22 April 1999
World Trade Growth Slower In 1998 After Unusually
Strong Growth In 1997
The rate of growth in the volume of world merchandise exports
slowed to 3.5 per cent in 1998, from over 10 per cent in 1997,
due largely to continuing economic contraction in much of Asia.
World output growth slipped to 2 per cent in 1998, compared to
3 per cent in 1997. Although trade growth still exceeded output
growth in 1998, it was by a smaller margin than the average for
the 1990s.
Export growth in 1999 is expected to match that of 1998, but
for this projection to be realized, trade growth will have to
accelerate during the course of 1999. This projection also assumes
that slowing output growth in the United States and Western Europe
will be offset somewhat by recovery in Asia. A faster than expected
slowdown in the United States or Western Europe, or slower recovery
in Asia, would clearly imply export volume growth below 3.5 per
cent in 1999.
These are among the findings of the WTO's first report on trade
developments last year and the outlook for this year (reproduced
below). Other highlights include the following:
- Trade contraction in Asia has been the biggest factor in
the global trade slowdown: But there has been a marked slowdown
in global export expansion throughout 1998, reflected in the performance
of all major regions.
- Trade performance measured in volume terms differed widely
among regions in 1998, particularly on the import side: Imports
into Asia fell by 8.5 per cent, stagnated or fell slightly in
Africa and the Middle East, and expanded by 7.5 per cent in Western
Europe and by some 10 per cent in North America, Latin America
and the transition economies. Export volume growth was strongest
in the transition economies and Latin America, at 10 per cent
and 6.5 per cent
respectively, and increased marginally in Asia (1 per cent).
Western Europe's export growth was slightly above the global average,
at 4.5 per cent, and that of North America was below the average,
at 3 per cent.
- Exports of merchandise and commercial services amounted
to US$6.5 trillion in 1998: In value terms, merchandise exports
amounted to US$5.2 trillion and commercial services to US$1.3
trillion. This represents a fall of almost 2 per cent in dollar
terms over exports in 1997, but still exceeds the level attained
in 1996. This is the strongest decrease since 1982. Exports
of commercial services recorded the first annual decline in value
terms since comprehensive statistics became available in the mid-1980s.
- Commodity prices fell sharply in 1998, pushing the share
of primary products in world exports below 20 per cent in current
price terms for the first time in the post-war period: Oil
prices fell by 30 per cent in 1998, or 40 per cent from a year-end
to year-end basis. This picture has been mitigated by increased
oil prices in the first quarter of 1999. Non-oil primary commodity
prices fell by 15 per cent on a yearly average basis in 1998,
and by some 10 per cent on a year-end basis. Prices of internationally
traded manufactured goods and services also declined in 1998,
but by considerably less than those of primary products.
- Reduced commodity prices have particularly affected the
export earnings of African and Middle Eastern countries: In
addition to the 11 member countries of OPEC, some eight other
countries depend on fuel exports for more than 50 per cent of
their export earnings. Over twenty, mostly developing countries,
depend on agricultural exports for 35 per cent or more of their
export earnings, but these countries are generally not as severely
affected as the oil exporters by commodity price falls.
I. Main features of world trade in 1998
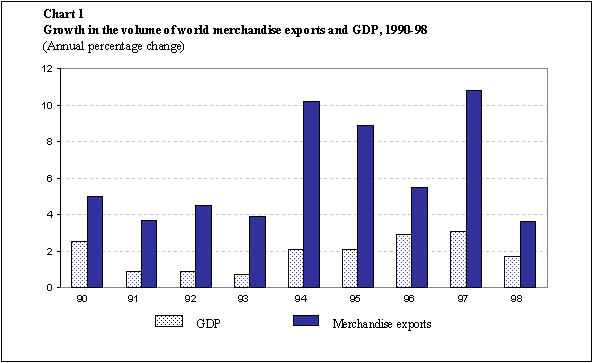
World GDP and trade growth slowed in 1998 as the Asian crisis
deepened and its repercussions were felt increasingly outside
Asia. The volume of world merchandise exports grew by 3.5 per
cent in 1998 after an outstanding growth rate of 10.5 per cent
in 1997. This export volume growth rate compares with an average
growth rate of 6.0 per cent in the period 1990-95. The deceleration
in global output growth was less pronounced than for international
trade in 1998, as world GDP rose by 2 per cent, or by 1 percentage
point less than in 1997 (Chart 1).
|
The deceleration of global merchandise trade growth continued
throughout the year, leaving the global trade level in the fourth
quarter of 1998 only slightly above the level reached at the end
of 1997. All major regions experienced a marked slowdown of their
trade growth in the course of 1998.
The recent cyclical fall in commodity prices, which started in
early 1997, continued unabated throughout 1998. Oil prices fell
by 30 per cent and non-oil commodity prices by 20 per cent in
1998, with very different implications for various countries and
regions of the world. While the share of primary commodities
(including processed food) in world merchandise trade was only
slightly above one-fifth in 1997, it was more than two-thirds
for the Middle East, Africa and Latin America (excluding Mexico).
In a sample of 91 developing countries, 67 of them recorded a
share of primary products in total merchandise exports above 50
per cent, reaching as high as 95 per cent in some cases.
Prices of internationally traded manufactured goods and services
also have declined in 1998, though considerably less than those
of primary products. Exchange rate variations, which were large
in the course of 1998, can have a major impact on the dollar prices
of internationally traded goods. However, as the dollar's average
annual appreciation vis-à-vis the ECU (now the Euro) was
considerably smaller in 1998 than in 1997, West European export
prices measured in dollar terms decreased far less last year than
in 1997. This smaller decrease in Europe's export prices more
than offset the stronger price declines in all other regions.
Therefore, despite the accelerated fall in commodity prices in
1998, the global price decline for all merchandise exports was
5.5 per cent, which was somewhat less pronounced than in 1997.
Trade performance in 1998 differed widely among regions. While
oil-exporting regions recorded the strongest annual value declines
in merchandise exports, countries directly affected by the Asian
financial crisis reported the strongest import decline. The contractionary
forces of the Asian crisis and falling commodity prices were,
however, attenuated by the robustness of continued economic growth
in the United States and strengthened demand in Western Europe.
The reversal of private capital flows away from the emerging
markets contributed to low interest rates in North America and
Western Europe. In addition, falling fuel prices led to weaker
import prices and real income gains for net-fuel importing countries.
Western Europe, the world's largest regional trader, was the
only region not to record a deceleration in import growth in 1998
compared to 1997. Western Europe's import growth rate of 7.5
per cent was, however, less than the 10 per cent rate recorded
by North America, Latin America and the transition economies.
In a sharp contrast, imports into Asia fell by nearly 8.5 per
cent, and a stagnation or a decrease in import volumes is estimated
for Africa and the Middle East.
Regional differences in the volume growth of exports are far
less pronounced than for imports. All regions recorded a lower
export expansion in 1998 than in the preceding year. The transition
economies and Latin America recorded the strongest volume growth.
Asia's export volume increased marginally, as the strong contraction
of intra-Asian trade was only just offset by a sharp rise in extra-regional
flows. Western Europe's export growth remained somewhat above
the global average of 3.5 per cent, while that of North America
fell below the average.
The dollar value of world merchandise trade declined by 2 per
cent, the strongest decrease since 1982. The export value of
manufactured goods continued to rise slightly while that of agricultural
products, metals and fuels declined. These divergent developments
by product category in 1998 pushed the share of primary products
below 20 per cent in current price terms for the first time in
the post World War II period.
Exports of commercial services recorded the first annual decline
in dollar value since 1983. All the three major services categories
(i.e., transport, travel and other commercial services) saw a
decrease. Exports of goods and commercial services both decreased
slightly but at $5225 and $1290 billion respectively, but were
still above the levels reached in 1996 (Table 1).
|
|
Table 1
World exports of merchandise and commercial services, 1996-98
(Billion dollars and percentage)
| | Value
| Annual change |
| | 1996 |
1997 | 1998
| 1996 | 1997
| 1998 |
| Merchandise | 5150
| 5325 | 5225
| 4.5 | 3.5
| -2.0 |
| Commercial services | 1275
| 1320 | 1290
| 6.7 | 3.5
| -2.0 |
II. World trade developments by country and region
In its seventh year of expansion, the United States economy experienced
an acceleration in private consumption and continued double-digit
investment growth. GDP growth was almost 4 per cent, unchanged
from 1997. The booming U.S. economy stimulated intra-NAFTA trade,
and sustained exports and output in other regions. North America's
merchandise import volume rose by 10.5 per cent in 1998, which
was the strongest growth of all regions (Table 2).
Table 2
Growth in the volume of world merchandise trade by selected
region, 1990-98
(Annual percentage change)
| Exports |
| | Imports
|
Average
1990-95
|
1996 |
1997
|
1998 | | Average
1990-95
|
1996 |
1997
|
1998 |
| 6.0 | 5.5 | 10.5
| 3.5 | World |
6.5 | 6.0 | 9.5
| 4.0 |
| 7.0 | 6.0 | 11.0
| 3.0 | North Americaa
| 7.0 | 5.5 | 13.0
| 10.5 |
| 8.0 | 11.0 | 11.0
| 6.5 | Latin America | 12.0
| 8.5 | 22.0 | 9.5
|
| 5.5 | 5.5 | 9.5
| 4.5 | Western Europe | 4.5
| 5.5 | 7.5 | 7.5
|
| 5.5 | 5.5 | 9.5
| 5.0 | European Union (15) |
4.5 | 5.0 | 7.0 |
7.5 |
| 5.0 | 6.5 | 12.5
| 10.0 | Transition economies
| 2.5 | 16.0 | 17.0
| 10.0 |
| 7.5 | 5.0 | 13.0
| 1.0 | Asia | 10.5
| 6.0 | 6.0 | -8.5
|
| 1.5 | 1.0 | 12.0
| -1.5 | Japan | 6.5
| 5.5 | 1.5 | -5.5
|
| 11.5 | 7.5 | 11.5
| 2.0 | Six East Asian tradersb
| 12.0 | 4.5 | 6.5
| -16.0 |
aCanada and the United States.
bChinese Taipei; Hong Kong, China; Malaysia; the
Republic of Korea; Singapore and Thailand.
Note: Separate volume data are not available for Africa and the
Middle East, although estimates for these regions have been made
in order to calculate the world total.
In value terms, North America's merchandise exports decreased
slightly in 1998, as volume growth decelerated and prices declined.
North America's merchandise imports, however, increased by 4.5
per cent in value terms, leading to a widening of the region's
merchandise trade deficit to $253 billion (Table 3). The evolution
in North America's commercial services trade mirrored that of
merchandise trade, with exports increasing only very slightly
and imports rising by 4.5 per cent, reducing further the region's
surplus in services trade.
Latin America's GDP and trade growth slowed sharply in
1998 from the exceptionally high levels recorded in 1997. Falling
commodity prices, a slowdown in private capital inflows in the
second half of 1998 and weaker export markets within the region
and in Asia contributed to this development. Marked differences
in economic performance occurred for the two largest economies
in the region, with trade and output growth slowing strongly in
Brazil, while Mexico's trade and output performance remained well
above the regional average. Better access to the rapidly expanding
United States market and a higher share of manufactures in its
merchandise exports are among the factors which explain why Mexico's
trade and output developments were, for the fourth year in a row,
superior to those of the other Latin American economies.
For Latin America as a whole, the growth in the volume of merchandise
imports continued to exceed that of merchandise exports by a large
margin, and the region's trade expansion - both imports and exports
- remained stronger than the global average. Latin America's
merchandise export value, on the other hand, decreased by 2 per
cent in 1998, as the expansion of Mexico's exports was more than
offset by the decline in exports of all other Latin American countries
combined. In particular, Ecuador and Venezuela, the two major
oil exporting countries in Latin America, experienced the strongest
setback, with decreases in excess of 20 per cent. Latin America's
outstandingly strong import growth performance throughout the
1990-97 period became less dynamic last year, although at 5 per
cent, this region, together with Western Europe, recorded the
highest import growth rate of any region. Mexico's import growth
rate of 14 per cent contrasted with the relative stagnation of
imports in other Latin American countries. As Mexico has enjoyed
an above average rate of growth in trade for a number of years,
its share of total trade in the region has risen considerably,
accounting for 40 per cent in 1998. Latin America's exports and
imports of commercial services are estimated to have expanded
by 4 to 5 per cent in 1998.
Table 3
Growth in the value of world merchandise trade by region, 1990-98
(Billion dollars and percentage)
|
| Exports (f.o.b.)
| | Imports (c.i.f.)
|
| Value | Annual percentage change
| | Value | Annual percentage change
|
| 1998 | 1990-95
| 1996 | 1997
| 1998 | |
1998 | 1990-95
| 1996 | 1997
| 1998 |
| 5225 | 7.5 |
4.5 | 3.5 | -2.0
| World | 5410 |
7.5 | 5.0 | 3.0
| -1.0 |
| 898 | 8.5 | 6.5
| 9.5 | -1.0 | North America
| 1151 | 8.0 | 6.0
| 10.5 | 4.5 |
| 274 | 9.0 | 12.5
| 10.0 | -2.0 | Latin America
| 339 | 14.5 | 9.5
| 19.0 | 5.0 |
| 118 | 14.0 | 20.5
| 15.0 | 6.5 | Mexico
| 129 | 12.5 | 25.5
| 23.5 | 14.0 |
| 157 | 7.0 | 8.0
| 7.0 | -7.0 | Other Latin America
| 211 | 15.5 | 2.5
| 16.5 | 0.5 |
| 2338 | 6.0 | 3.5
| -0.5 | 2.5 | Western Europe
| 2359 | 5.5 | 3.5
| -1.5 | 5.0 |
| 2171 | 6.5 | 3.5
| -0.5 | 3.0 | European Union (15)
| 2163 | 5.5 | 3.0
| -2.0 | 5.5 |
| 178 | 7.0 | 6.5
| 5.0 | -1.0 | Transition economies
| 207 | 5.0 | 17.0
| 9.5 | 3.0 |
| 99 | 7.5 | 6.0
| 8.0 | 9.0 | Central/Eastern Europe
| 133 | 11.5 | 17.0
| 7.0 | 11.5 |
| 106 | 0.5 | 16.5
| 2.0 | -16.0 | Africa
| 129 | 5.5 | -1.0
| 6.0 | -1.5 |
| 26 | 3.5 | 5.5
| 6.0 | -15.0 | South Africa
| 29 | 10.5 | -1.5
| 9.5 | -11.0 |
| 138 | 1.5 | 17.0
| 4.0 | -21.0 | Middle East
| 139 | 5.5 | 7.0
| 6.5 | -6.0 |
| 1294 | 12.0 | 0.5
| 5.5 | -6.0 | Asia
| 1090 | 12.0 | 4.5
| 0.5 | -17.5 |
| 388 | 9.0 | -7.5
| 2.5 | -8.0 | Japan
| 281 | 7.5 | 4.0
| -3.0 | -17.0 |
| 184 | 19.0 | 1.5
| 21.0 | 0.5 | China
| 140 | 20.0 | 5.0
| 2.5 | -1.5 |
| 504 | 14.0 | 3.0
| 2.5 | -7.5 | Six East Asian tradersa
| 438 | 15.0 | 3.0
| 0.5 | -25.0 |
aChinese Taipei; Hong Kong, China; Malaysia; the
Republic of Korea; Singapore and Thailand.
Stronger demand growth in Western Europe contrasted with
a weaker global economy in 1998, leading to an import expansion
which, for the first time since 1992, exceeded the region's export
growth rate. Western Europe was the only major region which recorded
an increase in the dollar value of its exports. Imports in value
terms increased by 5 per cent, very close to the expansion recorded
by both North America and Latin America. The share of Western
Europe in world merchandise trade recovered to 44 per cent following
a marked decrease between 1990 and 1997. Commercial services
imports expanded by 4 per cent in 1998, and commercial services
exports by 3 per cent.
The interaction between trade and output in the transition
economies in recent years has been unique among the major
regions. Sluggish overall economic activity, including a decline
in regional output in recent years, has been accompanied by export
and import growth rates above the global average. Merchandise
imports have expanded significantly faster than world trade in
both real and nominal dollar values. Merchandise export growth,
at 10 per cent in volume terms, was the highest among all regions.
Due to the sharp decline in the dollar export prices, however,
the dollar export value of the region decreased slightly.
Several factors have contributed to this situation, where trade
growth has been above the world average, while output growth has
been lower than the world average. First, inflows of private
capital have been strong, in particular foreign direct investment
(FDI) and portfolio investment. Second, FDI has been associated
with a strong increase in capital goods imports, which over recent
years has supported the expansion of exports. Third, a number
of East European countries advanced considerably with their integration
into the EU market, in particular Poland, the Czech Republic and
Hungary. The strong trade performance of these countries masked
a rather mixed picture in other transition economies.
The commercial services trade of the transition economies has
been far less dynamic than merchandise trade in the last two years,
with exports decreasing slightly and imports rising moderately.
The Russian Federation, the region's largest commercial services
trader, reported a decline in exports and imports of about 7 per
cent in 1998. For Central and Eastern Europe, an increase of
4 per cent was recorded last year.
Africa and the Middle East have suffered the brunt
of the decline in primary commodity prices in 1998. Despite a
moderate recovery in Africa's GDP - linked to the recovery of
agricultural output - Africa's trade remained sluggish. Export
values in the region decreased by 16 per cent in 1998. Oil-exporting
African countries recorded a decrease in exports exceeding one-quarter.
Import values declined only slightly in 1998, but higher trade
deficits raise the question whether the 1998 level of import demand
can be sustained in 1999. Available data on commercial services
also indicate decreases in the value of both exports and imports.
As was observed for merchandise trade, exports of services decreased
faster than imports.
Being the region with the highest share of fuels in its merchandise
exports, the Middle East recorded the strongest contraction in
export value of all regions. Exports for the region as a whole
shrank by one-fifth. The decline in the dollar export value was,
however, associated with an increase in the export volume. The
increase in the supply of oil from the region in a period of weak
demand has contributed to a steep erosion of oil prices. The
region's merchandise imports adjusted to some degree to lower
export revenues, falling by 6 per cent in 1998 (Table 4).
Asia recorded the strongest import contraction in volume
and value terms of all regions. Import volume decreased by about
8.5 per cent under the impact of Japan's import contraction of
5.5 per cent, and that of the Asia (5) of more than 20 per
cent. It is estimated that within Asia only a few countries recorded
an increase in import volumes (e.g. Australia, China and India).
As intra-Asian trade accounts for about one half of Asia's merchandise
exports, the contraction of the area's imports also held down
export growth. Asia's export volume rose marginally as the volume
decrease for Japan, Chinese Taipei and Hong Kong, China were more
than offset by the strong growth of exports of the Republic of
Korea and the Philippines. China's exports are also estimated
to have expanded moderately in volume terms.
Table 4
Merchandise exports of emerging markets by product category,
1997
(Percentage shares)
|
| | Fuels
| Metals and minerals
| Agricultural products
| Manufactures | Total
|
| Middle East | 73
| 2 | 4
| 21 | 100
|
| Africa | 44
| 8 | 19
| 29 | 100
|
| Latin Americaa | 19
| 11 | 36
| 34 | 100
|
| Emerging Asiab | 5
| 2 | 10
| 83 | 100
|
| World | 9
| 2 | 11
| 78 | 100
|
aExcluding Mexico.
bAsia, excluding Japan, Australia and New Zealand.
The dollar value of Asia's imports registered an unprecedented
decline of 17.5 per cent. In 1998 Asia (5) imports contracted
by one-third, and those of Japan by 17 per cent (Appendix Charts
1 and 2). Only certain South Asian countries recorded a slight
increase in their imports (e.g. India and Sri Lanka). The trade
performance of most Asian countries improved in the last quarter
of 1998, partly due to the strengthening of the yen and other
Asian currencies vis-à-vis the U.S. dollar.
The sharp import contraction in the Asia (5) countries (almost
one-third in value terms) is largely explained by the turnaround
in private capital flows and the associated drop in domestic investment
and consumption levels. The decrease in exports of the Asia (5)
countries, however, was stronger than expected even if one takes
into account the high share of intra-regional trade in total trade.
Despite the strong currency devaluations which boosted the price
competitiveness of enterprises in the Asia (5) countries, the
combined exports of these countries did not increase their market
shares in the major developed markets. In fact, China's exports
to the United States, Japan and major European markets expanded
faster than those of the Asia (5) countries in 1998.
One of the striking features of world trade in 1998 was the exceptionally
large variation in the growth rates among countries measured
in value terms. Consequently, the ranking of the leading traders
changed dramatically for both merchandise and commercial services
trade (see Appendix Tables 1, 2 and 3). The reversal of capital
flows in 1997-1998 forced many East Asian economies to cut back
sharply on their imports in 1998. Import declines ranged from
26 to 35 per cent (e.g. the Republic of Korea 35 per cent, Thailand
33 per cent, Indonesia 34 per cent and Malaysia 26 per cent).
Retained imports of Hong Kong, China and Singapore also contracted
in this range, despite their current account surplus position
and stronger internal demand.
Contractionary conditions in Japan and the fall in oil prices
led to a fall of 17 per cent in the dollar value of imports, to
a level below that of Germany, the United Kingdom and France.
In general, Canada, Mexico and many West European countries improved
their position among the leading importers (and exporters), while
those of Asian countries and Russia deteriorated.
Fuel exporters generally recorded the strongest decline in merchandise
export value among all countries. For a number of them, the dollar
value of export earnings decreased by one-quarter to more than
one-third in 1998 (e.g. Saudi Arabia, Libya, Nigeria and Venezuela).
Oil exporters and the East Asian traders lost, while Mexico and
most West European countries gained in market share.
Last year, China's merchandise exports exceeded those of Hong
Kong, China for the first time. The contraction of Russia's trade
under the impact of the fall in fuel prices and the outbreak of
the financial crisis have lowered Russia's (extra-CIS) exports
to below those of Ireland and its imports to less than those of
Poland.
Despite the decrease in the nominal value of world trade, a few
countries continued to expand their exports by more than 15 per
cent. This group comprises Ireland, the Philippines, Hungary
and Costa Rica. Throughout the 1990-98 period these countries
expanded their exports two times faster than the global average.
The United States consolidated its position as the world leading
trader in 1998, accounting for nearly one-sixth of merchandise
imports and services exports and one-eighth of merchandise exports
and services imports.
East Asian countries' exports of commercial services decreased
in 1998 significantly faster than their merchandise exports.
One explanation for this development might be that intra-Asian
trade is more important for services than for merchandise exports
and thereby more affected by the contraction of Asian demand.
However, the lack of statistical information on the destination
of services exports precludes confirmation of this possibility.
Although price variations in commercial services are estimated
to be far smaller than those for merchandise trade in 1998, the
variations in the performance of individual services traders were
at least as large as those for merchandise traders. Among the
leading commercial services exporters, the strongest declines
were recorded by Singapore and Malaysia, while India and Spain
recorded increases in excess of 10 per cent. The Asia (5) countries
recorded contractions in their services imports ranging from about
20 per cent to more than 30 per cent. India, Spain and Ireland
recorded import increases between 10 and 20 per cent. Given the
provisional nature of the above data and the past experience of
substantial revisions even for year-old data, caution is called
for in interpreting current services statistics.
III. Repercussions of the fall in commodity prices
In 1998, an increase in the supply of many primary commodities
coincided with a slowdown in economic activity, leading to a sharp
drop in commodity prices. Prices of non-fuel commodities and
crude oil fell by 15 per cent and more than 30 per cent, respectively.
Although prices of manufactures decreased as well, prices of
primary commodities decreased much faster (for the second year
in a row).
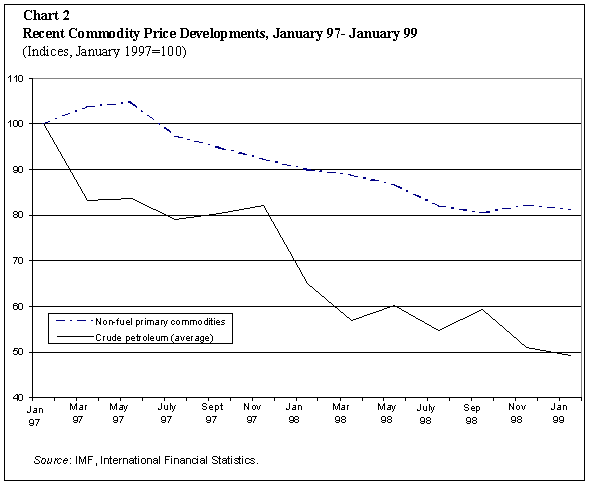
As the oil price decline accelerated during the course of the
year, the year-over-year change in December 1998 exceeded 40 per
cent. For non-fuel primary commodities, the period of weaker
prices started earlier and moderated in the second half, with
the result that the decline at the end of the year (about 10 per
cent) was smaller than the annual average for 1998 (Chart 2).
Oil exporters have yet to feel the full impact of lower spot oil
prices on their export earnings. Investment and government expenditure
is likely to be curtailed in 1999. Import levels will contract
further, as such a steep price decline cannot be fully absorbed
by a reduction in foreign exchange reserves.
|
|
As noted earlier, the steep fall in fuel prices affects in particular
the export earnings of the Middle East and Africa. Besides the
11 member countries of OPEC, in about another eight countries
fuel exports account for more than one half of export earnings.
It is important to note that in the first quarter of 1999, the
spot oil price recovered from its low level in December 1998 following
the announcement of production cuts by oil producers. It remains
to be seen whether this upward trend will continue or the present
price gains will prove sustainable. While these trends will lead
to downward adjustments in the imports of oil-exporting countries
in 1999, related income gains in oil-importing countries will
at least partially offset this contractionary tendency in world
trade.
Exporters of agricultural products are a larger group than oil
exporters. The decline in agricultural prices therefore affected
a larger number of countries, but generally less dramatically
than the oil exporters. This is for two reasons. First, the decline
in agricultural product prices was less steep than for oil. Second,
the exporters of agricultural products generally depend less on
a single commodity than do the fuel exporters (Appendix Table
4).
IV. Global trade outlook for 1999
The slowdown of world trade and output growth had not been reversed
by the end of 1998. While Japan's GDP continued to shrink in
the fourth quarter of 1998 and many West European countries recorded
a weakening in their economic performance, the U.S. economy accelerated.
Significantly slower GDP growth in Brazil in 1998 and contraction
in Russia will negatively affect the growth of neighbouring economies
with whom they have extensive trade ties. The sharp contraction
of output and trade in the Asia (5) countries appears to have
bottomed out, and a moderate recovery is the most likely scenario
for 1999. As there is generally a time-lag between reduced export
earnings and lower import levels, the steep fall of oil and commodity
prices will have its full impact on investment and consumption
in the commodity exporting countries only in 1999. The extent
of this impact may be mitigated in the case of oil prices, however,
should the recent increases in prices prove sustainable.
Global output growth may weaken slightly in 1999. Moderately
weaker growth in the United States and Western Europe may not
be offset by a lower rate of contraction in Japan. Given the
size of the Russian and Brazilian economies in regional output,
production levels in the transition economies and Latin America
is likely at best remain unchanged from the preceding year.
On the basis of this sluggish output growth, overall trade expansion
may not differ much in 1999 from the 3.5 per cent observed in
1998. Even this moderate expansion, however, is associated with
major downside risks and would imply an acceleration of trade
growth in the course of 1999. If slower output growth in the
United States or Western Europe turns out to be more pronounced
than presently expected, and if the recovery in East Asia (including
Japan) is more delayed than projected by most observers, world
trade expansion could be below 3.5 per cent. The United States
is expected to record the highest growth rate among the industrial
countries in 1999, but on the condition that U.S. consumers do
not rapidly correct their historically low savings rate, and that
any stock market correction will not have a major impact on investor
and consumer confidence.
Appendix Table 1
Leading exporters and importers in world merchandise trade,
1998
(Billion dollars and percentage)
|
| Rank
| EXPORTERS | Value (f.o.b.)
| Share | Change
| Rank | IMPORTERS
| Value (c.i.f) | Share
| Change |
| 1 | United States | 683.0
| 12.7 | -1
| 1 | United States | 944.6
| 17.0 | 5 |
| 2 | Germany | 539.7
| 10.0 | 5
| 2 | Germany | 466.6
| 8.4 | 5 |
| 3 | Japan | 388.0
| 7.2 | -8
| 3 | United Kingdom | 316.1
| 5.7 | 3 |
| 4 | France | 307.0
| 5.7 | 6
| 4 | France | 287.2
| 5.2 | 7 |
| 5 | United Kingdom | 272.7
| 5.1 | -3
| 5 | Japan | 280.5
| 5.0 | -17 |
| 6 | Italy | 240.9
| 4.5 | 1
| 6 | Italy | 214.0
| 3.8 | 3 |
| 7 | Canada | 214.3
| 4.0 | -1
| 7 | Canada | 205.0
| 3.7 | 2 |
| 8 | Netherlands | 198.2
| 3.7 | 2
| 8 | Hong Kong, China | 188.7
| 3.4 | -12 |
| 9 | China | 183.8
| 3.4 | 1
| | retained importsa
| 38.9 | 0.7
| -26 |
| 10 | Hong Kong, China | 174.1
| 3.2 | -7
| 9 | Netherlands | 184.1
| 3.3 | 4 |
| | domestic exports
| 24.3 | 0.5
| -11 | 10 | Belgium-Luxembourg
| 158.8 | 2.9
| 2 |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| 11 | Belgium-Luxembourg |
171.7 | 3.2 |
2 | 11 | China
| 140.2 | 2.5
| -2 |
| 12 | Korea, Rep. of | 133.2
| 2.5 | -2
| 12 | Spain | 132.8
| 2.4 | 8 |
| 13 | Mexico | 117.5
| 2.2 | 6
| 13 | Mexico | 128.9
| 2.3 | 14 |
| 14 | Chinese Taipei | 109.9
| 2.0 | -9
| 14 | Chinese Taipei | 104.2
| 1.9 | -9 |
| 15 | Singapore | 109.8
| 2.0 | -12
| 15 | Singapore | 101.5
| 1.6 | -23 |
| | domestic exports
| 63.3 | 1.2
| -13 | | retained importsa
| 54.9 | 1.8 |
-31 |
| 16 | Spain | 109.0
| 2.0 | 5
| 16 | Korea, Rep. of | 93.3
| 1.7 | -35 |
| 17 | Sweden | 84.5
| 1.6 | 2
| 17 | Switzerland | 80.0
| 1.4 | 5 |
| 18 | Switzerland | 78.7
| 1.5 | 3
| 18 | Austria | 68.3
| 1.2 | 5 |
| 19 | Malaysia | 73.3
| 1.4 | -7
| 19 | Sweden | 67.6
| 1.2 | 3 |
| 20 | Ireland | 63.3
| 1.2 | 19
| 20 | Australia | 64.7
| 1.2 | -2 |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| 21 | Austria | 61.7
| 1.1 | 5
| 21 | Brazil | 61.0
| 1.1 | -6 |
| 22 | Russian Fed.b
| 56.2 | 1.0 |
-16 | 22 | Malaysia
| 58.5 | 1.1 |
-26 |
| 23 | Australia | 55.9
| 1.0 | -11
| 23 | Poland | 48.0
| 0.9 | 13 |
| 24 | Thailand | 53.6
| 1.0 | -7
| 24 | Turkey | 46.4
| 0.8 | -4 |
| 25 | Brazil | 51.0
| 0.9 | -3
| 25 | Denmark | 45.8
| 0.8 | 3 |
| 26 | Indonesia | 48.8
| 0.9 | -9
| 26 | Russian Fed.b
| 44.7 | 0.8 |
-18 |
| 27 | Denmark | 47.0
| 0.9 | -4
| 27 | Ireland | 43.7
| 0.8 | 11 |
| 28 | Finland | 42.4
| 0.8 | 4
| 28 | India | 42.9
| 0.8 | 4 |
| 29 | Norway | 39.6
| 0.7 | -18
| 29 | Thailand | 41.8
| 0.8 | -33 |
| 30 | Saudi Arabia | 38.8
| 0.7 | -35
| 30 | Norway | 36.2
| 0.7 | 1 |
| | Total of abovec
| 4748.0 | 88.3 | -1
| | Total of abovec
| 4696.0 | 84.4 | -2
|
| | Worldc |
5375.0 | 100.0 |
-2 | |
Worldc | 5560.0
| 100.0 | -1 |
aRetained imports are defined as imports less re-exports.
bData exclude trade with the Baltic States and the
CIS. Including trade with these States would lift Russian exports
and imports to $73.9 billion and $59.5 billion, respectively.
cIncludes significant re-exports or imports for re-export.
Appendix Table 2
Leading exporters and importers in world merchandise trade
(excluding European Union intra-trade), 1998
(Billion dollars and percentage)
|
| Rank | EXPORTERS
| Value (f.o.b.) |
Share | Change
| Rank | IMPORTERS
| Value (c.i.f) | Share
| Change |
| 1 | European Union (15) |
813.8 | 20.3 | 0 |
1 | United States | 944.6
| 22.5 | 5 |
| 2 | United States | 683.0
| 17.0 | -1 | 2
| European Union (15) | 801.4
| 19.1 | 6 |
| 3 | Japan | 388.0
| 9.7 | -8 | 3 |
Japan | 280.5 | 6.7
| -17 |
| 4 | Canada | 214.3
| 5.3 | -1 | 4 |
Canada | 205.0 | 4.9
| 2 |
| 5 | China | 183.8
| 4.6 | 1 | 5 |
Hong Kong, China | 188.7 | 4.5
| -12 |
| 6 | Hong Kong, China | 174.1
| 4.3 | -7 | |
retained importsa |
38.9 | 0.9 | -26 |
| | domestic exports
| 24.3 | 0.6 |
-11 | 6 | China
| 140.2 | 3.3 | -2
|
| 7 | Korea, Rep. of | 133.2
| 3.3 | -2 | 7 |
Mexico | 128.9 | 3.1
| 14 |
| 8 | Mexico | 117.5
| 2.9 | 6 | 8 |
Chinese Taipei | 104.2 | 2.5
| -9 |
| 9 | Chinese Taipei | 109.9
| 2.7 | -9 | 9 |
Singapore | 101.5 | 2.4
| -23 |
| 10 | Singapore | 109.8
| 2.7 | -12 | |
retained importsa | 54.9
| 1.3 | -31 |
| | domestic exports
| 63.3 | 1.6 |
-13 | 10 | Korea, Rep. of
| 93.3 | 2.2 | -35
|
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| 11 | Switzerland | 78.7
| 2.0 | 3 | 11 |
Switzerland | 80.0 | 1.9
| 5 |
| 12 | Malaysia | 73.3
| 1.8 | -7 | 12
| Australia | 64.7 | 1.5
| -2 |
| 13 | Russian Fed.b
| 56.2 | 1.4 | -16
| 13 | Brazil | 61.0
| 1.5 | -6 |
| 14 | Australia | 55.9
| 1.4 | -11 | 14
| Malaysia | 58.5 | 1.4
| -26 |
| 15 | Thailand | 53.6
| 1.3 | -7 | 15
| Poland | 48.0 | 1.1
| 13 |
| 16 | Brazil | 51.0
| 1.3 | -3 | 16
| Turkey | 46.4 | 1.1
| -4 |
| 17 | Indonesia | 48.8
| 1.2 | -9 | 17
| Russian Fed.b | 44.7
| 1.1 | -18 |
| 18 | Norway | 39.6
| 1.0 | -18 | 18
| India | 42.9 | 1.0
| 4 |
| 19 | Saudi Arabia | 38.8
| 1.0 | -35 | 19
| Thailand | 41.8 | 1.0
| -33 |
| 20 | India | 33.2
| 0.8 | -3 | 20
| Norway | 36.2 | 0.9
| 1 |
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| 21 | Philippines | 29.3
| 0.7 | 17 | 21
| Philippines | 32.0 | 0.8
| -17 |
| 22 | Czech Rep. | 26.4
| 0.7 | 16 | 22
| Argentina | 31.4 | 0.7
| 3 |
| 23 | South Africa | 26.3
| 0.7 | -15 | 23
| South Africa | 29.3 | 0.7
| -11 |
| 24 | Poland | 26.3
| 0.7 | 2 | 24 |
Israel | 29.1 | 0.7
| -5 |
| 25 | Turkey | 26.1
| 0.7 | 0 | 25 |
Czech Rep.c | 28.8 |
0.7 | 6 |
| 26 | Argentina | 25.2
| 0.6 | -1 | 26
| Indonesia | 27.4 | 0.7
| -34 |
| 27 | United Arab Emirates |
24.2 | 0.6 | -16 |
27 | United Arab Emirates | 27.0
| 0.6 | -10 |
| 28 | Israel | 23.3
| 0.6 | 3 | 28 |
Hungary | 25.8 | 0.6
| 22 |
| 29 | Hungary | 22.9
| 0.6 | 20 | 29
| Saudi Arabia | 23.7 | 0.6
| -13 |
| 30 | Venezuela | 17.2
| 0.4 | -25 | 30
| Chile | 18.8 | 0.4
| -4 |
| | Total of aboved
| 3704.0 | 92.2 | -4
| | Total of aboved
| 3786.0 | 90.1 | -4
|
| | Worldd |
4018.0 | 100.0 |
-4 | | Worldd
| 4200.0 | 100.0
| -3 |
aRetained imports are defined as imports less re-exports.
bData exclude trade with the Baltic States and the
CIS. Including trade with these States would lift Russian exports
and imports to $73.9 billion and $59.5 billion, respectively.
cImports are valued f.o.b.
dIncludes significant re-exports or imports for re-export.
Appendix Table 3
Leading exporters and importers in world trade in commercial
services, 1998
(Billion dollars and percentage)
|
| Rank | EXPORTERS
| Value | Share
| Change | Rank
| IMPORTERS | Value
| Share | Change
|
| 1 | United States
| 233.6 | 18.1 | 1
| 1 | United States
| 161.5 | 12.5 | 6
|
| 2 | United Kingdom
| 99.5 | 7.7 | 8
| 2 | Germany
| 121.8 | 9.4 | 3
|
| 3 | France |
78.6 | 6.1 | -2 |
3 | Japan | 109.5
| 8.5 | -10 |
| 4 | Germany
| 75.7 | 5.9 | 1
| 4 | United Kingdom
| 76.1 | 5.9 | 7
|
| 5 | Italy |
70.1 | 5.4 | -2 |
5 | Italy | 69.3
| 5.4 | -1 |
| 6 | Japan |
60.8 | 4.7 | -11 |
6 | France |
62.8 | 4.9 | 1 |
| 7 | Netherlands
| 48.3 | 3.7 | -1
| 7 | Netherlands
| 44.8 | 3.5 | 2
|
| 8 | Spain |
48.0 | 3.7 | 10 |
8 | Canada |
34.8 | 2.7 | -3 |
| 9 | Belgium-Luxembourg
| 34.7 | 2.7 | 4
| 9 | Belgium-Luxembourg
| 33.6 | 2.6 | 6
|
| 10 | Hong Kong, China
| 34.2 | 2.6 | -11
| 10 | Austria
| 28.7 | 2.2 | 1
|
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| 11 | Austria
| 31.0 | 2.4 | 6
| 11 | China
| 28.6 | 2.2 | -5
|
| 12 | Canada
| 28.8 | 2.2 | -2
| 12 | Spain
| 27.3 | 2.1 | 12
|
| 13 | Switzerland
| 26.3 | 2.0 | 3
| 13 | Chinese Taipei
| 23.4 | 1.8 | -3
|
| 14 | Korea, Rep of
| 23.6 | 1.8 | -7
| 14 | Korea, Rep of
| 23.0 | 1.8 | -21
|
| 15 | China |
23.0 | 1.8 | -6 |
15 | Hong Kong, China
| 22.7 | 1.8 | -2
|
| 16 | Turkey
| 22.4 | 1.7 | 17
| 16 | Sweden
| 20.6 | 1.6 | 6
|
| 17 | Singapore
| 18.2 | 1.4 | -40
| 17 | Brazil
| 18.9 | 1.5 | 7
|
| 18 | Sweden
| 17.4 | 1.4 | -1
| 18 | Ireland
| 18.0 | 1.4 | 20
|
| 19 | Chinese Taipei
| 16.6 | 1.3 | -2
| 19 | Singapore
| 18.0 | 1.4 | -7
|
| 20 | Australia
| 15.8 | 1.2 | -14
| 20 | Russian Fed.
| 17.8 | 1.4 | -7
|
| | | |
| | | |
| | |
| 21 | Denmark
| 15.7 | 1.2 | 4
| 21 | Australia
| 16.7 | 1.3 | -9
|
| 22 | Norway
| 13.9 | 1.1 | -2
| 22 | Switzerland
| 15.0 | 1.2 | 6
|
| 23 | Russian Fed.
| 12.9 | 1.0 | -7
| 23 | Denmark
| 14.9 | 1.2 | -1
|
| 24 | Thailand
| 12.8 | 1.0 | -18
| 24 | Norway
| 14.8 | 1.1 | 2
|
| 25 | Mexico
| 11.9 | 0.9 | 6
| 25 | Saudi Arabia
| 13.9 | 1.1 | 0
|
| 26 | Malaysia
| 10.9 | 0.8 | -27
| 26 | India
| 13.7 | 1.1 | 12
|
| 27 | India |
10.5 | 0.8 | 22 |
27 | Mexico |
12.5 | 1.0 | 6 |
| 28 | Greece
| 9.9 | 0.8 | 8
| 28 | Thailand
| 12.2 | 0.9 | -29
|
| 29 | Poland
| 8.9 | 0.7 | -1
| 29 | Indonesia
| 11.9 | 0.9 | -26
|
| 30 | Israel
| 8.7 | 0.7 | 4
| 30 | Malaysia
| 11.9 | 0.9 | -32
|
| | Total of above | 1123
| 87.0 | -1 | |
Total of above | 1100 | 85.2
| -1 |
| | World | 1290
| 100.0 | -2 |
| World | 1290
| 100.0 | -1 |
Note: Secretariat estimates based on incomplete or preliminary
data.
Appendix Table 4
Traders with a high share of agricultural products in their
merchandise exports, 1990 and 1997
(Percentages)
| | 1990
| 1997 |
| Malawi | … | 92
|
| Belize | 91 | 90
|
| Paraguay | 90 | 82
|
| Mozambique | … | 78
|
| Iceland | 80 | 75
|
| | | |
| Madagascar | 70 | 72
|
| Costa Rica | 64 | 67
|
| Nicaragua | 89 | 63
|
| Uruguay | 61 | 61
|
| New Zealand | 63 | 61
|
| | | |
| Ecuador | 46 | 61
|
| El Salvador | 41 | 56
|
| Argentina | 61 | 53
|
| Zimbabwe | 44 | 51
|
| Honduras | 86 | 43
|
| | | |
| Bolivia | … | 40
|
| Cameroon | 36 | 37
|
| Chile | 33 | 37
|
| Colombia | 37 | 37
|
| Brazil | 31 | 35
|
| | | |
| Morocco | 29 | 35
|
| Peru | 25 | 34
|
| Mauritius | 33 | 31
|
| Australia | 30 | 30
|
Source: WTO, Annual Report 1998.
Appendix Chart 1
Appendix Chart 2
| |