
Special Interest Group on Maritime Transport and Ports
a member of the WCTR Society
INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP
Genoa - June 8-10, 2000
Topic area: A2 Maritime Transport and Ports
The measurement of port efficiency using Data Envelopment Analysis
V.F.Valentine and R.Gray (Corresponding author and speaker)
Institute of Marine Studies, University of Plymouth,
Drake Circus,
Plymouth, PL4 8AA United Kingdom
Email: vvalentine@plymouth.ac.uk and rgray@plymouth.ac.uk
Telephone: +44 (0) 1752 232442
Fax: +44 (0) 1752 232406
Introduction
Understanding performance is a concept fundamental to any business,
whether it is the measuring of achievements against set goals
and objectives or, against the competition. Ports are no exception
and it is only by comparison that performance can be evaluated.
Ports are, however, a complex business with many different sources
of inputs and outputs which makes direct comparison among apparently
homogeneous ports seem difficult. The subject is further complicated
by the various types of port ownership and organisational structures
that exist throughout the world. During the last two decades the
ownership of one of the most important trade entry points into
any country, the seaport, has changed from being solely in the
hands of national or local governments into, either wholly or
partially, private hands. It is this change which is called privatisation
that has attracted much interest from both academics and those
working within the industry. This paper will look at how these
seaports are owned and how their structure is organised to determine
whether these factors have any relation to its performance. The
results of this paper will help serve as a guide for governments,
port administrators and port owners on the different ways they
can structure their ports which may lead to greater efficiency.
Background
Privatisation is a concept rather than an actual definable process.
The word came into being during the late 1960s and was later attributed
to the UK government's reforms to ownership and operation of numerous
companies managed by the state. Chapman (1990) has accredited
Drucker (1969) as the author of the word 'privatization', in its
American spelling. The actual process of implementing privatisation
is not however a new concept. Neither can it be said to have originated
in the UK. It was rather a christening of an established process,
a renaissance of an earlier idea on the ownership and management
of a company. What can be said is that the extent to which the
UK government pursued this course of action certainly attracted
attention from other countries which no doubt contributed to the
sudden global desire to privatise during the 1980s. A comprehensive
review of privatisation methods is given in Abdel-Fattah et al
(1999).
Privatisation in developing countries is often the first phase
in a process of industrial liberalisation and a move towards industrial
progression. Viewed as this first step towards creating free trade
it has therefore not surprisingly been a high priority for developing
countries. It begins with the transferring of absolute control
of industry away from the government to private partners with
particular expertise. The reasons for this change are numerous
but can be summarised as follows: improvements in efficiency through
private sector management skills; enhancement of service quality
through improved commercial responsiveness; reduction in the
fiscal burden of loss making state enterprises or the need for
the future subsidy; a reduction in the fiscal demands on central
and local government through access to private sector capital;
and additional revenue streams (Port Development International,
March 1999).
More than 40 countries have committed to some form of port privatisation
and more are likely to do so (Cass 1996). Some countries have
rapidly progressed towards this goal of privatisation whilst others
have been hindered by political, fiscal, labour or a general unwillingness
to accept change.
One of the 'problems' with privatisation is the perception that
it reduces jobs. Indeed, this is often the immediate reality in
many industries that are privatised, as companies no longer have
to accept restrictive employment practices. The longer term view
that it creates efficiency, profitability and growth are not issues
that are considered by those faced with the prospect of redundancy.
Ownership structure
Cass (1997) in his study of world port privatisation concluded
that there were only really three types of port ownership, public,
private or joint public/private. He points out that the most
common type of port privatisation are (1) the sale of operating
concessions, (2) joint public/private venture, (3) private orientated
but port authority controlled operating subsidiaries, (4) the
'corporatisation' of government port agencies or (5) the dissolution
of government owned cargo handling monopolies. The 'lock, stock
and barrel' approach of Great Britain and New Zealand are the
exceptions. The degree of public involvement is naturally dependent
upon national ideology. Cass (1997) and Heikkila (1990) both state
the examples of the United States where the municipal authority
plays a major part in the operation of the port. Here ports compete
against other ports along the coast for business. However, at
the other end of the scale is Taiwan where the administration
of the ports is centralised.
Boardman and Vinning (1989) found that different types of ownership
structure, the state owned enterprises and mixed economies performed
substantially worse than similar private companies. They concluded
that there were performance differences between public and private
companies in competitive environments and, that where there was
a partial privatisation the performance was sometimes the worse.
They cited that conflicting ideologies between the two different
owners cause what they term 'cognitive dissonance'. However, Bos
(1991) looked at what Tandon (1997) called the survey of all the
surveys on the efficiency of public and private firms and came
to the opinion that Boardman and Vinning (1989) were at direct
opposing views with a previous study by Borcherding et al (1982).
Tandon's (1997) explanation of these apparent conflicting views
relies not upon the ownership structure but upon the market conditions
in which they operate. Private firms are likely to be in a more
competitive environment and thus more in tune with the need to
be efficient than public enterprises that perhaps operate in a
restrictive environment. He argues that in studies involving public
and private firms in the same business, such as airlines, some
private airlines are more profitable but on balance it is approximately
equal. This research aims to see whether this is the case for
ports.
Caves et al (1982) in looking at United States private railways
and Canadian public railways concluded the Canadian public firm
was more efficient. Tandon (1997) states that the process of identifying
which approach is more efficient depends upon disentangling ownership
from the effects of deregulation and competition. Everett and
Robinson (1998) in their research into Australian port reform
suggest that the corporization of some ports has not resulted
in the liberalisation and the near private performance that was
anticipated. Frech (1980) in looking at the role of property rights
within the firm suggests that if the ownership structure is attenuated
this leads to lower firm wealth and more nonpecuniary benefits.
Thus, privatisation, by shortening the ownership structure should
have an opposing effect. Likewise the organisation structure should
also play a significant role by suggesting that simple structures
be inherently more efficient than the more complex machine bureaucracy
and divisional structures. De Alessi (1980) states that not only
are government firms less efficient but are also less successful
in satisfying the consumer's needs. Thus, efficiency of ports
owned in a variety of ways needs to be measured and applied to
a conceptual model in order to test these notions.
Organisational structure
Roe (1999) in looking at the newly privatised subsidiaries of
the state owned Polish Ocean Lines observed that there was a desire
to avoid control of the parent company and to change the organisational
structure soon after privatisation. Mintzberg (1979) looked at
organisational structures and reached the conclusion that there
are essentially five different types of organisational structure.
Simple, Machine bureaucracy, Professional bureaucracy, Divisional
and Adhocracy. As far as ports are concerned only three of these
seem to fit into the modern day port structure. First let us consider
the options that do not fit. The adhocracy does not fit into the
structure of any port because of its lack of rigidity. Suitable
for software companies and film producers, its role within a port
would likely lead to chaos. Ports require careful planning and
development based upon what may be needed 10 or 20 years into
the future. Without the rigidity of a formal structure each element
in the chain would not know the whole picture, only the person
at the top may see everything. Likewise the professional bureaucracy
is not suitable in a port because of the routine and repetitive
tasks that are commonplace within a port's day to day service.
The professional bureaucracy is typical of industries that require
highly professional people to perform routine tasks in an unsupervised
manner such as solicitors and accountants. Whilst professional
people are required in certain areas and qualified personnel needed
to operate expensive and dangerous machinery, a professional bureaucracy
would not be appropriate. This leaves us with the three remaining
structures that are prevalent in the port industry, viz. simple
structure, machine bureaucracy and divisional.
The simple structure is the most flexible, allowing separate divisions/departments
reporting straight to the top decision-maker. As the name suggests
it is usually the first stage through which a company progresses
through in its evolution. In the conceptual model this has been
chosen as the best description of a private port owner. This structure
by its simplicity is therefore likely to be the most efficient.
The machine bureaucracy is characterised by its many departments
reporting up a chain of command to a line manager before reporting
to the top decision-maker. Because the decision making has to
follow a long process before it reaches the top decisions tend
to be slower. These structures tend to be found in government
owned enterprises and hence the inclusion of port bodies and corporatisation
in this category.
The divisional structure occurs when companies operate within
large areas. Each department has to report to a regional office
that in turn reports to a select group of managers before information
is passed to the top decision-maker. This structure can be best
seen in the municipal ports of the UK and the port societies of
Chile. These divisional structures tend to operate where there
are joint public/private enterprises or where conglomerates own
the port.
Conceptual model
The use of models in looking at the organisational and ownership
structures within the port industry is a necessity since the theory
of organisation and ownership structure is abstract to the operation
of the port. In order to see how the structure of the port can
affect the efficiency of its operation the designing of models
is imperative. The benefit of a conceptual model is that it enables
real ports to be categorised and placed together according to
their similarities. Ports that do not fit into the defined categories
enable the research to be developed further by adapting the model
and devising theories to take account of differences and previously
unforeseen eventualities.
Using the three different types of organisation structure and
the four different methods of ownership, mentioned earlier, it
has been possible to create the following table (1). There are
of course many different combinations of port ownership depending
on the percentage of ownership by any of the categories, but essentially
they can be broken down into ten categories.
Table 1 - Categories of port structures
| Ownership Structures | Organisational Structures
|
| Public | Public simple structure
| Public divisional | Public bureaucracy
|
| Private | Private simple structure
| Private divisional | Private bureaucracy
|
| Joint Public/Private | Private/Public
simple structure
| Public/Private divisional | Private/Public
bureaucracy
|
| Mixed | Mixed Public/Private/Municipal
|
By using the above ten categories of ports the conceptual model
seen in figure 1 has been designed. One of the findings reached
by this work is that the organisational structure of ports varies
considerably throughout the world making it difficult to place
certain ports into specific categories. Into this model were placed
a random selection of ports to illustrate its applicability to
the real world.
Ports may be divided into three distinct types of organisations,
the first is the private simple structure, that of the wholly
owned private company. This relates to the singly owned private
port such as Boston, UK. The next is the public/private divisional
structure which includes ports such as Portsmouth. The third type
of port ownership listed is the machine bureaucracy which in terms
of ports relates to the corporatisation which is present in South
Africa and Singapore. The corporatisation is in effect a public
concern which is due to be privatised within the near future,
it is commonly the stage before privatisation.
Figure 1 - Ownership and organisational structure applied
to ports
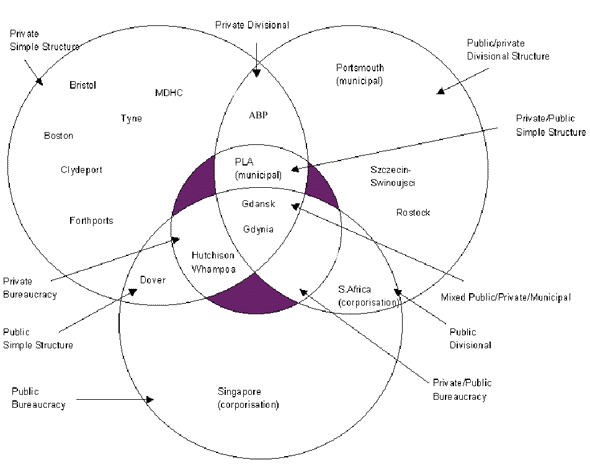
It is possible that the labelling itself may lead rise to opposition
from within the industry because of the language used. To label
a port such as Singapore as a machine bureaucracy will no doubt
cause contention within its management, since the term machine
bureaucracy tends to denote a rather old fashioned and inefficient
structure. However, the port of Singapore rates as the largest
in the world in terms of container throughput with figures that
consistently year after year compete with its strong and next
biggest competitor Hong Kong.
However, in the context of organisational theory, the term is
not a derogatory label but refers to a system marked by pronounced
procedures and regulations with the regularity and functionality
of a clockwork machine.
The relationship between both the structure of the organisation
and it ownership has a direct influence on the decisions made
by the company. This is therefore seen as an input into an equation
with the output being efficiency. The research associated with
this paper sets out to establish whether the input functions have
a bearing upon the final output, namely does structure, whether
organisational or ownership affect efficiency. The results so
far indicate that it does. This has been further compounded by
other research such as Boardman and Vinning (1989).
Technique
Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) is an established statistical
technique which measures the relative efficiencies of units where
simple efficiency measures are difficult to obtain (Farrell 1957;
Charnes et al 1978). The main attraction of DEA is that it can
deal with multiple inputs and outputs. The units in any DEA assessment
are generally homogeneous and independent units performing the
same function, and it is of most use where there are a large number
of units providing an 'identical' service in relative isolation
(Szczepura et al 1992). DEA was first developed as a way of measuring
service units by Charnes et al. (1978). The model has since been
added to and developed over the years. Warwick Business School
in the UK has pioneered the research and are regarded as one of
the leading institutions working in this field. DEA has been successfully
used in airports, local government authorities, courts, hospitals
general medical practices and bank branches to test efficiency
where there are multiple centres of inputs and outputs. Its application
to the port industry would therefore appear to be ideal. As far
as the authors are aware there have been no studies using DEA
within actual seaports. However, Roll and Hayuth (1993) state
that DEA is a most suitable tool for measuring port efficiency,
although they have only applied it hypothetically.
Sachish (1996) looked at the different techniques for measuring
productivity and confirmed DEA's usefulness. However his research
adopted an engineering method to take account of the technological
investments when looking at the efficiency of Israeli ports. Various
other studies have been made using the assessment of productivity
based upon output per worker (DeMonie 1987), output per wharf
(Frankel 1991) whilst others use production functions, (Kim and
Sachish 1986, DeNeufville and Tsunokawa 1981). Gillen and Lall
(1997) looked at airport terminals and chose two outputs, number
of passengers and pounds of cargo. They chose six inputs, number
of runways, number of gates, terminal area, number of employees,
number of baggage collection belts and number of public parking
places. They conclude that the number of gates has the most overall
affect upon efficiency. In terms of ports, gates, which facilitate
the loading of the cargo could be equated to loading cranes and
runways to berths.
Efficiency can simply be expressed as a ratio of output to input
provided that the product only produces one output. However, as
most institutions produce multiple outputs from multiple inputs
each variable must be given a weighting to produce a more accurate
result. Efficiency then begins to resemble the sum of weighted
outputs over the sum of weighted inputs. As the method of weighting
can be biased towards one particular outcome, the DEA technique
allows for each weighted input/output to be seen in its most favourable
light. The number of variables entered into the formula cause
for there to be more of a discriminatory power of DEA. This means
that the more variables included into the equation may lead to
a lack of emphasis on particularly important piece of data. Therefore
Szczepura (1992) argues the number of variables should be kept
to as low as possible. However, by weighting the variables it
is still possible to reduced this limitation and include more
variables.
Findings
For the purpose of this research data has been collected from
21 container ports in the Cargo Systems Journal 1999 list of top
100 container ports. The plan is eventually to obtain data for
all 100 ports. The ports chosen for this preliminary study were
those that either provided adequate statistics on their web sites
or who responded for a request for information. The raw data collated
for analysis by DEA as inputs and outputs is shown in Table 2
Table 2 Inputs and Outputs
| Output | Output
| Input | Input
|
| Port | Containers
| Total throughput | US$- Assets
| Quayage (m) |
| Auckland | 499,285 |
4,200,000 | 165,137,688
| 6,046 |
| Charleston | 1,277,514 |
10,270,000 | 520,402,000
| 3,844 |
| Goteborg | 519642 | 30,394,000
| 205,506,788 | 11,955 |
| Halifax | 435,425 |
13,173,353 | 59,500,633
| 5,948 |
| Houston | 968,169 |
169,100,000 | 740,542,000
| 24,648 |
| Jacksonville | 753,823
| 7,377,000 | 549,394,000
| 12,728 |
| Johor | 460,000 | 19,322,363
| 208,379,772 | 2,665 |
| Liverpool | 487,000 |
33,000,000 | 429,558,525
| 18,785 |
| Long Beach | 4,100,000 |
60,800,000 | 2,215,034,000
| 18,182 |
| Los Angles | 3,378,218 |
82,126,624 | 2,431,141,000
| 13,758 |
| Melbourne | 1,044,000 |
42,108,000 | 234,733,746
| 12,969 |
| Miami | 860,000 | 5,850,000
| 452,124,219 | 5,686 |
| Montreal | 932,701 | 206,000,000
| 185,684,200 | 15,537 |
| New York/Jersey | 2,465,993
| 56,000,000 | 3,505,136,000
| 9,000 |
| Penang | 510,307 | 16,480,000
| 119,060,620 | 3,388 |
| Port Klang | 1,820,018 |
40,000,000 | 88,396,401
| 5,973 |
| Rotterdam | 6,010,000 |
315,000,000 | 1,418,117,624
| 77,000 |
| Seattle | 1,544,000 | 13,000,000
| 2,635,262,000 | 22,912 |
| Southampton | 846,257 |
35,000,000 | 1,604,014,008
| 10,053 |
| Sydney | 801,081 | 16,450,000
| 219,119,780 | 5,888 |
| Vancouver | 800,000 |
71,405,000 | 361,969,878
| 11,243 |
This above raw data has been computed using the DEA technique
mention earlier. The two columns labelled outputs and the two
columns labelled inputs have been compared with each other to
produce a table of relative efficiency. This table of relative
efficiency is shown in Table 3. However, it must be stressed that
this is not an absolute efficiency measurement and that those
ports that are at either end of the scale can neither be said
to be efficient or inefficient. The results merely show that the
ports can be ranked in order to show which ports achieve a greater
throughput with the minimum of assets and least berth space, i.e.
quayage. In order to achieve an absolute efficiency rating additional
data needs to be included within the equation. Such additional
data would have to include all the port's outputs such as number
of passengers; amount of general, liquid, bulk or other type of
cargo that pass through the port as well as other inputs, such
as number of employees or cranes utilised.
Table 3 shows that in terms of container ports the Port Klang
along with Johor and Charleston rate amongst the highest of this
sample. These figures are capped to ensure that the ceiling of
relative efficiency of any port does not exceed 100%. However
if the scale is not adjusted then Port Klang has a score of 110.23
whilst Johor stands at just 110.13 and Charleston 109.07. This
therefore denotes that these ports main specialisation is likely
to be in containers.
Table 3 - Relative efficiency of ports
| Rank | Relative Efficiency rating
| Port |
| 1 | 100 | PORT KLANG
|
| 2 | 100 | JOHOR
|
| 3 | 100 | CHARLESTON
|
| 4 | 92.28 | NEW YORK/JERSEY
|
| 5 | 91.77 | HOUSTON
|
| 6 | 87.16 | LOS ANGLES
|
| 7 | 84.96 | VANCOUVER
|
| 8 | 70.85 | LONGBEACH
|
| 9 | 67.73 | PENANG
|
| 10 | 54.72 | ROTTERDAM
|
| 11 | 46.84 | SOUTHAMPTON
|
| 12 | 45.51 | MIAMI
|
| 13 | 44.27 | SYDNEY
|
| 14 | 43.82 | MELBOURNE
|
| 15 | 34.01 | GOTEBORG
|
| 16 | 31.16 | HALIFAX
|
| 17 | 24.91 | AUCKLAND
|
| 18 | 23.50 | LIVERPOOL
|
| 19 | 20.33 | SEATTLE
|
| 20 | 19.78 | MONTREAL
|
| 21 | 18.02 | JACKSONVILLE
|
The figures for Asian ports may be distorted by the fact that
they include within the equation the asset value converted to
USD. Due to the difference in land values and the value of assets
in general Port Klang would naturally be expected to rate more
favourable than a port in the West where land and other goods
are relatively more expensive. Therefore by including assets within
the equation it is likely that a port situated in the East would
achieve a higher ranking than a port in the West. Thus the position
of Jacksonville at position (21) at the bottom of the scale does
not mean that this port is inefficient but does highlight that
this port has a higher asset value than say, Vancouver, which
has approximately the same container throughput but ranks at position
(7).
Indeed in terms of valuation the port of Seattle, ranked at position
(19), is equivalent to almost 30 ports the size of Port Klang
and 8 ports the size of Houston (5). The results of this test
therefore show that assets valuation is a questionable raw input
in the equation. However by adjusting the asset figure to reflect
the economic situation of the country by say, comparing it to
the Gross Domestic Product (GDP), it should be possible to compare
ports from different countries. This method will be left open
for further research but meantime another way to compare ports
in different countries is to use a measurement that can cross
national barriers and exchange rates. The method which has been
chosen for this research is to include the size of the port by
using the length of berth against the same outputs. It however
should be noted that the results may be misleading since by utilising
in the equation container traffic it assumes that this is the
port's sole activity. The results do not allow for the number
of passengers or quantity of bulk or liquid cargo that is handled
by the port. Consequently Miami receives a rating below fifty
percent which does not reflect the several millions of passengers
that transit the port each year.
However using these ports as a guideline and ignoring the limitations
of the present data the next stage of assessment is to analyse
the data in terms of ownership and organisational structure. As
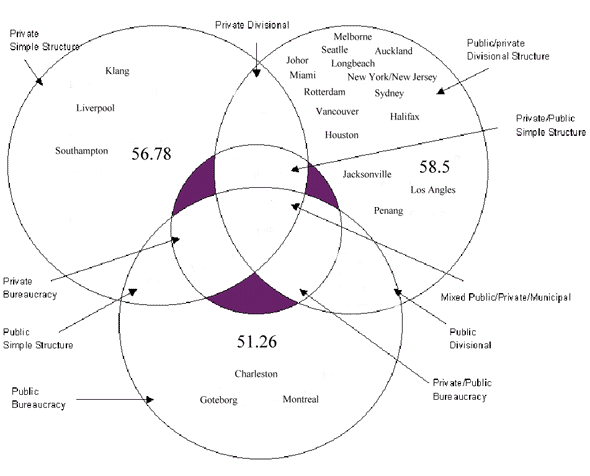
a guide figure 2 shows the sample ports results placed into the
conceptual model using just ownership structure. Further research
needs to be undertaken on the organisational structure of these
ports in order to utilise the model for its intended purpose.
The numbers contained with the diagram indicate the average efficiency
of ports in that particular category. The most efficient ownership
structure is indicated to be joint private/private at an average
of 58.5, followed by private ports at 56.78 and lastly publicly
owned ports at 51.26. It must be stressed that in order to see
whether this is indicative of the port industry more ports will
need to be examined.
Figure 2
Conclusion
This research has shown that organisation theory and ownership
structure can be incorporated into a conceptual model of the port
industry that can in itself enable a simple comparison of the
efficiency of differing patterns to be made. The research has
highlighted the need for additional inputs into the equation as
well as emphasising the limitations of using assets as an input.
Data which knows no national boundaries such as size of the port,
length of berth and the primary function of the port need to be
included in order to compare ports on an equal basis. However,
the results have shown that DEA's ability to handle multiple inputs
and outputs combined with the ability to add weights will allow
for a meaningful analysis to be accomplished.
References
Abdel-Fattah, N, Gray R., Cullinane S. (1999) Road freight and
privatisation: the case of Egypt, Ashgate, Aldershot
Boardman, A.E. and Vining, A.R. (1989) Ownership and performance
in Competitive Environments: A comparison of the performance of
Private, Mixed and State-owned Enterprises, Journal of Law and
Economics, Vol. 32, pp 1-33
Borcherding T.E., Pommerehne, W.W. and Schneider, F. (1982) Comparing
the efficiency of Private and Public Production: A Survey of the
Evidence from Five Federal Stated, Zeitschrift fur Nationalokonomie/Journal
of Economic Theory: Public Production, Suppl.2, pp 127-56
Bos, D. and Nett, L. (1991) Employee share Ownership and Privatisation:
A comment, The Economic Journal, Vol. 101, pp 966-969
Cass, S. (1996) Port Privatisation, Cargo Systems, IIR Publications
Ltd., London
Caves, D.W., et al (1982) Economic Performance of U.S. and Canadian
Railroads, In Managing Public Enterprises, edited by Stanbury,
W.T. and Thompson, F., Praeger, New York
Charnes, A., Cooper, WW and Rhodes, E (1978) Measuring the Efficiency
of Decision Making Units, European Journal of Operational Research,
Vol.2, No.6, pp 429-444
De Alessi, L. (1980) The Economic of Property Rights: A Review
of the Evidence, In Research in Law and Economics, Vol. 2, edited
by Zerbe, R.O., JAL, Greenwich, Conn., pp 1-47
DeMonie, G (1987), Measuring and Evaluating Port Performance and
Productivity, UNCTAD Monographs on Port Management, Geneva
De-Neufville, R and Tsunokawa, K. (1981) Productivity and returns
to scale of container port, Maritime Policy and Management, Vol.
8, No. 2, pp121-129
Everett, S. and Robinson, R. (1998) Port reform in Australia:
issues in the ownership debate, Maritime Policy and Management,
Vol. 25, No. 1, pp41-62
Farrell MJ (1957) The measurement of productive efficiency, Journal
of Royal Statistical Society, Vol. 120 pp253-281
Frankel, E.G. (1991) Port Performance and Productivity Measurement,
Port and Harbours, Vol. 36, No.8, pp 11-13
Frech H.E. (1980) Property Rights, the Theory of the Firm, and
Competitive Markets for Top Decision-Makers, In Research in Law
and Economics, Vol. 2, edited by Zerbe, R.O., JAL, Greenwich,
Conn., pp49-63
Gillen, D. and Lall, A. (1997) Developing Measures of Airport
Productivity and performance: An Application of Data Envelopment
Analysis, Transportation Research -E, Vol.33, No.4, pp261-273
Heikkila E.J. (1990) Structuring a national system of ports, Portus,
Vol. 5 (3), pp19
Kim, M and Sachish, A. (1986) The Structure of Production, Technical
Change and Productivity in Port, Journal of Industrial Economics,
Vol. 35, No. 2, pp 209-223
Mintzberg, H. (1979) The structuring of Organizations, Prentice-Hall
Inc., Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey
Port Development International, Public Participation, March 1999
Roe, M.S. (1999) The commercialization of East European liner
shipping: the experience of Poland, Maritime Policy & Management,
Vol. 26, No.1
Roll, Y. and Hayuth, Y. (1993) Port performance comparison applying
data envelopment analysis (DEA), Maritime Policy and Management,
Vol. 20, No. 2, pp 153-161
Sachis, A. (1996) Productivity functions as a managerial tool
in Israeli ports, Maritime Policy and Management, Vol. 23, No.
4, 341-369
Szczepura, A. Davis, C., Fletcher, J. and Bousoffiane, A (1992)
Applied Data Envelopment Analysis in Health Care; the Relative
Efficiency of NHS General Practices, Warwick Business School Research
Bureau, Coventry
Tandon, P. (1997) Efficiency of Privatised Firms - Evidence and
implications, Economic and Political Weekly, Vol. 32, No. 50,
pp 3199-3212