
Special Interest Group on Maritime Transport and Ports
a member of the WCTR Society
INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP
Genoa - June 8-10, 2000
Railfreight Deregulation and Revival: A Study of
Rail-Port Integration in European Port Traffics
Author: Dr.Merv Rowlinson*, Senior Lecturer in Shipping
and Transport, Centre for International Transport Management,
London Guildhall University, 84 Moorgate, London EC2M 6SQ. Tel:
44 020 7320 1456; Fax: 44 020 7320 1465; E.Mail: rowlinsn@lgu.ac.uk
* With many thanks to the following for sharing their expertise:
David Cross, General Manager Sales, ABP, London,
Paul Davey, Corporate Affairs Manager, Hutchinson Ports, Felixstowe,
Robert Goundry, Director of Strategy, Freightliner, London,
John Healy, General Manager, Port of Boston,
Miller Howieson, Inland Operations Manager, P&O-Nedlloyd, Southampton,
David Hutson, Director Operations, NYK Line(Europe),
Bill Stoker, Freight Services Manager, Harwich International Port
Frank Worsford, University of Westminster.
Abstract
This paper reports on research carried out on the subject of
developing railfreight linkages in European ports. In particular,
attention is given to the critical factors determining rail's
competitiveness. The large volumes of freight generated by maritime
trade provide excellent potential for inland shipment by rail,
given improved marketing and competitiveness. The context is
derived from the forces of de-regulation, sharpened entrepreneurialism
and heightened awareness of environmental factors in transport
and logistics. The concept of sustainable transport and distribution
is coming increasingly to the forefront. This provides considerable
opportunities for a revived railfreight business. These have
all helped to increase the profile of railfreight in Europe, particularly
in the UK. Rail linkages with the ports have, therefore, become
increasingly important, particularly given the extent of expansionist
plans in a number of key hub ports. The environmental debate
surrounding port development has raised the controversial question
of increased road building and intensified road haulage movements;
railfreight can offer an alternative inland linkage with the port.
In such ports as Antwerp, Felixstowe and Southampton, railfreight
linkages have become central to the debate on expansion. It is
now evident that a new paradigm is called for in assessing the
role of railfreight in port trades.
The evidence from the UK is that privatisation and deregulation
have proved to be catalysts for a railfreight revival, reversing
the long term trends of decline. This is particularly evident
in rail linkages with ports. Key international traffics - containers,
steel, coal, chemicals, foodstuffs - have been won from road competition.
UK ports now actively market their rail linkages. It is, however,
highly apparent that many obstacles to rail growth still exist.
Rail congestion is already manifest in the UK's two largest container
ports, Felixstowe and Southampton. Nationally, there is acute
competition for track space with the passenger operating franchises.
Appraisal of the barriers to rail development , as well as opportunities
will be made.
The objectives of this paper are to establish the
key economic and environmental factors that influence railfreight-port
linkages vis-à-vis road haulage competition. This will
involve the identification of best-practice in European rail-port
logistics and the critical factors of modal selection in port
generated traffic flows. Generally, the success of railfreight
in port trades will depend upon the level of provision, its competitive
response to customer needs and inter-modal integration.
Four case studies have been drawn from the UK experience
of privatisation and deregulation in both railways and ports;
the intention is to consider the impact of such changes and to
assess the implications for continental systems now pursuing a
similar strategy. Exciting new projects such as the "Iron
Rhine" railfreight link between Antwerp and Duisburg and
the proposed mega-container hub, "Jade" at Wilhelmshaven
offer great opportunities for railfreight businesses. Open access
soon to be enjoyed by new railfreight providers could prove a
flexible, dynamic and competitive and inland linkage to continental
ports. It will be, therefore, of interest to consider the evidence
from the UK rail and port industries.
1.0 INTRODUCTION
This paper considers the many issues surrounding the attempts
to secure a European railfreight revival. The selected area of
freight transportation is that of the port-rail interface. Considerable
organisational, political and operational changes are currently
impacting on the European rail network. The evidence of de-regulation
and privatisation in the UK network has significant implications
for the rest of Europe, forcing a re-evaluation of rail performance
vis-à-vis road haulage. Additionally, the heightened
focus of rail in European sustainable mobility strategies has
emphasised the inland alternatives to road haulage. The increase
in UK railfreight, particularly in new markets, contrasts somewhat
with the disappointing performance of Channel Tunnel and other
intra-European freight in recent years. Table One features the
first five years of privatisation. It can be seen that that the
1994-8 period brought a 139 percent increase in Channel Tunnel
traffic. However this was predicted to fall by 18 percent between
1998 and 2000. The two railfreights featured here, coal and intermodal
are largely derived from deepsea traffic movements. The import
of large coal shipments in panamax and capesize ships to such
deepwater quays as Hunterston (Clyde) and Immingham (Humber) generates
significant demand for rail haulage.
Table One: Privatised Selected Railfreight Million
Tonne-Kilometres, 1994-2000
| 1994/5
| 1998/9
| 1999/2000
|
| Coal | 6,899
| 9,960
| 10,779
|
| Domestic Intermodal
| 5,009
| 9,010
| 9,783
|
| Construction |
3,709
| 3,902
| 3,686
|
| Channel Tunnel |
1,183
| 2,828
| 2,311
|
| Oil/Petroleum
| 3,492
| 3,290
| 3,179
|
| Metals
| 3,625
| 4,416
| 4,442
|
| Other
| 7,713
| 9,806
| 10,456
|
| Totals
| 31,630
| 43,213
| 44,636
|
Source: Railtrack (2000) The Challenges Ahead. London:
Railtrack.
Similarly, box movements to and from such ports as Southampton,
Thamesport, Tilbury, Felixstowe and Liverpool provides demand
for mainline Freightliner trains, usually for distances in excess
of 160 kilometres. The forty percent increase in total railfreight
movements points to the freight success of the early privatisation
period.
1.1 The Problem
It is apparent that the case for sustainable transport alternatives
to road is gaining considerable momentum in political and some
industrial circles. Essentially, the railfreight industry needs
to be able to promote its economic and logistical advantages within
the environmental context. This means competing over shorter
distances, achieving costings, timings and reliability standards
comparable to road haulage. Given the decline in the traditional
staple freights - coal, iron ore, steel, bulk chemicals - brought
about by changes in the industrial structure, new markets need
to be re-entered. This includes time sensitive goods. Train loads
of perishables such as bananas from Avonmouth docks and fresh
fish from Aberdeen and West Country milk were lost to road due
to the poor rail services of the post-1960s (Bonavia). The challenge
of the new rail imperative is to win back such traffics by a combination
of cost, quality and environmental attributes. It is apparent
that despite the renewed attractions of the rail case, the environmental
advantages of switching freight from road, many economic, logistical
and perceptual obstacles need to be overcome. The historic problems
of an ageing infra-structure, shortages of track capacity, under-investment
and the years of malaise and uncertainty had atrophied the network.
In mainland Europe it is evident that poor co-operation between
state railway corporations and limited entrepreneurial dynamism
is stifling rail's potential to make significant impact on road
haulage's dominance.
1.2 Outlining The Rail Case
The recognition of rail's environmental advantages was made evident
in the Commission of the European Communities report, The
Future Development of theCommon Transport Policy(1992).
This report highlighted the external costs of road haulage, including
pollution, congestion and road surface damage. The Royal Commission
on Environmental Pollution Eighteenth Report, Transport
and the Environment (1994), was testament to the growing
awareness of the road problem in the UK.By declaring the
positive environmental advantages of the freight transfer from
road to rail and water transport, the Royal Commission justified
the tripling of railfreight in a ten year period. The target
was later to be adopted by the UK's major railfreight operator,
English, Welsh and Scottish Rail (EWS) and was endorsed by the
1998 Government White Paper, A New Deal for Transport: Better
for Everyone (DETR). Notably, this paper identified the
strategic needs to up-grade rail links into ports (DETR).
In addition to political forces promoting the rail imperative
it is becoming apparent that many business activities are concerned
by environmental issues and, as a consequence, wish to pursue
a greener transport strategy.
Another dynamic of freight transfer is drawn from the economic
and logistical advantages inherent in some sectors of railfreight
operations. The ability of rail to move large consignments over
long distances at low tonne-km costs does prove attractive to
a section of service users. McKinnon found that:
in terms of direct line-haul costs, trains are a
much more efficient means of transporting
freight than lorries, mainly because they consume
less energy per tonne-kilometre and achieve
much higher levels of labour productivity
(McKinnon pp.163-3).
|
This aspect of railfreight economics has not been lost on port
users faced with the task of moving large volumes to and from
the ship. The concentration of key container, ro-ro and bulk
traffics in the leading ports has enhanced the prospects for rail.
1.3 The Obstacles to Freight Transfer
Despite the growing momentum of the railfreight case, a number
of critical considerations need to be made. The critical areas
for the rail mode option have been identified as:
- goods not suitable and/or time sensitive;
- low level of potential users connected to rail network;
- majority of freight flows short-distance;
- poor perception;
- passenger train priority (Worsford and Blair).
Unsuitable goods include just-in-time flows highly specific to
the customer's needs. Railfreight has not achieved a widespread
domestic success in meeting the demands of fast moving consumer
goods, particularly when serving the needs of the retail sector.
The low levels of rail connection for potential customers can
be explained by the two principal factors: (1) the severance of
many businesses from the rail system resulting from the rationalisations
of the 1960-90 period; (2) the location of new business enterprises
on motorway access points and away from the rail network. The
net result is the costly and time consuming transhipment of freight
from road at the nearest railhead.
The distance factor also militates against rail. It has long been
regarded that railfreight's high fixed cost burden in terminal
and infrastructure costs would preclude short distance freight
movement (Nash p.258). The poor perception of railfreight service
levels is another obstacle to freight transfer. The historic image
of under invested, bureaucratic and unreliable freight services
has prevailed in the minds of many potential users. Finally, the
priority given to passenger services invariably reduced the point
to point timings of freight trains and in many cases limits freight
pathways to overnight slots. Recent increases in passenger-kilometre
movements and the dedication of fast lines to incipient high speed
services such as the 225 kph Virgin Tilt Trains, will serve to
increase the difficulties of freight diagramming.
In considering the prospects for extending railfreight linkages
with the ports, then, it is apparent that considerable opportunity
exists but also that many obstacles have to be overcome. This
paper now goes onto discuss the evidence and issues of a rail
renaissance in the port trades.
2.0 THE CONTEXT
The context for this research is made up from a number of fast
moving changes that are affecting both the ports and the inland
shipping sectors. After years of decline in the UK railfreight
industry, the impact of deregulation, privatisation and the emergence
of entrepreneurial, customer focused, operators has enlivened
the scene. This has registered in several ways. Considerable
investment in traction and rolling stock has been undertaken by
the two main operators, EWS and Freightliner. Labour productivity
and empowerment has increased. New services have developed;
and, importantly, a number of UK ports have had their severed
rail linkages restored. EWS has enjoyed considerable success
in extending its wagonload, Enterprise service, which provides
customers with a network of overnight routes. The deepsea ports
of Southampton, Felixstowe and Thamesport and the predominantly
shortsea ports - Purfleet, Harwich, Goole, Immingham and Hull
- have induced EWS Enterprise services to a wide range of destinations
(Lloyd's List 14.10.99). The UK experience has considerable
implications for Continental operators embarking on various types
of de-regulation and privatisation.
In the ports' industry similar pattern of de-regulation and privatisation
have brought radical changes and served to accelerate competition.
Increasingly ports are seeking to market a range of services to
their customers. In recent years the rail linkages have been heralded
as a major asset in the service portfolio of ports. Additionally
expansion programmes in growing ports have focused attention on
the railfreight option as a way of limiting the extra road haulage
journeys. The massive dredging and container key expansion at
Felixstowe has been accompanied by a £5.6m expansion to the
Port's Northern Rail Terminal, providing for a 50 percent increase
in container capacity by rail (Lloyd's List 19.3.99). The
controversial proposal for a new, New Forest Rim, deep water container
in Southampton has placed significant emphasis on railfreight
linkages to Central and Northern England and Scotland. Huge
container handling development plans in Antwerp, involving new
terminals and a deepening of the River Schelde, are being pursued
in conjunction with the new rail link, "Iron Rhine,"
to Duisburg. (Lloyd's List. 15.5.00).
Changes in shipping, particularly, the scale of organisation,
in the 1990s has significant implications for the railfreight
imperative. In the liner sector the mid-late 1990s have brought
a series of mergers and takeovers. These include P&O-Nedlloyd,
American President Lines (APL) - Neptune Orient Line (NOL), Maersk-Sealand
and Canadian Pacifics buy-out of both Cast Line and Lykes Lines
in the container sectors. In the deepsea ro-ro trades, Norway's
Wilhelmsen Line and Sweden's, Wallenius Line, have joined forces
to produce global leadership in vehicle carriage. Such developments
are usually followed by a rationalisation of port calls. The
Maersk-Sealand partnership and eventual merger led to the designation
of the Port of Felixstowe as their sole UK call. Canadian Pacific's
buy out of Cast Line saw the re-location of Cast's weekly North
America service from Zeebrugge to Antwerp, much to the chagrin
of port officials in the former! Additionally, the North Europe-Far
East container service has witnessed a jump in container ship
sizes from the 4000 teu panamax to the 5000-7000 teu post-panamax
vessel. In the deepsea coal trades the enduring recession in
freight rates has instigated the search for the lower tonne-nautical
mile costs of larger bulk vessels. This necessitates an increase
in vessel size from the 65,000 deadweight tonne panamax size to
the >180,000 deadweight tonne cape size vessel.
The large cargo volumes resulting from these changes should
prove conducive to the rail option as it increases the likelihood
of increased rail competitiveness. For example, the Southampton
call of P&O-Nedlloyd's post-panamax "Southampton Class"
vessels generates a box exchange in excess of 3000 teu. The
concentration of cape size coal shipments on Clyde Port's, Hunterston
Terminal, generates considerable tonne-km rail demand for movements
to English power stations.
3.0 THE DECLINE OF RAILFREIGHT 1960-95.
Discussion on rail revival needs to give some attention to the
serious decline of European railfreight in the post 1960s period,
particularly in the UK. A number of changes in the structure
of industry in Europe are most apparent as catalysts for decline.
The run down of the staple coal and steel industries, accompanied
by rationalisations in petro-chemicals, has reduced the traditional
bulk flow which had proved conducive to rail. In addition, under-investment
has led to shortages of traction and rolling stock and has prevented
the necessary modernisation of the essentially 19th century infrastructure.
In addition, poor labour relations and a bureaucratic management
and organisational structure has proved an encumbrance to efficient
customer focused services. Train crew productivity suffered as
a consequence. One particularly acute example of this was provided
by the Southampton-Leeds Freightliner maritime service which required
five sets of train crew to complete its 400 km journey!
The withdrawal of wagon load traffics, followed by the uncertainties
of the run up to privatisation, has also led to traffic loss.
EWS president, Ed Burkhart, has not resisted from criticising
the "scorched earth policy" of British Rail's freight
management in the immediate post privatisation period. It is
apparent that the commercial policy was to concentrate on exclusively
on the most lucrative, high volume, block train movements. The
40 percent hike in Trainload Freight's charges for steel movements
from the Port of Boston in 1993 left little option to switching
to road and severing the rail connection (Track Today 13.8.97).
As a consequence, at least an extra 8000 lorry journeys between
the West Midlands and the Lincolnshire port were generated. Another
failure in the port trades was the inability of rail, Freightliner
in particular, to respond to the increase in container sizes in
the deepsea container trades. The replacement of the 8 ft 6ins
and 9 ft 6 ins boxes by the "high cube" 9 ft 6 ins in
the deepsea trades precluded the use of rail for UK distribution.
This was due to the loading gauge limitations of the network,
prior to the recent arrival of low platform wagons.
In growth areas where rail could have expected to prove competitive
with rail such as the long distance movements of containers, rail
performance had proved disappointing largely due to high terminal
costs (McKinnon pp.167-8).
4.0 RAILFREIGHT RENAISSANCE?
Writing at the end the century, it is apparent that the years
of atrophy and decline are at last in reverse. The combined forces
of deregulation, privatisation and environmental concern appear
to generating a new rail imperative. This can be observed in
a number of examples, including:
- investment in new traction and rolling stock;
- reinstatement of track linkages into ports;
- the return of wagon load traffics.
The net result has been a growth in rail tonne-km movements and
some examples of freight transfer from road. Port traffics have
been a particular feature of this revival. Significant investment
by the new freight companies has helped secure existing core freights
such as steel. EWS' reopening of the York rolling stock works
allowed for the rapid delivery of steel carrying Thrall wagons.
The new wave of low platform container wagons has allowed for
Freightliner and EWS to win high cube box maritime trade. By late
1999, Freightliner had taken delivery of 200 low platform wagons
and EWS was reported to have had 980 wagons close to delivery
(Lloyd's List 14.10.99). The traction shortage has been
addressed by the arrival of imported General Motors locomotives
and the re-conditioning and up-grading of existing engines.
The reinstatement of rail linkages into ports has been a particular
feature of EWS' expansion strategy. In the three decades up to
the mid-1990's port linkages were consistently run down and withdrawn.
Busy East Coast ports including, Hull, Grinsby, Goole, Ipswich
and Boston, and Purfleet, and Chatham on the Medway lost their
direct rail links.
5.0 SAMPLE RAIL-PORT CASE STUDIES
The research now pursues a case study approach.
Four UK ports have been selected - Boston, Felixstowe, Harwich,
Southampton. All four have witnessed significant rail revival
in recent years. The aim of the investigation here is to establish
the principal forces driving these developments. Consideration
has been given in particular to:
- Traffic Demand Factors;
- Distance Factors;
- Road Alternatives.
The quantitative factors in traffic demand are considered. These
include the frequency and volume of flows and comparative pricing
between transport modes. Attention is given to main qualitative
concerns of the freight shipper - reliability, timekeeping, security,
flexibility, handling.
Distance factors, in conjunction with volumes are examined in
order to consider the critical mix of tonne-kms necessary for
rail to exert competitive advantage.
Finally, the "litmus test" of the rail imperative rests
with the challenge it presents to road haulage.
5.1 Boston's Steel Trade
The Lincolnshire up-river port, Boston, markets itself
as the provider of the nearest East Coast ship discharge to
the Birmingham and West Midlands industrial region. Primarily,
the trade is European shortsea and reflects East Anglia's agricultural
base.
The steel business is a result of the re-organisation,
integration and rationalisation of European production sites.
The selective run down of UK steel production during the 1980s
placed emphasis on imports from Belgium, the Netherlands and Germany.
competition for the handling of steel coils - bound for the automotive
and metal fabrication industries of the West Midlands - is considerable,
totalling at least ten ports. Included are the Humber and Trent
ports, the East Anglia ports, Kings Lynn, Ipswich and even the
South Coast ports, Shoreham and Poole, all vying for the business.
Although cost competition is at a premium in the steel trade,
quality factors are also paramount in the handling, transportation
and storage
The withdrawal of railfreight facilities in 1993
can now be seen as a result of the uncertainties of the privatisation
period. However, a number of demand and supply factors in favour
of rail's return in the mid-late 1990s converged. These included
(1) the preference of the West Midland's steel stockists for
trainload deliveries of steel, approximating 1000 tonnes net;
(2) the enduring energy of the port management in traversing the
prolonged, complex and cumbersome planning processes, in order
to attain the logistical and environmental benefits of rail; (3)
the emergence of a business led culture in railfreight following
the US railroad corporation, Wisconsin Central's setting up of
EWS in order to takeover British Rail's railfreight companies;
(4) finally, the provision of Freight Facilities Grants(FFG)
to assist with the specialist handling and storage equipment
at both ends of the rail journey and a Track Access Grant, proved
an inducement to freight transfer to rail. Despite the considerable
pressure exerted by these forces for a return to rail in the port
it took over three years to get the trains running! Additionally,
during this prolonged planning period, it was necessary for the
local council to act rapidly to prohibit the selling off of an
essential component of the rail linkage to a supermarket chain!
The distances involved are on the low side of orthodox
rail threshold being in the 140-170 kms range. The bulk flows,
however, compensate somewhat: vessels arrive with between 2000
and 4000 tonnes of steel. This proves conducive to rail haulage,
providing for at least three services per week.
The early experience of Boston's rail mission was
marred somewhat by intensive road competition, with haulage rates
reported to be falling by up to £1.50 per tonne (Lloyd's
List 16.10.97). However, local haulage rates fluctuate in
accordance with the seasonal demands of the regions agricultural
trades. This provides some advantage to the rail carrier, EWS,
given their ability to offer a more stable rate over longer periods
of time.
The signs in mid-late 1999 were that both sea and
rail steel carriage were about to increase significantly at Boston.
5.2 Felixstowe's Rail Expansion
The Suffolk port is the UKs leading deepsea container
handling facility. Recent years have brought a significant increase
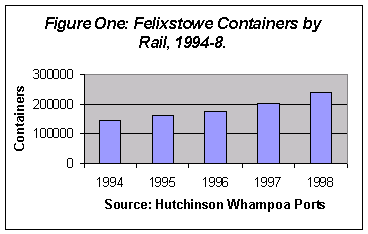
in the boxes moved by rail. Figure One shows the 64 percent increase
in Felixstowe boxes moving by rail in the five year period up
to 1998. Additionally, rail has been able to increase its share
of the port's UK traffic from 15 to 20 percent in this period
(Hutchinson Whampoa Ports).
The problems of growth facing the principal rail
operator in the port, Freightliner, has been track capacity, particularly
on the single line branch line from Ipswich. Recent layout up-grading
by Railtrack has improved the situation by the construction of
a passing loop. Together with the opening of the port's £5.6m
Northern Rail Terminal, the track improvements have increased
(theoretically) train capacity from 24 to 32 per day (Modern
Railways April 1999). The expansion of railfreight was implicit
in the 1998 five year partnership agreement between the Port's
owners, Hutchinson Whampoa and Freightliner (Lloyd's List 27.4.98).
This complemented the large expansion in deepwater handling capacity.
The considerable environmental issues of quayside expansion and
dredging, have placed a premium on the port's green profile. The
expansion necessary to increase capacity and to accommodate the
new generations of post-panamax container ships involved expensive
environmental mitigation. The port's Harbour Authority, Harwich
Haven, has sought to off-set the negative impact of development
with environmental management projects in excess of £10m
at 1988 prices (John). From this perspective, the port's commitment
to rail expansion can be seen as having "green" as well
as logistical benefits. With an estimated 3-4000 container movements
by road per day, freight transfer to rail achieves enhanced strategic
importance for Felixstowe.
Freightliner are currently operating around 26 trains
per day to 11 locations - Birmingham, Cardiff, Crewe, Daventry,
Doncaster, Glasgow, Leeds, Liverpool (2 railheads), Manchester,
Tees. Distances vary to between 225kms to Birmingham and 800kms
to Glasgow. Daily freight flows are primarily deepsea traffics.
In addition, EWS have recently started a container service which
will integrate Felixstowe with the Enterprise network (Lloyd's
List 14.10.99).
Explanation of Felixstowe's rail expansion can be
seen partly as a result of the upsurge in deepsea boxes handled.
Between 1994 and 1998 UK destination containers grew by 22 percent.
The 64 percent growth in rail-borne boxes represents a shift
from road to rail and requires further consideration. The four
principal reasons are: (1) the commitment of the port to rail,
apparent in the £5.6m railhead investment; (2) the support
of Government with its Freight Facility Grant (£1.8m contribution
to the port's £5.6m investment); (3) the commitment of Railtrack
to up-grading the Felixstowe branch; (4) the entrepreneurial
stance of Freightliner in winning the custom of the
deepsea operators by a mix of pricing and quality factors, including
investment in rolling stock and traction.
The predictions of a further growth (10 percent)
in 1999 points to a sustained and robust rail revival. However,
this must be measured by a number of structural restraints.
The EWS decision to load Felixstowe traffics in the Port of Ipswich
involves a costly 20 minute road journey leg for the new service.
Moreover, this points to the limited capacity of the Felixstowe
branch. The routing of the majority of northbound Freightliner
services via London, in order to benefit from 9 ft 6 in loading
gauge, places and additional 180 kms on the journey and faces
the capacity limitations of the West Coast Main Line (WCML).
Business consternation over the impact of the imminent WCML
up-grade on Freightliner services is evident.
5.3 Harwich's Inter-modal Venture
Harwich's history is very much that of a railway
port. As the ferry terminal for the Great Eastern Railway's passenger
and freight services to the Benelux countries, the port's fate
has invariably intertwined with the rail interest. British Rail's
innovatory intermodal service in 1968 proved to be an early
example of railsea logistics in the shortsea trades. As the service
provider between Ford's Dagenham and mainland European plants,
British Rail achieved a market leader status in fully cellular
container shipping in the shortsea trades. Unfortunately, for
the port, the trade easily leant itself to transfer to the Channel
Tunnel; as a consequence, railfreight services were withdrawn
in 1994.
The return to rail in 1997 was something of a shock
in that it offered a lo-lo route to Zeebrugge as an alternative
to Channel Tunnel intermodal services. The dynamics of rail's
return to Harwich can be seen as the result of four factors: (1)
the desire of shippers to link UK freight flows with continental
services from Zeebrugge to Central and Southern Europe; (2) the
quest by shippers for both a quality and a cost competitive alternative
to the premium tariffs of the Channel Tunnel; (3) the participation
of road hauliers in the service; (4) the considerable intermodal
expertise that the port has accumulated, providing for optimum
efficiency in railsea integration; (5) finally, the willingness
of EWS to invest in new traction and rolling stock on the routes.
Rail Haulage distances in the UK are in the 400-600
kms range. The daily link with Doncaster combines with EWS services
to Teesport, an important source of chemical traffics. The Harwich-Wembley
service offers connections to Newport and Widnes and the Seaforth
container terminal in Liverpool. The Widnes link features a collaboration
with a local haulier and has led to the opening of an international
terminal, supported by a Freight Facility Grant. The 44 tonne
dispensation for road-rail interchange and the strategy to minimise
the road trunking of hazardous goods has proved attractive to
chemical shippers in the Widnes-Runcorn industrial region. The
new delivery of EWS' low platform megafret wagons has helped boost
services by allowing for the unhindered carriage of 9 ft 6 in
containers.
The regular flow of traffics is balanced by the
foodstuffs moving North from Milan with chemicals moving South
from the UK's Merseyside and Teeside industrial regions. Essentially,
the UK rail operation is the result of the astute combination
of regular traffic flows and the highly efficient Stena Line nightly
container service carried out by the 200 teu sister vessels,
Hera and Apus. The integration with road haulage
operations in the Widnes area and the custom generated by P&O
Ferrymasters has enhanced co-operation rather than competition
with hauliers.
5.4 Southampton Rail Revival in a Traditional
Railway Port
The port of Southampton can claim to be the textbook railway port.
Its current quayside layout resulted originally from 19th
Century investments by the London and South Western Railway Co,
and the large inter-war constructions of the Southern Railway.
The port is served by two Freightliner terminals, Millbrook and
Maritime. Additionally, both the Eastern and Western Docks are
served by rail offering close to quayside linkages. . Southampton
is also the UK's number one port for automobile shipments. Substantial
railhead investment by the distributors of Ford and Rover automobiles
has been undertaken recently, with rail being used to integrate
with Southampton's network of ro-ro liner services (Lloyd's
List 25.10.99). Southampton is the UK's major port for Far
East container services, of which P&O-Nedlloyd are a principal
carrier The influence of the Anglo-Dutch line is also evident
in the part ownership of Southampton Container Terminals (SCT),
shared with Associated British Ports (ABP). The P&O-Nedlloyd
connection is also critical to the rail imperative, with 55 percent
of the shipping line's inland freight moved by rail (Lloyd's
List 26.8.98) and over half of Southampton's 26 Freightliner
services running as P&O-Nedlloyd block trains. This factor,
coupled with the port's historic rail links has provided for in
excess of 30 percent of container movements by rail, the highest
level of all UK ports. As with Felixstowe's container services,
Southampton's growth in recent years
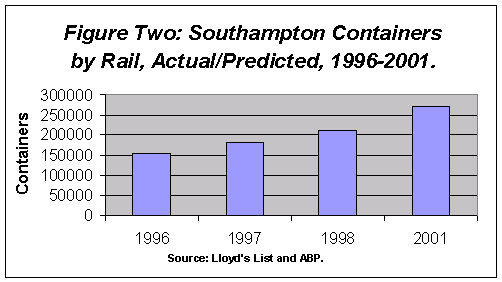
has been dramatic. Figure Two shows a 35 percent increase in
containers by rail, between 1996 and 1998 and almost a doubling
by predicted by 2001. In addition to the Freightliner services
, the port also has up to six trains per day providing direct
quayside access these have to share track capacity with Ocean
Liner passenger services that provide direct services to such
liners as the QE.2and Oriana. EWS
run a mixture of automobile, bulk and container trains with the
latter being linked with the Enterprise network offering national
coverage between Plymouth and Inverness. (Lloyd's List 14.10.99).
Again, the growth has been significant considering that in the
early 1990s the disruption of privatisation, accompanied by a
sudden large increase in track access charges, looked certain
to bring a severance with the South Western mainline. A recent
Lloyd's List market report praised the port's commitment
to rail:
|
Southampton port has been vindicated in its decision over
the years to maintain and nurture its rail links, in the
interests of providing its clients with the widest transport
options, to the extent that it rates today as a substantial
rail freight hub (Lloyd's List 25.10.99).
|
Container rail flows are predominantly in excess of 300kms. However,
one exception is provided by Freightliner's shortest service,
Southampton-Barking (160 kms), which operates on a daily basis.
This has proved to be a blueprint for other relatively short
distance services: Southampton-Cardiff (190 kms) and Tilbury-Daventry
(160 kms). The strategy here is for the daytime utilisation of
the traction and rolling stock for the shorter routes, allowing
them to be slotted in between the long distance overnight services.
Other newly won freight services operating relatively short distances,
<200kms include stone and gypsum flows. It is apparent that
direct rail linkages were a key factor in Southampton winning
these bulk traffics.
Looming large in the controversial plans to extend container operations
on the New Forest side of the port - Dibden Bay - is the question
of inland transport. Rail, along with coastal shipping, has
been given an important role in the debate, given its ability
to move large volumes at low environmental cost vis-à-vis
road haulage. The plans of Associated British Port's (ABP) are
for a twelve track rail siding which will connect, via the Fawley
branch line, to the main South Western mainline. The ABP position
was stated clearly in their 1997 Dibden update press release:
|
Putting freight onto rail as a method of reducing
congestion on Britain's roads is an important
objective for Government and County Council
and ABP is working hard with Railtrack to
ensure the maximum use of rail as a freight
transport mode for Dibden Bay (ABP).
|
The growth in Southampton freight by rail is a result of three
key factors: (1) the heavy commitment of P&O-Nedlloyd to
rail; (2) the port's desire to promote the environmental and logistical
advantages of rail; (3) the ability of EWS and Freightliner to
offer a cost competitive and quality alternative to road haulage,
even over short distances.
Road haulage competition in the container and automobile trades
is considerable. However, the ability of the rail carriers to
achieve a high level of loading capacity has provided for rail's
competitive edge. As with Felixstowe, track capacity issues are
of some concern. The South West mainline supports an intensive
passenger train schedule, including, a London shuttle service
(4 trains per hour in each direction), cross country and local
stopping services. This places a premium on track space. Freight
services to Birmingham and points North also face congestion
on the Great Western mainline in the Reading area.
6.0 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION
The initial findings of this study are that the upsurge in
UK railfreight linkages with ports points not only to the under
achievement of the mode's potential prior to the mid 1990s but
also to the convergence of a number of favourable factors. These
include customer preference for rail, the active support of port
management and a new surge of railfreight enterprise and investment.
The commitment of government, supported by its financial packages,
has helped to raise the "green" profile of rail.
A culmination of these factors have allowed for rail to compete
on cost and quality over shorter distances and in accordance with
the just-in-time restraints of modern logistics.
The experience of Boston's steel trade demonstrates, despite
the relatively short distances involved, the capability of rail
to move large volumes in order to meet the customer's preferences.
In doing so considerable alleviation of road traffic on Lincolnshire
roads is achieved. Harwich's return to rail demonstrates the potential
for intermodal activities, given efficient planning and co-ordination.
The story from Felixstowe and Southampton is that rail is becoming
increasingly integral to both the large volumes involved and the
contested environmental issues of port expansion. The scheduled
co-ordination of rolling stock utilisation between long and short
distances is allowing for full utilisation of assets and allowing
rail to compete within the 160 km threshold.
Attention to achieving full capacity loadings and maximum utilisation
of traction, rolling stock and train crews appears to be a key
component of the rail revival. EWS' Enterprise network has the
additional task of combining wagon load traffics with freight
flows. Ports that support regular flows are particularly suitable
for this service.
The poor perception of rail services is now eroding, however,
the freight companies still have much to do in convincing customers
that rail is the best linkage to the port. It appears that many
of the globalised players in deepsea shipping remain to be convinced
of the ability of rail to provide quality services and on-line
information of freight movements. However, the service improvements
at Freightliner and EWS will go some way to rectifying rail's
poor perception.
Considerable obstacles will need to be overcome if the rail renaissance
is to continue. Mostly, the problem will be one of the track capacity
to sustain this growth.
The implications of railfreight revival in the UK ports trades
has implications for continental Europe. With Europe's ports and
railways on the verge of deregulation the UK experience has much
to offer. Similarly, the experience of European railways in intermodal
freight has much to offer the UK port and rail companies. The
second part of this research programme will focus on comparison
with such ports as Duisburg, Bremerhaven, Le Havre, Zeebrugge.
Challenging new rail-port projects such as the "Iron Rhine"
linkage between Antwerp and Duisburg point to a rebirth of the
rail system. It is apparent that rail has been something of a
sleeping giant in recent decades; ultimately, the challenge to
realise its potential in the ports' trades rests with the European
rail industry, how it is managed and how it performs.
7.0 REFERENCES
ABP Press Release, Dibden update, Issue 4. Southampton:
ABP, November 1997.
BONAVIA,M.R. (1985) Twilight of British Rail? Newton Abbot:
David and Charles. P.145.
DETR (1998) A New Deal for Transport: Better for Everyone
London: DETR. p.80.
JOHN, S"The Harwich Haven Approach, Channel Deepening
- Good Environment al Value?" A paper given to the International
Navigation Association Conference, Investing in the Environment
- Value for Money? Institute of Civil Engineers, London. 21.10.99.
Lloyd's List 16.10.97. "Hauliers derail UK port
plan," p.1.
Lloyd's List 27.4.98. " Freightliner signs deal with
Port of Felixstowe," p.3.
Lloyd's List 26.8.98, "P&O Nedlloyd railfreight
deal," p.12.
Lloyd's List 19.3.99. "Rail terminal expansion set
to continue," p.8
Lloyd's List. 14.10.99. "EWS extends port network,"
p.3.
Lloyd's List 25.10.99. "Southampton deal with Ford
strengthens its role as inward hub," p.9.
Lloyd's List. 15.5.00. "Scheldte deepening is the
priority." p.11.
McKINNON,A.C. Physical Distribution Systems London: Routledge.
Modern Railways April 1999. " Felixstowe Upgrade,"
pp.244-6.
NASH,C. (1985) "European railway comparisons - what can we
learn?" in BUTTON,K.J. and PITFIELD,D.E. International
Railway Economics: Studies in Management and Efficiency Gower:
Aldershot p.258.
"Track Today," a supplement to Rail 13.8.97.
"Rail Returns to Boston Docks,"
pp.14-17.
WORSFORD,F. and BLAIR,B. (1996) Freight Transport and the Environment:
the British Distribution Industry's Response to the Environmental
Challenge London: British Library. pp.27-8.