the
new shipping environment imposes on the shipping companies, that
is only if they succeed in achieving improved reliability at minimum
cost levels. This can be better achieved if they move towards
strategic decisions that will allow them to exploit economies
of scale and to overpass their structural characteristics that
reduce their competitiveness, thus simultaneously preserving those
that are related to their capabilities.
5. STRATEGIC CHOICES FOR
SMALL SIZE COMPANIES
The strategic choices that
are available to small shipping companies wishing to increase
their reliability and to remain competitive in the market no matter
what the level of demand would be, except of course to remain
in the same position, that is independent, are the following:
- To assign technical management
of their fleet to a shipmanagement company
- To move toward strategic
alliances with other, preferably bigger companies
- To merge with other small
companies
Decision makers must arrive
at one of the above choices after having successfully completed
the analysis of the external environment and the internal analysis
of their firms. Each choice offers numerous advantages and disadvantages
to companies, which could not be examined or mentioned in this
analysis.
Independence does not help
them to overpass the difficulties of the new shipping environment
unless internal development is pursued as a method to obtain the
critical mass. However, as we shall shortly see, independence
as a selection either of stability or of internal development,
might offer a few advantages to the companies if it is properly
combined with their investment strategy.
Assignment of technical management
of ships to shipmanagement companies is a choice free of any
cultural implications and at the same time it secures for the
companies the achievement of higher reliability, through the increase
of the HWR and SWR. Furthermore, it allows companies to retain
their flexibility in the sale and purchase market. However, this
choice will not drastically reduce their cost level as it will
be achieved by paying fees to shipmanagers. These fees will not
necessarily be less than their present technical management cost.
In addition, it will force them to assign an element that is related
to one of their core competence, that is their cost effective
technical management.
The third choice is to look
for a strategic alliance with a preferably bigger company. By
forming an alliance, companies will have the ability to coordinate
their activities in order to improve their competitiveness. This
choice will allow small companies to obtain access to the value
chain of the bigger company and to have their cost reduced. Furthermore
it will ensure that the company accesses wider information channels.
On the other hand alliance presupposes also mutual leadership
and decision making (Papadakis, 1999), a fact that could eliminate
small shipowners' ability to retain the commercial management
of their ships and to deliberately apply the strategy of buying
and selling ships. Moreover, it can not be considered certain
that the alliance will lead to the increase of the reliability
of the company, which is the other target of this selection. Factors
that might cause obstacles to this aim are the non-permanent character
of the alliance, the level of integration between the companies
and also the compatible cultures or managerial styles.
The last choice concerns the
merger with other small and medium size companies in order to
obtain the critical mass. This is a choice of long run commitment,
whose benefits will be also gained in advance. Following this
choice they will form a corporate structure based on the equality
of the partners and will benefit from the synergy effects. Forming
mergers, they will be able to combine their core competencies,
that is their cost effective technical management and at the same
time exploit the economies of scale in order to improve their
humanware and software and to increase their reliability. One
critical factor for the success of this choice is the entrepreneurial
philosophy of shipowners and the prevailing organizational culture
of the companies which might create disagreement regarding power
and control. However, as the merger will be based on the basis
of equality, these obstacles can be eliminated.
Based on the level of reliability
that is desirable for each company and on the cost level that
is pursued to be achieved we can draw the matrix 2 (Figure 3)
whichshows
that each choice gives certain combinations of cost and reliability.
However as the choice of each company will be strongly affected
by its investment strategy, it is necessary to include this parameter
in the analysis. The investment strategy is critical for the survival
and development of a shipping company due to the vulnerability
of the markets. Timing is the factor that defines the potential
of investments. There are two types of strategy that allow the
exploitation of timing. The first is that of "beat the market"
buying and selling ships in the short run and the second, that
of long run selling of transport services. In the first strategy
profits are mainly derived from sales and purchases of ships while
in the second from the trading of ships.(Hope & Boe) It is
evident then that the choice of a company is strongly related
to its investment strategy. For a company whose profits mainly
come from the sales & purchases, either cost level or reliability
are factors of secondary importance. As it has been stated, in
this case companies' reserves allows both the finance of the vessels'
operation and the exploitation of the chances in the s&p market
during periods of low freight rates (Goulielmos, 1999). On the
contrary, for a company that is more interested in trading its
ships, cost level and reliability are of primary importance.
Matrix 3 (Figure 4) embodies this additional factor trying to
combine the desired reliability level with the investment strategy
that the company intends to apply.
As it can seen in the
Matrix 3, the strategy of "beating the market" is more
compatible with choices of independence and assignment to third
party management, as both give to the shipowner flexibility. On
the contrary, choices of high commitment are more suitable for
the strategy of long run selling of the ships services.
Figure 3
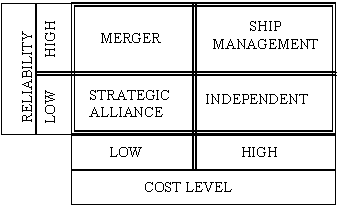
Reliability/
Cost Matrix
Figure 4
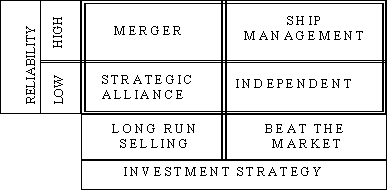
Reliability/ Investment
Strategy
Combining the two matrices
a shipowner can decide which strategic option is more suitable
to his aims. For the shipowner who is short-term oriented and
interested in applying the strategy of beating the market, buying
and selling ships, the choice would be either to assign the technical
management of his ships to a shipmanagement company, or remain
independent. In the first case he will succeed in increasing the
reliability of his services, while in the second he will face
both low reliability and high operational cost. On the contrary,
the shipowner who is more dedicated to the long run selling of
his ships' services, preferable choices are to merge or to form
an alliance. However, only merging leads to both low cost and
increased reliability which is the optimum.
Therefore the above strategies
may be defined as follows:
- Merger (M)
- High Reliability HR
- Low Cost Level LC
- Long Run Selling LRS
- Ship
Management (SM)
- High Reliability HR
- High Cost
HC
- Beat the Market BM
- Strategic Alliance (SA)
- Low Reliability LR
- Low Cost Level LC
- Long Run Selling LRS
- Independent (I)
- Low Reliability LR
- High Cost Level HC
- Beat the Market BM
The consolidation of Matrices
2 and 3 give us the Combined Matrix where the decision maker can
place company's Reliability, Cost Level and Investment Strategy.
The new consolidated Matrix appears in Figure 5.
Figure 5
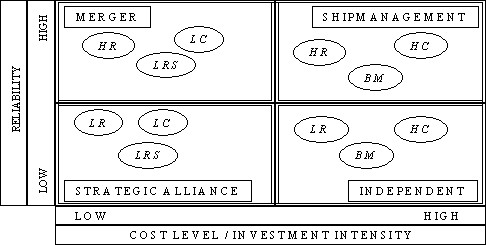
Consolidated
Matrix presenting Reliability and Cost Level/Investment Strategy
Combining the above analyzed
matrices we can draw a flow chart that a shipowner could follow
in order to identify both what is the present situation of his
company and also what the desired situation would be, according
to his intention. Following the chart and replying to the questions
the shipowner completes the external and internal analysis. A
shipowner for example may find, following the chart, that his
company faces high reliability and high cost while following the
strategy of the long run selling the services of his ships. However
this is not an efficient placement because his investment strategy
is not backed by company performance. Using Porter's analysis,
he is "stuck in the middle" lacking any competitive
advantage (Porter, 1990). In order to decide on the optimum choice,
he will follow the chart again, selecting the points that will
support this choice. For example, if he prefers the strategy of
long run selling, he is interested in facing low cost and high
reliability. Then the choice for him is to merge.
Figure 6
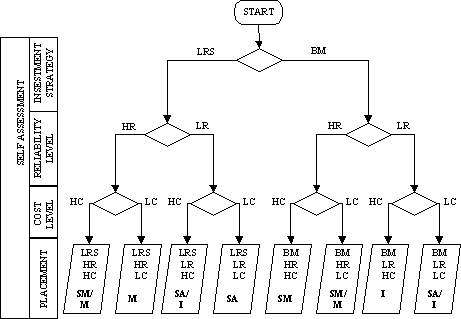
Maritime Decision
making flow chart based on Reliability, Cost Level and Investment
Strategy
CONCLUSIONS
The new environment that the
regulations create for shipping companies seems to alert the competitive
standing of the industry. This environment creates opportunities
for a certain number of companies and threats others. In the new
environment critical factors for the survival of the companies
is not only their cost level but also their reliability. In the
reliability/cost relation however, the significance of scale is
evident. Here the disadvantage of small companies emerges. Being
unable to exploit economies of scale, they face a higher operating
cost and their ability to achieve increased reliability levels
is constrained. In order to overcome this disadvantage and to
remain competitive in the market it is necessary to move towards
strategic decisions that will allow the effective adaptation to
the new environmental requirements.
The choices for the small companies
are to remain independent, to assign the technical management
of their fleet to third party management, to form strategic alliance
or to merge with other small companies on the basis of equality.
The final choice however, must be take into consideration the
implemented investment strategy of the company. In order to analyze
and evaluate the present situation of their companies and also
to decide what the ideal placement could be, a methodology that
combines decision matrices and flow charts has developed. This
methodology constitutes a decision making tool that leads to strategic
choices compatible to external environment requirements and to
companies internal environment.
REFERENCES
- V.A. Angelis and E.D. Katarelos,
(2000), "Risk analysis: A business process reengineering
step and a prerequisite for shipping quality management",
In Proccedings of 'INFORMS-KORMS SEOUL 2000', 1558-1565.
- Keneth R. Andrews, (1996),
"The concept of corporate strategy", in Henry Mintzberg
& James Brian Quinn, The Strategy Process, Third edition,
Prentice Hall.
- Stavroula Chorinou, (1999)
"Shipping seeks new global role", Lloyd's Shipping
Economist, November.
- Efoplistis,
(2000) "TSH Erika: Interests' war" May. (in greek)
- A.M. Goulielmos, and K.
Giziakis, (1998), Quality Control in Shipping Companies and
Ships, Stamoulis, Athens [in Greek]
- Harrington, H. J. (1991).
Business Process Improvement. The Breakthrough Strategy for Total
Quality, Productivity and Competitiveness
- Einar Hope, & Oystein
Boe , "Investment Behaviour in Norwegian Bulk Shipping"
óôï Hope, Einar, (ed.), Studies in Shipping
Economics in Honour of Professor Arnljot Stromme Svendsen,
Bedriftsokonomens Forlag A/S, Oslo
- Bengt Karlof, & Svante
Ostoblom, (1993). Benchmarking. A signpoint to excellence in Quality
and Productivity
- Chengi Kuo (1998). Managing
Ship Safety. LLP, London, Hong Kong, 99-101
- Alex Miller, (1998), Strategic
Management, third edition, Mc Graw Hill.
- E. Mitropoulos, (1998).
"The standard- setting Process: A synergy between Market
forces and Optimum Regulation; A Contribution to Debate",
in Haralambides, H. E., (ed.), Quality Shipping. Market Mechanisms
for Safer Shipping and Cleaner Oceans, Erasmus Publishing.
- Naftemporiki,
(2000),"Perceptible increase of Greek shipping companies",
May, 4th.
- Basil M. Papadakis,(1999)
Business Strategy, Athens.
- M. Porter, (1990), The
competitive advantage of nations, MacMilan.
- H.E Ronald,. and Moriarty
(1990). System safety Engineering and Management, Second
Edition, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
- G. Sletmo and S.Holste,
(1993), "Shipping and the competitive advantage of nations:
the role of international ship registers", Maritime Policy
and Management, vol. 20, no. 3, 243-255
- Murray R. Spiegel, (1975).
Statistic and Probability, Mc Graw- Hill New York
- John Spruyt, (1990) Ship
Management, Lloyd's of London Press, London.
- M. Stopford, (1997), Maritime
Economics, Routledge, London
- M.N. Tamvakis, and H.A.
Thanopoulou, (1998), "Does Quality pay? The case of the Dry
Bulk Market", 8th WCTR, Antwerp
- Ioannis Theotokas, (1997),
'Organizational and managerial patterns of Greek-Owned Shipping
Companies, 1969-1990', PhD thesis, Department of Maritime Studies,
University of Piraeus, (in Greek)
- J. Theotokas - A.B. Alexopoulos,
(1998), "Shipping Management in the post-ISM Code period.
The case of dry bulk shipping companies", Fourth International
Symposium on Quantitative Methods, University of The Aegean.
- O.E. Thorstensen, and D.A.
Shield, (1998), "Quality shipping: The role of the ISMA",
in Haralambides, H. E., (ed.), Quality Shipping. Market Mechanisms
for Safer Shipping and Cleaner Oceans, Erasmus Publishing,
Rotterdam.