
The containership market in 2005
2005 has been the best year ever seen for liner trades in modern times, with volumes outstripping ship capacity -at least until the autumn-, leading to consequent increases in box rates and amazing charter rates. The year has, however, ended on a softer note, attributable to the traditional winter lows and to the beginning of a massive delivery wave of giant ships.
Container shipping is indeed at a crossroads, as overconfident owners and operators have ordered a huge quantity of ships in 2003-2004, which are to pour onto the market during 2006 and 2007. The 2008 orderbook is also well filled. During the three years to come, the fleet will grow on average by 14 % p.a. in teu terms and 13 % p.a. deadweight terms.
Even more worrying is the huge gap in the growth of large ships when compared to that of smaller ones. The fleet of ships above 4,000 teu is to grow by 20 % per annum over the next three years, against only 9 % for ships under 4,000 teu (the gap will however decrease as large ships are usually ordered ahead of smaller ships, for comparable delivery dates). The most astonishing development will come from the VLCS (ships over 7,500 teu), with an inventory jumping from 86 to 232 units within the space of three years.
Consequently, many east-west ships of 3,000-4,000 teu are expected to migrate to north-south trades (a phenomenon which took off during the last weeks of 2005).
The resulting offer/demand imbalance will have to be credited to this supply growth, rather than a weakening in transportation demand, which is expected to remain strong.
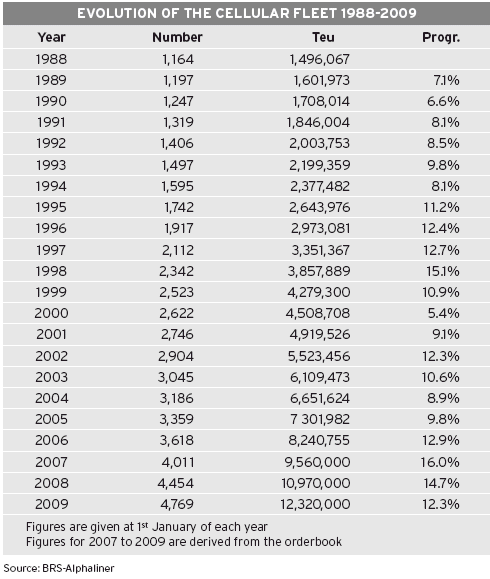
2006 is thus expected to yield lower returns than 2005, as 1.3 million teu of newbuildings will push the existing cellular fleet of 8.2 million teu up by 16 % for this sole year. It will be the largest fleet increase since the 15 % growth logged in 1997.
Fall in fortunes
With such a fleet increase, it does not require a crystal ball to anticipate a fall in fortunes. The big questions are: is there a rate collapse awaiting around the corner? And if so, when will it happen?
Answering such questions is a challenge in this fast changing world, where the future transportation demand is so delicate to forecast. What is for sure is that the fall in rates observed during the last quarter of 2005 has generated a gloom, although it appears to be a psychological one. After all, charter rates still remain above the previous record highs of 2000, and box rates remain at remunerative levels.
Once the next peak season opens, around May-June, there may well be a revival. During this period, which lasts until October, a lot of goods -including toys- are imported in the perspective of the Christmas and New Year period of high consumption. This phenomenon is particularly prevalent on the Asia-US trade, and last year it appeared to have affected Asia-Europe cargoes as well.
It is a paradox, but large ships available for charter will remain in short supply for most of 2006 (because operators have anticipated their needs by securing tonnage well in advance). So, in the case of a bullish peak season, the extra demand could push rates up again temporarily. But they are not expected to reach the mid-2005 levels.
The big worry is for the end of the 2006 peak season, in September-October. The market will then feel the full impact of the newbuildings delivery wave as the demand plunges to its seasonal lows. If a rate collapse is to happen, it will be in this period.
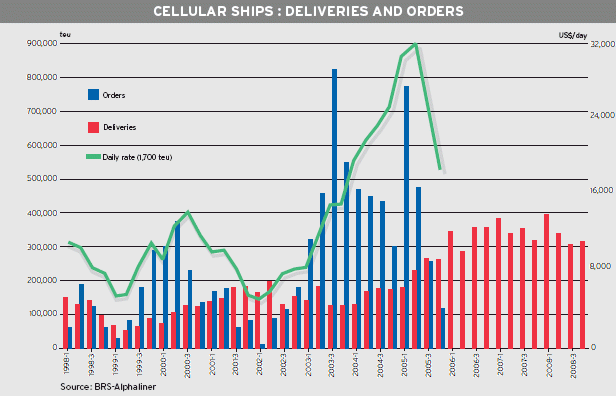
October 2006 could thus be a black month in container shipping memories. A collapse in rates could come at a period when some 120,000 teu of new ships come on stream every month, mainly big ships. And prospects of massive demolitions are poor (see insert).
And then newbuildings will continue to amass in 2007, without much hope for further significant scrapping, given the age profile of the cellular fleet. A big question mark is: will the market grow sufficiently in 2007 to scoop up all the new leviathans?
Expectations of a 7 % growth in trade in 2006 and -hopefully- in 2007 (a perilous assumption) will help at least to dampen the container market downturn and would allow operators and owners to bridge the gap until 2008, when the delivery rate of new ships would slow down; provided of course that orders cease to flow, which is yet another perilous assumption.
Demolition prospects
No cellular ships were scrapped in 2005. Even if non cellular ships are included, only one 609 teu container-friendly ship went to the scrapyard, and that was because of a damaged engine. The only other ships with some teu capacity that were broken up were a half dozen of aged cargo vessels which did not, however, interfere with container trades. The year has seen the recommissioning of a 1,113 teu ship, which had been sold for scrap in 2002 after having been gutted by fire. So, in one sense, the scrapping statistics were negative!
As oldies do continue trading, the potential for scrapping increases as months pass, with expectations that a lot of ships will suddenly join the scrapyard when the next recession bites on.
It is thus interesting to compare the age profile of the fleet with newbuilding
deliveries. Containerships are usually scrapped at an average age of 27 years. With this figure in mind, there is a potential to scrap 333 ships for 350,000 teu before 31 December 2007, and a further 43 ships for 46,000 teu during the year 2008.
Even if all these ships were broken up by then, the capacity removed would correspond to 10 % of the newbuilding deliveries (i.e. 400,000 teu removed against 4 million teu of expected entries during the three year period 1/1/2006 to 1/1/2009).
Decisions to scrap ships are strongly linked to gain expectations. In a context of high box and high charter rates on a background of ship shortage, it is worth spending money on older ships when comparing the cost of charters for replacement ships. Taking a 3,000 teu ship as an example, a replacement ship chartered for three years at $ 30,000 a day would cost a minimum of $ 7 million per year above operational costs, compared with a well amortised veteran.
For a 27 year old ship, it is worth spending $ 7 million on steel renewal, class extension work and routine repairs, in order to stretch its commercial life to 30 years. In this case, it would lead to savings of up to $ 14 million. Given this, no containerships, big or small, are expected to join the scrapyards in bullish periods. It may soon change.
|
The Box as a magnet?
As box rates fall, together with the filling ratio of ships, more non-containerised cargoes could end in boxes (mainly agriproducts, forest products and metallurgical products).
How much of it could end in containers is difficult to assess, as such cargoes can swing from Handysize bulk carriers to boxships and vice versa depending on bulk rates as well as box rates. Also, for these cargoes, rates are not the only parameter, with logistical constraints on the inland side and established commercial practices playing their parts too, not to mention shippers engaged in long term contracts with bulkship owners.
So, container carriers will remain mostly dependent on the world economic health. Trade is expected to remain sustained. The IMF puts the trade growth at +7.4 % for 2006 (including goods and services), against 7.0 % in 2005, which was itself down from 10.3 % in feverish 2004.
The fundamentals remain good, as China, Southeast Asia and India continue to export massively, with the USA and Europe at the receiving end. The drawback is, that this bi-polar pattern results in heavy imbalances with which carriers have to live, as this issue -implying the repositioning of huge quantities of empty boxes- will continue to affect their bottom line for many years to come.
And there are some reasons to remain optimistic. China seems quite sure that its growth will remain sustained at 8 % p.a. for at least a decade, with its coastal regions enjoying the fruits of growth (and hence heavier consumption), while western China starts to emerge with a vast pool of cheap manpower and low overheads.
This optimism is counter-balanced by pessimistic views on the US deficit and energy prices. There are fears that the growth in US consumption could be thwarted by the growing deficit and steeper rises in interest rates, leading to a downturn in house buying and a spending change in consumer behaviour.
As for energy, a surge in oil prices could not only lead to a slower economic growth, it would also have an impact on the carriers. Bunkers now account for half the total daily expenses for large ships running at 24-25 knots, and this already huge share would increase further.
For shippers, high oil prices mean that high BAFs (bunker adjustment factors) are here to stay. But more pain could be around the corner, with a looming clash between Iran and the West over nuclear matters, Iraqi uncertainties, and Venezuelan politics. The development of a crisis situation would send the price of the barrel soaring to $ 100 or more, thus seriously denting the carriers profits, provided they manage to raise a profit at all, given the impact of bunker rates within vessel operating costs.
Everyone would suffer as a result, and operating ships at a slower speed could be considered, although it remains to be seen if the fuel savings from slowdown programs could match the total savings raised from simply putting a few ships into lay up and keeping others sailing at nominal speed.
Actually, slowing down is not as straightforward a solution for containerships as it is for tankers or bulk carriers. Transit times are essential for a lot of containerised goods, and carriers which would test slowdown programs could lose cargo to competitors who maintain higher ship speeds.
Therefore, lay-up is a more likely option in case of oversupply. It has already been experienced during the October 2001-March 2002 depression. The idle capacity gathered up during the fourth quarter 2001 to reach 170,000 teu in January 2002, stagnating around this figure until April-May, when it plummeted down to 60,000 teu in the space of a few weeks, thanks to a market recovery and the approach of a promising transpacific peak season.
Mega mergers
2005 has also been a year rich in M&A activity, dominated by three large transactions with A.P. M'ller-Maersk buying P&O Nedlloyd, TUI (Hapag-Lloyd) buying CP Ships and CMA CGM swallowing Delmas.
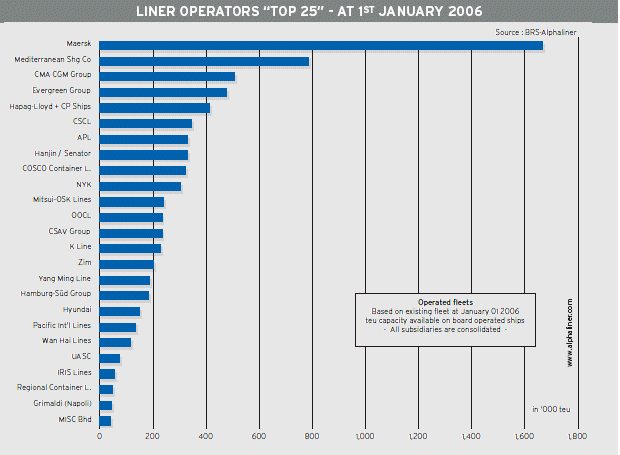
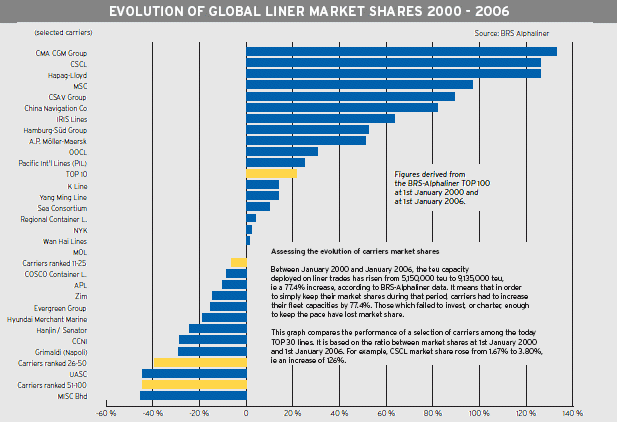
A.P. M'ller-Maersk has reinforced its top position, with a fleet now reaching 1.65 million teu and a global market share of 18 %, almost twice the size of its nearest rival, MSC (785,000 teu. CMA CGM climbed to the third slot with a fleet of 508,000 teu. Hapag-Lloyd took the fifth position wit a fleet of 412,000 teu. The fourth position is held by Evergreen, with 478,000 teu (see graphs: TOP 25 and Evolution of market shares).
These deals occurred at the top of the market, and the targets have been far from cheap. It reflects the confidence of carriers for the future, and raises new challenges for those left behind.
The five largest carriers currently boost a 42 % market share, against 36 % at the beginning of 2005. This consolidation movement is to continue, with medium-sized carriers worrying about the role they could play in the future.
Maintaining a wide pallet of sailings to as many destinations as possible, while investing in very large ships in order to benefit from economies of scale are contradictory goals that only the largest mega carriers can achieve. This argues in favour of further M&A activity or in a widening of alliances.
It is in this context that the remaining partners of Grand Alliance (which loses P&O Nedlloyd) and of the slimmer New World Alliance have concluded an agreement allowing them to swap boxes between services. The drawback is that such an agreement is not flexible and the partners cannot reorganise rotations or adapt capacities at will.
The CKYH partners (COSCO, K Line, Yangming, Hanjin) have also confirmed the strengthening of their ties in order to maintain the quality of their services.
As for future M&A possibilities, they are rather limited, given the fact that many of the large carriers in the Top 30 lines are privately owned, and often family-controlled. Unless there is a will to sell, nothing is expected from their side (and they would even be more buyers than sellers).
Having said that, the next round of consolidation could well come from Japan, where a regrouping of the liner divisions of NYK, MOL and K Line would create the world second largest carrier, rivalling in size with MSC.
There have been numerous smaller deals and other corporate moves, which are summed up in the accompanying table.
Operators: transactions and significant moves in 2005
Straight sales & mergers
A.P. M'ller-Maersk (APM - parent of Maersk Sealand and Safmarine) (Denmark) purchased Royal P&O Nedlloyd (Netherlands) and its subsidiary P&O Nedlloyd Containers Ltd (UK).
TUI A.G. (parent of Hapag-Lloyd A.G.) (Germany) purchased CP Ships Ltd (Canada & UK).
CMA CGM (France) purchased Delmas (France) and its subsidiaries (OTAL and share in Setramar) from Bollor' Technologies.
CMA CGM (France) took over the whole of SudCargos (France).
Jindo Corp. (Korea - part of the Seven Mountain Group) purchased Dongnama Shipping Co Ltd) (Korea).
Mitsui-OSK Lines (MOL) bought the SAECS operations of P&O Nedlloyd from A.P. Moller-Maersk.
Wan Hai (Taiwan) took control of the whole of Interasia Line (Japan) through the purchase of the 43.75 % MOL stake.
Samskip (Iceland) purchased Geest North Sea Line (GNSL) (Netherlands).
Samskip (Iceland) purchased Seawheel Ltd (UK) from its management and merged it with Geest North Sea Line (GNSL).
Eimskip (Iceland) went under control of the Avion Group (an Icelandic holding specialising in services to the aviation industry).
Eimskip bought a 50 % stake in HAL Shipping Inc. (Halship), a company set up at Halifax in December 2004 to provide a feeder service linking Halifax to Portland and Boston.
DFDS A/S (Denmark) took control of the whole of Lys Line (Norway) through the purchase of the remaining 34 % of the shares from Simonsen Holding.
Grimaldi (Napoli) bought 11.61 % of shares and votes of Finnlines PLC (Finland).
D'hle (IOM) Ltd, part of the Peter D'hle Group, became the sole owner of Swan Container Line.
Magsaysay Lines Inc. (Philippines ' manager of NMC Container Lines) took over the management of Lorenzo Shipping Corp. (Philippines).
Norfolkline (Netherlands - a subsidiary of A.P. M'ller-Maersk) purchased Norse Merchant Ferries (UK).
Spliethoff (Netherlands) acquired the remaining 49 % of the shares in Transfennica Ltd (Finland) from UPM-Kymmene, M-real and Myllykoski Paper.
Rettig Group Ltd / Bore Line took control of Bror Husell Chartering Ltd and Rederi AB Engship (all Finland).
New operators of liner services
Yaiza Shipping, a division of Grupo Logistico JSV (Spain), launched its own service on Spain-Canary Islands.
Chrysobel Asia Line, a Singapore-based freight forwarder, launched its own service linking Jakarta, Singapore and Mumbai.
Saturn Container Lines (Pte) Ltd, a Singapore-based subsidiary of the India-controlled WW Group launched a service linking Singapore and Chennai in partnership with HubLine Bhd.
Soci't' Malgache de Transports Maritimes (SMTM - The Madagascar state-owned carrier) made a come back on the liner shipping scene with services linking Madagascar, Mauritius, Reunion and South Africa.
Gunes Container Line, Turkey, launched a service between Turkey and Libya.
Cessations of activity in liner shipping
<
Mer Austral ceased its Indian Ocean Islands services.
Sarlis Container Services filed for bankruptcy.
Significant other moves
COSCO Holdings (parent of COSCON) (China) was listed on Hong Kong Stock Exchange.
STX Pan Ocean Ltd (Korea) was listed on the Singapore Stock Exchange.
Horizon Lines LLC (USA) was listed on the New York Stock Exchange.
TBS Shipping Ltd was listed on the New York Stock Exchange.
Seaspan (Canada) listed the newly formed Seaspan Corporation, created to own the containerships of Seaspan Container Lines Limited (SCLL), on the NY Stock Exchange.
Norwegian shipowner John Fredriksen bought Heung-A shares.
China Shipping Container Lines (CSCL) (China) increased its share in the Shanghai Puhai Shipping Co, Ltd (SPS) from 50 % to 90 %.
CP Ships Limited re-branded its container shipping services under the CP Ships name and has retired its seven operating brands.
The Malaysia International Shipping Co Berhad was renamed MISC Berhad.
Lloyd Triestino di Navigazione SpA (Evergreen Group) becomes Italia Marittima SpA (ITS).
|
 The charter market
The charter market
Lessors of container tonnage have been at feast since the 2002 upturn. Charter rates have increased five fold between early 2002 and mid-2005 as ships went in short supply, but this bullish trend has now faded away.
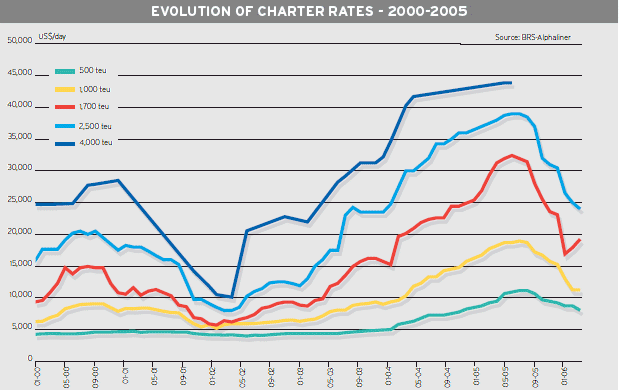
Rates have slipped since the peak of April-May 2005, and even literally plunged during November, before stabilising in mid-December. But they are still far from the abyss, as they are still above historical records.
Interestingly, this plunge concerned ships chartered for periods of around 6 months while rates remained firm for longer periods of 12-24 months. It gave the strange feeling that, contrary to the good order, short term fixtures were commanding discounted rates against long term ones! In fact, it reflects the confidence of owners that the medium to long term demand will remain firm, whereas lower rates were accepted only to cover the winter gap. As a result, the market was very confused over the last weeks of 2005, with charter rates showing large discrepancies.
Actually, the plunge was exacerbated by the traditional low which follows the peak transpacific season. Adding to the lower resulting demand is the fact that operators anticipated their needs by chartering ships well in advance, with most positions covered for the winter.
On the contrary, the Europe-North America trade is enjoying -at last- a revival, triggering the shifting of larger ships there and even the launch of a new loop in November 2005 by MSC, while CMA CGM and CSCL plan to launch their own loop in March 2006.
The softening in volume growth has also been translated in the carriers' figures. The growth in containers carried has slowed, while the pressure exerted on freight rates has had a negative impact on profits. Although still there, the growth in container volumes is not expected to be as sustained in 2006 as it has been in 2004-2005.
Once past the Christmas-Chinese New Year festivities (say in March), if the world economy remains bullish, and 'if China and India exportations continue growing' even at a slower pace, the market could well remain tight for a few months, despite the large influx of newbuildings.
Operators may need to charter additional tonnage ahead of the 2006 peak season. It is also at this time that things will start to settle after the big deals of 2005 (Maersk-PONL, CMA CGM-Delmas, Hapag-Lloyd-CP Ships), with a possible increase of chartering activity linked to service restructurings and enhancements.
Indeed, the withdrawal of P&O Nedlloyd from a number of agreements is leading to loops splitting, resulting in more ships being needed.
As far as the supply is concerned, it is interesting to note that there is not much unemployed tonnage left for 2006, compared to the overall fleet, as shown by the table 'Availability of ships for charter (comparison 12 months).
More interesting still is to compare the availability today with the same data 12 months and 24 months ago, which has been summed up in the accompanying table. It shows that available ships of more than 3,000 teu are today as rare as they were two years ago, but remain above the low availability level reached 12 months ago. The big difference is that today it is on the downward slope.
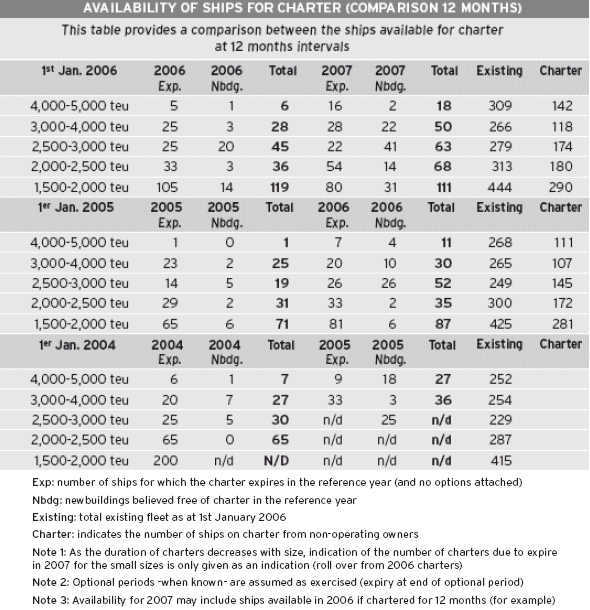
A more worrying figure concerns the 1,500-2,000 teu range where 25.7 % of ships this size come out of charter over the next 12 months, against 16.7 % one year ago.
Conversely, an encouraging sign of future market tightness is the low ratio of tonnage on order still left unfixed. We found that some 80 % of the total capacity on order (4.5 millions teu) is assigned to operators (as owners or charterers). When broken down by year of delivery, we observe that 86 % of the capacity planned for delivery in 2006 is assigned, leaving only 14 % of the fleet still without employment, almost exclusively ships under 4,000 teu.
This low rate of availability must however be weighted against the fact that large operators have anticipated their needs for 2006 well, and they may not be under much pressure to charter extra ships. This pool of 14 % of available newbuildings for 2006 totals only 180,000 teu, which could be quickly mopped up if there is a surge in demand during the next peak season.
So, there are some positive signs among the fears that the market will slide next year, as there is more capacity coming on stream than the trade can absorb. And although the cellular fleet is to grow by 16 % in 2006 in teu terms, the figure stands just under 15 % in dwt terms, and the deadweight is probably a better yardstick to assess future imbalances.
The fleet
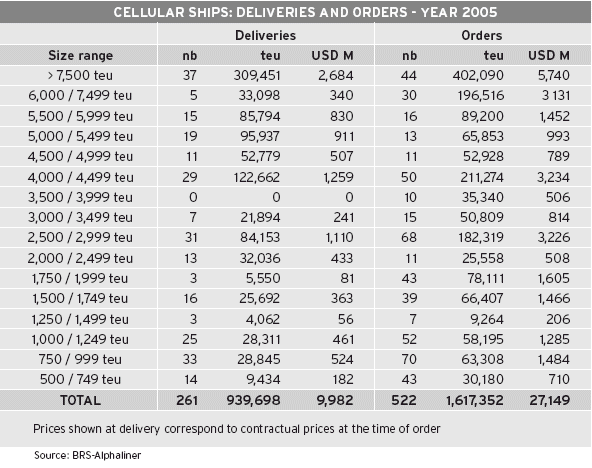
The cellular fleet will grow from 8.2 million teu in January 2006 to 12.3 million teu in January 2009, taking into account the existing orderbook without including demolitions.
Assuming reasonable demolition volumes (see related insert) and a few more orders for 2008 deliveries, the cellular fleet in January 2009 is likely to stand at around 12 million teu, i.e. twice its level in mid-2003.
Orders flowed into hungry shipyards from early 2003 to summer 2005, despite hefty price increases. This order wave came to an end in September 2005, when the rosy barometer took a plunge, with receding box rates on the east-west lanes and carriers issuing warnings of lower profits.
All of a sudden, orders plummeted. Only 64 ships, totalling 120,000 teu, were ordered during the 4th quarter 2005, compared with 458 ships, totalling 1.5 million teu, during the first 9 months of the year, and a total of 3.8 million teu during the years 2003 and 2004. Despite this fall in the number of orders, the orderbook still made up 54 % of the existing fleet on the 1st January 2006, down from 60 % at its peak, in July 2005. Orders extend until end 2009 for large ships.
This gap in orders will only have an impact on 2008-09 deliveries. In the meantime, the fleet is to grow at a fast pace. After the 16 % increase expected in 2006, it is expected to increase by 14.7 % during 2007 and 12.3 % during 2008. As there is still spare building capacity available for medium and small size ships for 2008 delivery, the latter figure could still be higher.
The world liner fleet
The world liner fleet will reach 10 million teu in September 2006
The world liner fleet (see note) passed the 9 million teu mark in November 2005, for a total tonnage of 130 million dwt, according to BRS-Alphaliner data. The figure includes all types of ships effectively deployed on liner trades, in the common acceptance of the term (5,360 ships are involved). The cellular ships contribute to 90 % of this figure. The remaining 10 % is shared by non-celled container ships, multipurpose tonnage and ro-ro ships. We expect that the 10 million teu mark will be reached in September 2006.
Previous and forecasted 'round' million teu capacities stand as follows:
> 6 million teu (94 million dwt = > 15.67 tons per teu) in July 2001
> 7 million teu (106 million dwt = > 15.14 tons per teu) in April 2003
> 8 million teu (118 million dwt = > 14.75 tons per teu) in October 2004
> 9 million teu (130 million dwt = > 14.44 tons per teu) in November 2005
> 10 million teu (140 million dwt = > 14 tons per teu) in September 2006 (forecast)
Time to reach the 'next' million teu
> 6 million teu to 7 million teu in 21 months
> 7 million teu to 8 million teu in 18 months
> 8 million teu to 9 million teu in 13 months
> 9 million teu to 10 million teu in 10 months (expected)
Note: This count includes all the ships deployed on liner services in the common acceptance of the term. Given this common acceptance, we exclude a number of specific, more or less regular services such as the parcel trades (steel and other neo-bulk products), pure forest product trades or pure vehicle carrying services. Given this, the numerous multipurpose cargo vessels and conbulkers deployed on non-liner trades or on tramp trades are NOT included in the above figures (even if container fitted), although they are listed in the Alphaliner database for the sake of exhaustiveness.
|
 Ships of over 2,000 teu
Ships of over 2,000 teu
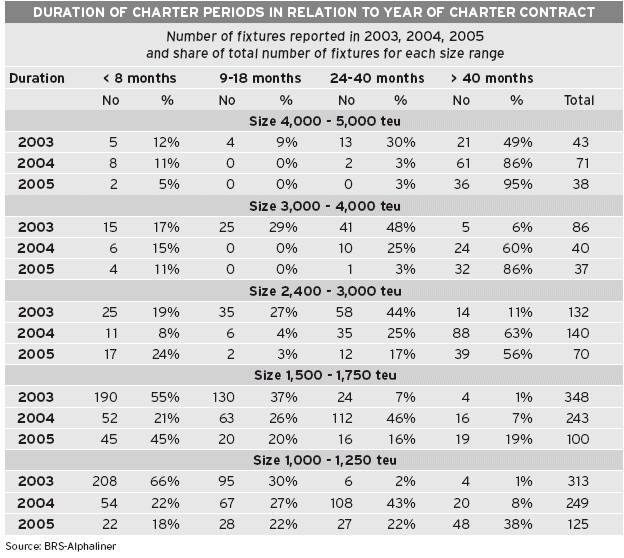
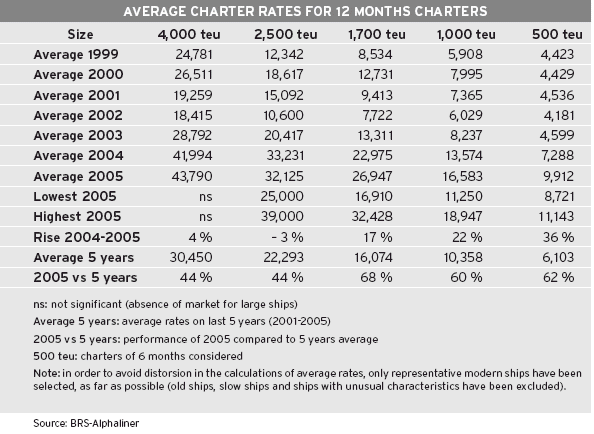
The charter market for ships of 4,000-5 000 teu has virtually disappeared in 2005, in the absence of available ships - at least for 12-24 months charters. The charter deals concluded concerned mainly newbuildings fixed for long term periods of 5 to 15 years, and such contracts have more to do with financial engineering than conventional market play.
There are only 6 ships of 4,000-5,000 teu which will see their charters expire in 2006 (and free of optional periods), while only one newbuilding in this size range is left available.
Rates for 2,500 teu ships have peaked at $39,000 in March-April, before falling to more reasonable levels of $25,000 in December.
It is worth noting that the 2,500-3,000 teu size range is more exposed than neighbouring ranges, with 16 % of the capacity in this range coming on the market in 2006 (45 ships - charter expiry and newbuildings without charters). By comparison, it stands at only 11.5 % for the 2,000-2,500 teu range (36 ships) and 10 % for the 3,000-4,000 teu range (24 ships).
Medium-sized units of 1,500-3,000 teu, which were employed as stopgap ships during the first three quarters of 2005 on services normally employing larger tonnage have since left to accommodate adequate tonnage.
Ships of 1,500-2,000 teu
Rates for 1,700 teu ships reached an astounding $ 32,000 in April for 12 months periods. Such rates were unthinkable two years ago. They have since fallen to half this level, but in January 2006 they still remained above the record $ 15,000 of the year 2000.
The 1,500-2,000 teu range is a populous one, counting almost 450 ships, of which 290 are charter market ships. There are another 130 units on order for this size range only. Many of these ships are squeezed out from the north-south trades by larger units and many of them happily find other employments on intra Asia services (including South Asia). But should the market collapse, our feeling is that this range could suffer more than others, simply because there are not enough regional niches to accommodate them, while they are still too big to be flowing in large quantities onto feeder trades.
Ships of 500-1,500 teu
Smaller ships, under 1,500 teu, are doing well, and there is even a forthcoming shortage of ships of 900-1,200 teu (especially geared ones). The demand is high for this size range. Several regional services in Asia or along the west coast of the Americas have been launched, or are being launched, with such ships. Meanwhile, the demand for feeders of this size remains strong, especially in the Mediterranean, West Asia and Southeast Asia.
In 2006, there could be even more pressure developing as ships of 900-1,200 teu could replace ships of 700-800 teu on services linking Northwest Europe to the Baltic and UK-Ireland.
Besides, there is a fair amount of multipurpose (non-cellular) ships being used as pure containerships, which at other times are mostly used on non-container trades. This is especially true for the 1,300-1,400 teu range.
For example, ten out of the eleven ships of the 'C-box' class (1,301 teu - built 1998-2000), are currently employed on container services (five of which by MSC). Half of the 15-strong CEC-controlled 'Confidence' type (650 teu - built 1997-2002) are more or less permanently employed on container services, although unlike the 'C-box', a few of them come and go, acting as extra ships often chartered for short periods or round trips.
Even the rather old and slow 'OBC-25' ships (1,300-1,400 teu - built 1978-82) have made a comeback, with five of the 12 'OBC-25' in service currently used on container trades (a 13 th one was converted into an Orange Juice carrier). These ships had disappeared from the container scene in 2001-2002 and came back progressively in 2004-2005. This December, a 1,167 teu ship, de-celled six years ago, is making a come back on the container scene.
With so many non-cellular ships drawn from tramp or parcel trades to be employed as full containerships, there is not much left to swing tonnage, and this helps to keep the market under pressure for 1,000-1,500 teu ships. It is not by chance that Delphis chartered three 1,118 teu newbuildings for 5 years at $ 12,500 in December 2005.
Having said that, rates for 1,000 teu ships flirted with the $ 19,000 level in April-May, and fell to $11,000 at the end of the year.
As for smaller modern ships of 500-700 teu, they continue to attract good rates, especially the geared ones. After years of flat rates, this size range at last saw a revival during the first months of 2004, reaching a climax in May-June 2005, with $ 11,000 for 12 months. Rates have since receded to around $ 8,000, but are still way above their early 2000s flats of $ 4,000-5,000.
The containership second-hand market
'The calm after the storm'
The containership second-hand market began to contract as of March and April 2005, with a more pronounced reduction from the beginning of September. Prices stabilised at the end of the year at levels close to those achieved at the beginning of 2004.
Already at the end of 2004 there were signs of weakening, particularly for ships of 1,000 to 1,500 teu. In addition, it is in this size category, that the biggest drop in prices was witnessed.
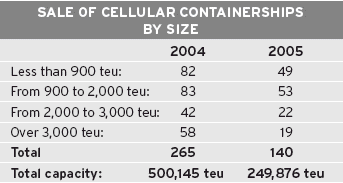
Sale statistics for 2005 (for all sizes) show a net decline in activity, with the total transactions reported being 206 (cellular, non-cellular and ro-ro's) against 391 in 2004, including 145 cellular ships (with 33 ships under construction).
The volume of ships purchased or long term charters signed up in 2004 was sufficient to cover most of the tonnage needs in 2005. No less than 60 ships, out of the 145 cellular containerships were sold to German investors, either with charters back, or with long t/c attached to the sale. These German investment funds, the KG's, made a show of strength this year by taking a predominant role in the purchase of containerships. They come in second place, after the Swiss operator MSC, which has been in the lead these past two years, with over 50 ships being purchased.
With declining freight rates not inciting traditional buyers to invest, it was left to the fiscal operators being the only players to help uphold the second-hand market as well as they could. Uncertainties concerning the trade flow, bunker prices or even the exchange rates, have contributed to owners-operators' lack of optimism.
Paradoxically, owners' asking prices remained very high compared to freight rates, which continued to drop as from the spring. This caused an important gap and a negative return on investment ratio in the short and medium term, making it even harder to carry out transactions. The situation was such, that at the end of the year neither traditional buyers, nor the German and Norwegian investment funds were in a position to conclude a deal. Only the biggest ships, of 2,500 teu or more, were able to emerge unscathed, given the few ships being offered and their popularity with the investors.
The pursuit of economies of scale on the regular liner services justifies in the same way the relative price resistance for ships of 2,500-3,000 teu and over. Large ships seem to reassure investors, who consider them to be less exposed to the vagaries of the market.
Amongst the main en-bloc sales we can list:
4 ships of 9,700 teu, built by Daewoo, for delivery in 2008, sold by CMA CGM to Conti Rederei against a 15 year time charter at $48,000 per day.
The German group Schoeller sold 6 ships of 3,388 teu, which are being built in Germany, for delivery in December 2006, April, May, June 2007, February and April 2008 respectively to two different German buyers: NSC Schiffart (4 ships for $60 million each) and Thien & Heyenga (2 ships).
The same owner, Schoeller, sold 6 units of 2,742 teu, which are being built at Aker for delivery in March, April, June, August, September, and October 2006 respectively to 3 different buyers: Far Eastern Shipping (Russian), Salamon (German) and Zim (Israeli).
Evergreen (Taiwan) sold 3 units of 4,229 teu, built in 1993 by Onomichi, to Dainichi Invest for a price of $ 45 million each, backed by a 10 year charter.
Containerships less than 900 teu
In this size category, the market has returned to its traditional habits for second-hand transactions. Last year, due to a scarcity in the larger and faster ships, owners had to fall back on the smaller and slower units, of which there are plenty in this category of the fleet. Under much less pressure this year, buyers were able to be far more selective. Only 11 ships with a speed of under 15 knots found buyers out of the 49 transactions registered in this sector. Even the non-cellular ships, of which the vast majority of existing units are relatively slow, followed the same pattern, with 24 ships having a speed under 15 knots being sold out of a total of 50 deals.
On the other hand, the nationalities of buyers remain extremely varied. This year, again, the Far East is well represented in this category, as well as Greece, Italy and, of course, Germany.
Values of these ships have suffered the most during the course of 2005, with a drop of around 30 to 35 % between January 1st and December 31st, depending on age and quality.
Containerships from 900 to 2,000 teu
There was far less activity compared to 2004, but with an average of one ship being sold per week, this sector remained the most active. The three buyers who enlivened this market in 2004, Zim, MSC, and CMA CGM were relatively quiet this year, with respectively 1, 2, and 3 ships being purchased in this category.
The market's peak was achieved in March 2005, with the sale of two Flensburg-type resales 'Viking Hawk' and 'Viking Eagle', 1,740 teu, for delivery in 2005 by the Chinese shipyard Guangzhou Wenchong, to owner Seatankers (Fredriksen) for $49.5 million each!
Another interesting sale took place in the summer, with three 1,155 teu, gearless, resales from the operator Kasif Kalkavan and of the improved Mark XI-type, built at Orskov, to MPC Capital (Germany) for a price close to $ 33 million per unit. These ships were nevertheless inspected by a large number of potential buyers during 8 to 9 months, without any takers able to find employment justifying such a price being found.
In January 2005, Foresight sold two units of the BV1700 type, 'Pride of Mumbai' (geared), and 'Pride of Delhi' (gearless), built respectively in 1993 and 1994 in Germany, for a price of $ 31 million each to Marconsult (Germany). This price was justified by a 36 month charter, fixed at $ 23,700 per day with Hapag-Lloyd, being attached. It is interesting to note that a sister ship of these two, the 'Lina' was sold at the end of the year by Zim to Marconsult at a price of $ 24.5 million, against a charter for less than 30 months with Evergreen at a level of 'only' $ 19,750 per day.
Containerships from 2,000 to 3,000 teu
This market also faced a reduced number of transactions in 2005 compared to 2004, with 22 against 42 respectively, and no less than 14 sales of ships on order or under construction.
The few ships on the market for sale explain the weak activity in this sector. It was not, however, the buyers that were in short supply. The confidence of operators was particularly felt in this size category, which, to a large extent, explains the relatively firm prices being proposed. In addition, the majority of ships had been financed thanks to the German KG system or by way of British tax-lease schemes, which prohibited their resale for several years.
The owner Schoeller, already mentioned, stood out with the sale of 6 of its ships of the CS2700 type, all for delivery in 2006, at a unit price of $ 57 million.
Half of the remaining sales were made up of 4 old ships belonging to MC Shipping, the 'Maersk Belawan', 'Maersk Brisbane','Maersk Bahrain' and 'Maersk Barcelona', 2,824 teu, built between 1975 and 1976, sold to KGAL (Germany) for $ 7.5 million each, including a 24 month time charter to Maersk Line, and some other less significant transactions.
Containerships of over 3,000 teu
Less than 20 ships over 3,000 teu changed hands in 2005, compared to nearly 60 the previous year. Except 5 ships, of which 2 units (4,334 teu and built in 2004) sold to Danaos, and 3 ships (of 4,229 teu and built in 1993) sold to Dainichi, the German KG's swallowed up all the other transactions.
The entirety of these sales was confined to just 7 en-bloc deals! We can make the same comment as for the previous category, namely that the scarcity of transactions was due to the virtual absence of sellers'
Conclusion
A year which proved all in all to be fairly morose in terms of number of sales and a slackening trend which progressively developed throughout the whole year. The decline in market prices became noticeable as from the autumn of 2005. It is always difficult to give a definite view as to the evolution of the container market in the medium and long term, as the mini crisis at the end of 2003 is still fresh in one's mind and is witness to the speed at which the market can turn around.
However, the forecast of slight weakening in Asian economic growth, the long list of ships to be delivered in 2006 (which has not really put a dampener on the continuing chase for orders) and the umpteenth hike in the price of bunkers gives cause for concern'
Without actually falling into a deep pessimism, the market can begin to worry about the enthusiasm which potential buyers will demonstrate in the face of ships which will be coming off charter in 2006. The only containerships which will be still intensively pursued, will be those being committed for the next two to three years, and at a reasonable charter rate'
Shipping and Shipbuilding Markets in 2005
I N D E X