
Special Interest Group on Maritime Transport and Ports
a member of the WCTR Society
INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP
Genoa - June 8-10, 2000
TRANSITION TO A NEW
REALITY: THEORISING THE ORGANISATIONAL RESTRUCTURING OF PORTS
Constantinos I. Chlomoudis
School of Maritime
Studies, University of Piraeus, Greece
40 Karaoli Dimitriou
St, 18532 Piraeus, Greece,
Tel.: +30 (01) 4142548,
Fax: +30 (01) 4142575, E-mail: chlom@unipi.gr
Apostolos V. Karalis
Freelance Researcher,
40 Karaoli Dimitriou
St, 18532 Piraeus, Greece,
Tel.: +30 (01) 4142517,
Fax: +30 (01) 4142575, E-mail: akarl@tee.gr
Athanasios A. Pallis
Research Centre,
University of Piraeus, Greece
40 Karaoli Dimitriou
St, 18532 Piraeus, Greece,
Tel.: +30 (01) 4142540,
Fax: +30 (01) 4142575, E-mail: apallis@unipi.gr
|
ABSTRACT
The port industry has
experienced a wide restructuring during the last decades. New
dimensions of port production have become evident representing
an across-the-board break with the conventional Mass Production
System (MPS). This paper proceeds to a theoretical discussion
that tackles the issue of port reorganisation. In the light of
the changes in the world economy and the new competitive environment,
it focuses on the new structures of the port industry and the
characteristics of the contemporary port product within a more
general analytical framework of 'Worlds of Production'. This conceptualisation
suggests that neither the industrial model of mass production,
nor any other model alone, can provide by definition an effective
pattern of port production organisation. Within the new reality,
modern ports must provide a greater variety of services to port
users than in the past. The diversity and complexity of the contemporary
port product demand the application of multiple organisational
transformations incorporating elements of different possible frameworks
of action. In this vein, the introduction of intra-port competition,
the development of strategic or regional networks, and the reconsideration
of the role of port authority turn to critical parameters of the
essential restructuring.
1. Introduction
It is widely acknowledged
that the port industry has experienced a wide restructuring during
the last decades. For long, the organisation of the industry had
been dominated by the post-war industrial paradigm of mass production,
characterised by standardised port products and long production
runs, and served as a motor of steadily rising productivity levels.
Since the late 1970s new dimensions of port production systems
have become evident representing an across-the-board break with
the conventional mass production system. The main reasons being:
technological changes (unitisation or containerisation, introduction
of informatics), organisational changes (just-in-time manufacturing,
logistics, multimodal transport operation), liberalisation of
world markets (creation of the European Union, globalisation)
and a shift of political attitudes in favour of less state intervention
in the economy (i.e. privatisation in the case of public ports
etc.). These changes have affected profoundly the port industry
and have intensified port competition.
During an era of new
and intensive competition ports are facing significant challenges
that require both productive and organisational restructuring
to secure a competitive edge. The traditional perceptions of port
activities have been widely expanded to include a variety of new
tasks and operations under a qualitatively new operational logic.
The main aim of this
paper is to initiate a theoretical discussion by charting the
new realities and proposing an analytical framework that explicitly
tackles the issue of port reorganisation in the light of the diversity
and complexity (a) of the new competitive environment and (b)
of the port industry itself.
In order to achieve
this aim the paper proceeds by briefly presenting the contemporary
changes in the world economy and the port industry. Secondly,
it details the new structures and characteristics of the port
industry by focusing on the port product itself within a more
general analytical framework of "Worlds of Production".
In this vein, it discusses the implications of this approach to
the productive and organisational restructuring of ports, and
presents some concluding thoughts on the state of the debate along
with some proposals from this new point of view.
Rather than suggesting
a single new alternative model, the authors present several possible
forms of restructuring under which the port production process
might be effective in the new reality. Given the heterogeneity
of ports around the world, those responsible for decision-making
need to take into account the peculiarities of each port and decide
which of the suggested forms fits best on a case-by-case basis.
2. Changes in the
World Economy and the Port Industry: Challenges to the Existing
Patterns of Port Production
The world economy during
the last three decades has undergone a period of rapid change
and transformation. These changes have had a significant impact
on the way economists and other social scientists perceive the
operations of an economy (cf. Piore and Sabel, 1984; Best, 1990).
The certainties that prevailed until the early 1970's were strongly
challenged by a plethora of new phenomena (a few examples would
include: a fragmentation of markets, increased and unpredictable
shifts in demand patterns, a general rise in the levels of risk
and uncertainty concerning all aspects of economic action). Further,
not only the previously mentioned scholars but also many more
(for a reader: Amin, 1994), agree that various organisational
forms, alternative to mass production and the 'market', are gaining
a significant competitive edge; these include various kinds of
network-like structures.
Industrial growth and
success has been interpreted as a result of the adoption and widespread
diffusion of mass production during a specific historic period
(cf. Piore & Sabel, 1984). Mass production should not be understood
in terms of simplistic references to size and efficiency but in
terms of a system of markets, technologies, and scientific management,
complemented at the institutional level by a comprehensive code
of social ethics and economic regulations designed to stabilise
and sustain demand. Thus, the creation of the large, vertically
integrated, hierarchical corporation has been the outcome of strategies
to balance supply and demand in mass production industries.
Rather than a consequence
of any inherent supremacy of that model in terms of efficiency
(i.e. economies of scale etc.), the rise and dominance of mass
production (defined as Fordism complemented by Taylorism) was
a result of conscious and/or strategic consideration and choice.
The alternative was, and still is, a strategy based on craft principles
of production, which might be termed flexible specialisation.
The latter is "a strategy of permanent innovation: accommodation
to ceaseless change, rather than an effort to control it. This
strategy is based on flexible - multiuse equipment;
skilled workers; and the creation, through politics, of an industrial
community that restricts the forms of competition to those favouring
innovation" and not price (ibid: 17).
The system of mass production
started to face a prolonged crisis whose origins can be traced
in the earlytomid 1970s. It was suggested that the
system itself had reached its limits of growth under the particular
institutional and regulatory framework.
The reasons behind this
crisis have been attributed to both endogenous and exogenous factors.
One of the most important exogenous factors was the emergence
of some qualitatively new forms of industrial organisation (i.e.
in Japan, Germany, Italy) whose competitive power put great pressure
on the mass production firms/regions/nations. The apparent success
of newly formed industrial agglomerations was attributable to
the new and qualitatively distinct principles of productive and
socio-political organisation. This, further, was interpreted as
an event signifying the possibility, and not the certainty,
of flexible specialisation becoming a dominant paradigm of industrial
organisation.
Although the analysis,
as well as much of the empirical evidence, tends to associate
flexible specialisation with industrial districts of small and
medium enterprises, it also do distinguishes between distinct
organisational forms ("faces") of flexible specialisation,
namely regional conglomerations or industrial districts; federated
enterprises; solar firms; and workshop factories (ibid: 265-268).
Thus, flexible specialisation is a theory of industrial organisation
that applies to both Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) clustered
in industrial districts and large firms that explicitly pursue
a strategy alternative to vertical integration.
2.1 Changes in the
Port Industry
At the same time ports
around the world were facing new challenges, not least because
the port product had undergone a great transformation. As ports
are a mixture of industry and services that serve specific production
processes (Suykens, 1986), these changes have been partially the
result of the preceded fundamental changes in the production processes
world-wide, and partially the result of endogenous technological
developments.
Nowadays, ports are
transformed into areas where highly sophisticated logistics activities
are concentrated, largely due to fundamental modifications in
the production and distribution of goods. The creation of functionally
comprehensive 'industrial networks' and the implementation of
logistics - that is, the management of physical and informational
flows into, through, and out of a business - resulted in a new
trading context and altered the industry-transport relationship.
Transport services are developing to an integral part of production
and marketing strategies. All types of seagoing trade, even cabotage,
are becoming increasingly integrated into logistics chains. Foremost,
the rapidly expanding feedering traffic requires its' integration
into the individual links of the inland transport chain and the
co-operation between short-sea and inland transport operators.
Freight corridors should go further and ports develop the conditions
for setting up networks dedicated solely to intermodal freight
transportation.
Then, the increasingly
widespread use of unitisation has led to the incorporation of
further criteria in deciding the route of a cargo as well as in
modal choice. Once the efficiency of port cargo handling and of
ocean and inland transportation services have significantly increased,
the geographical monopoly powers of ports have been eroded (Heaver,
1995). Nowadays the market powers of ports mostly depend on the
provision of more specialised facilities. Ports compete to attract
containers and/or traditional freights that are transported via
novel transport methods. Port users, either shippers or shipowners,
have assumed the role of multimodal operators and are increasingly
demanding 'new' services. Capital-intensive terminals that serve
few logistics systems, and the ability to provide value added
services based on both economies of scale and variety, are becoming
more important parameters of the selection of port routings. The
provision of specialised warehousing, or other technological infrastructure
and facilities that guarantee the uninterrupted multimodal transportation
have become substantial income generators. Thus the importance
of the traditional port selection criteria is in decline and the
core business of ports no longer consists of loading/unloading
activities. Port productivity is related to the improvement of
the total transport chain, rather than maritime transport alone.
Subsequently, port competitiveness depends on the other elements
of the transport network (i.e. railroads, road transhipment),
so port planning is becoming the focal point of a holistic planning
of this multimodal transport network.
A vital consequence
of these structural changes is the expansion of the port zone.
Apart from the 'internal' geographical area, it includes cargo
and passenger corridors determined by the requirements of the
inland parts of the transport chain. To the extent that value
added services are supplied by production units located in wider
geographical areas and integrated through communication networks,
two types of activities develop: (a) port specific activities,
essential for the daily operation of the port and provided by
production units located within the 'internal' port zone (i.e.
vessels' loading/unloading); and (b) port related activities,
which are essential for the transportation of goods but whose
efficient supply does not necessitate the location of the production
units within the port zone (i.e. warehousing). The decentralisation
of production and the effective connection of the port with other
semi-autonomous (in relation to the port) areas influence its'
competitive position. In several European ports (i.e., Rotterdam,
Hamburg, Marseilles) a number of complementary services are already
supplied by enterprises located in the hinterland, and virtually
co-ordinated via communication systems (BCI, 1996).
The transformation of
the port industry has been accelerated by the advent of technological
developments and informatics and their widespread application
in ports. Through the application of technological developments,
ports are able to supply specialised, 'clever', port services
- based less in materials and more on innovation, knowledge, decentralised
planning, and intra-industry support. The traditional port-gate
is gradually replaced by the port logistic centre (a transformation
realised in the early 1990s: Pesquera & De La Hoz, 1992),
which provides complementary transport operations, logistics services
and co-ordinates the integrated multimodal traffic. Along with
conventional services, it provides innovative services such as
integrated management systems and Electronic Data Interchanges
(EDI) linking port authorities, shippers, stevedores, and shipowners,
and facilitates multimodal transportation within the just-in-time
requirements. In this respect it is possible to talk in terms
of logistics polarisation.
Without ignoring the
importance of modern infrastructure and superstructure, within
this polarisation, high productivity levels can be achieved through
the organisational restructuring of port production and the adoption
of operational methods that respond to the new requirements of
the port users. Until early 1970s ports operated as forces of
regional and industrial development, within the principles of
the aforementioned Mass Production System. This process incorporated
linear production - the combination of specific operations and
the harmonisation of the rhythms of various industrial operations
(the 'assembly line') - and the standardisation of services. The
direct result was the benefits associated with large-scale production
such as the significant decreases of the average production cost
per service. Port businesses had to be large enough to satisfy
the demand for massive quantities of standardised services, generate
sufficient returns to the substantial funds that were invested
in ports, and achieve the steady employment of the production
factors. The existence of huge and stable markets required (or
was more efficiently served by) large-in-size, horizontally and
vertically integrated, hierachical and labour intensive port enterprises.
The new trading context
demands the adoption of a different orientation and organisational
structure of port businesses. The main reasons are: (a) the stagnation
of the demand for specific 'traditional' port services complemented
by more rapid and unpredictable shifts in demand patterns (the
MPS is characterised by an endogenous trend towards the homogenisation
of the market and the standardisation of the produced services
thus suffering from inflexibility and incapability to adjust to
the structural demand changes); (b) the difficulty to synchronise
the flow of the MPS huge markets when port operations perplex
due to the expanding geographical disparity of the production
functions (i.e. quay, warehouse, distribution centre); (c) the
absence of integrated qualitative control mechanisms within the
MPS model (in the manner it was applied in the port industry);
and (d) the costly maintenance of the, essential to achieve economies
of scale, port infrastructure and superstructure.
The traditional mass
production model of port management and organisation has been
significantly challenged since the late 1970's. Thus, the issue
that needs to be addressed is how to implement efficiently the
fundamental re-engineering and redesign of port activities. In
other words, which characteristics should the organisational restructuring
of a port incorporate in order to ensure competitiveness? Understanding
the nature of the contemporary port product and the port production
activities is critical.
3. The Nature of
the Port Product in the New Reality
As presented in the
previous section, ports face increasing levels of competition
whose qualitative characteristics are entirely new to the industry.
The challenges posed by the new competition have direct implications
both to the organisational structure of an individual port and
to the productive activities. Competition between ports, as is
the case for most other industries, is centred on a range of products
that are offered to the port users. Thus it is necessary to discuss
the potential nature of the port product since a major criterion
of an enterprise's success is whether the final users demand its'
product. Especially as "the port product may be regarded
as a chain of interlinking functions, while the port, as a whole,
is in turn a link in the overall logistics chain" and "within
the port itself, the respective significance of the constituting
links has clearly changed in the course of time" (Suykens
& Van de Voorde, 1998:252). When earlier definitions (i.e.
Jansson and Shneerson, 1982; Goss, 1990) become obsolete or need
adjustments, a clear understanding of "which product do ports
have to offer" is critical to the future of port management.
Conceptualisations regarding the 'product' in general can advance
this discussion.
First, a product can
be either generic or dedicated. A generic product has general
applications and is defined through a process of "consolidation"
by the producer (i.e. its' qualities and characteristics are classified
and defined in advance by the producer without consideration of
the specific needs of an individual consumer). On the other hand
a dedicated product is the result of the producer's response to
individual demands of consumers.
Second, the provision
of a product can be achieved either through a process of standardisation
or a process of specialisation. Both cases refer to the way various
resources are mobilised in production. In the first case, standardised
production involves the use of interchangeable and reproducible
resources resulting in a product that does not reflect the individuality
of it's maker. The product simply reflects general and objective
characteristics. In the opposite side of the spectrum, specialised
production involves the mobilisation of highly specialised, idiosyncratic
and even unique resources whose characteristics are directly reflected
on the observed qualities of the product.
Third, a production
process can exhibit characteristics that favour increased volume
or range of products. In the first case, which is closely related
to productive standardisation, there are economies of scale at
work. These economies of scale are associated with the production
of long-series of standardised products in order to minimise unit
costs since these products have to face strong price-competition.
In the second case, which is closely related to productive specialisation,
there are economies of variety (or scope) at work. These economies
of variety are associated with the production of a relatively
broad range of products by a single port enterprise. Competition
in this case is not centred primarily on price but on a variety
of strategic variables such as innovation and differentiation,
design, promptness of response and various after-sales services.
Finally, the market
structure of a product may be characterised by conditions of predictability
or unpredictability. The first case refers to calculable risk,
while the second refers to conditions of true uncertainty. Whether
the market of a product exhibits characteristics of risk or uncertainty
has direct and profound implications on both producers and consumers
and their respective behaviours.
Table 1 represents an
attempt to decompose the contemporary port product and classify,
according to the conceptualisation developed in the previous paragraphs,
the various products/services/facilities that might be offered
by a port nowadays. This classification represented in this table
is not exhaustive and is rather schematic. It nonetheless serves
as an analytical tool to advance the theorisation of port organisational
restructuring.
Thus, in the second
column (nature of port product) port products are characterised
as either generic or dedicated. The classification refers to whether
a port product is conceived as being impersonal and having general
applicability to all port users (generic), or whether it's conception
and design takes into account the specific and individual needs
of particular port user(s) (dedicated). In the third column (nature
of productive action) there is a classification according to the
principles governing the production of the respective product.
These principles can be materialised and applied as either a process
of specialisation or a process of standardisation of the activity
of production. Apparently, as the products, services, and facilities
that a port can potentially offer increase there is a variety
of different possible combinations that lead to various forms
of port organisation. These are discussed and theorised in the
forthcoming section.
Table 1: The Contemporary
Port Product
| Port Product
| Nature of
Port Product
| Nature of Productive Action
|
| Water Transportation Services
|
| Pilotage
| Generic or/and Dedicated
| Standardised
|
| Pilotage infrastructure
| Generic
| Standardised
|
| In-port Vessels Traffic Management
| Generic
| Standardised
|
| Waste management / bunkering
| Generic
| Standardised
|
| Towing of ships
| Dedicated
| Specialised
|
| Generic
| Standardised
|
Vessels Reception Infrastructure
(i.e.quays)
| Generic or/and
Dedicated
| Standardised
|
Other services to ships
(i.e. electricity, other utilities)
| Generic
| Standardised
|
| Cargo Administration
|
| Loading/unloading onto the quay
| Dedicated
| Specialised
|
| Generic
| Standardised
|
| Transportation towards/from warehouses
| Dedicated
| Specialised
|
| Generic
| Standardised
|
| Warehouses
| Dedicated
| Specialised or/and Standardised
|
| Generic
| Standardised
|
Goods processing in the warehouses
(i.e packing , crating)
| Dedicated
| Specialised or/and Standardised
|
| Preparation for distribution to the hinterland
| Dedicated
| Specialised or/and Standardised
|
| Services related to inland transport modes
|
| Transloading in inland modes
| Dedicated
| Specialised and/or Standardised
|
| Generic
| Standardised
|
| Inland mode networks
| Generic
| Standardised
|
| Communication Services
| | |
| Electronic Data Interchange
| Dedicated
| Specialised and/or Standardised
|
| Generic
| Standardised
|
| Vessel Traffic System
| Generic
| Standardised
|
| Other Services
| | |
| Security Services
| Dedicated
| Specialised and/or Standardised
|
| Generic
| Standardised
|
| Port Free Zone
| Dedicated
| Specialised and/or Standardised
|
| Generic
| Standardised
|
| Ship Repairing Services
| Dedicated
| Specialised and/or Standardised
|
| Traffic management in inland port area
| Generic
| Standardised
|
4. Port Industry
and the Possible Worlds of Production
4.1 Possible Worlds
of Production
Each production activity
represents a coherent action framework that shapes, and at the
same time is conditioned by, the understandings, the expectations,
the ways of action and interaction of all those involved in the
production and exchange of a product (producers, labour, consumers
or users and the various institutions involved).
Taking into account
all the possible combinations of: a) products (generic or dedicated),
b) production processes (standardised or specialised), c) the
technology associated with each production process (economies
of scale or economies of variety or scope), and d) the conditions
characterising the market of a product (risk or uncertainty) four
distinct action frameworks, or possible worlds of production,
can be constructed. According to (Storper and Salais, 1997), these
are: the "Interpersonal World", the "Market World",
the "Industrial World" and the "World of Intellectual
Resources". The world of Intellectual Resources refers to
the research and development activities that lead to the creation
of new products. Thus it has little or no direct significance
to the port industry. The three other worlds of production are
more relevant and are presented in more detail.
4.1.1 The Industrial
World
The Industrial World
is a framework of economic action that exhibits the following
characteristics:
- Production of generic-standardised
products whose qualitative characteristics are defined in advance
by the producer;
- The production process
is characterised by standardisation, using interchangeable and
reproducible resources;
- Inter-firm competition
is centred around the price of similar products whose quality
characteristics are codified;
- Production technology
often involves high levels of investment in fixed capital to reap
the benefits of economies of scale;
- In most cases labour
is semi-skilled and is expected to perform according to pre-defined
rules;
- The market of the
product is characterised by conditions of predictable risk, thus
a firm's strategy usually involves practices such as risk management,
production planning, strategies of market expansion and seasonal
or temporary layoffs.
The organisational model
associated with the Industrial World (the industrial model) corresponds
closely to the 20th century mass production system
(large, vertically integrated corporation, strict hierarchy, separation
of conception and execution, Taylorism etc.).
4.1.2 The Market
World
The Market World is
a framework of economic action that exhibits the following characteristics:
- Production of dedicated-standardised
products in series for specific clients;
- The production process
is characterised by standardisation, using interchangeable and
reproducible resources;
- Inter-firm competition
is centred around price and promptness of response to demand;
- Production technology
involves the use of flexible and multi-use machinery in order
to achieve at the same time economies of scale and a degree of
product differentiation (mass customisation) according to specific
demands;
- In most cases labour
is semi-skilled but is expected to be able to perform several
tasks;
- The producers face
conditions of market uncertainty since it is not possible to predict
future demand and prices for their products.
The organisational model
associated with the Market World (the Market model) corresponds
to enterprises with variable sizes (small, medium, large), which
may be order-takers (sub-contractors) or order-givers. These enterprises
pursue a strategy of product differentiation and rely on their
sub-contractors to achieve promptness of response to customers.
Two broad organisational structures that correspond to the Market
Model may be distinguished. The first refers to the case where
medium or relatively large firms, with potential to exploit economies
of scale, use the services of smaller companies on an input-output
chain. The selection of input-providing firms by the order-giving
firm is based on price and promptness of response within a biding-out
framework. Such an arrangement provides the order-giving firm
the necessary flexibility required when demand conditions are
unstable. A major drawback of a system based on anonymous and
impersonal inter-firm relations is that it is unstable and may
lead to market failure in transactions due to conditions such
as opportunistic behaviour, asymmetrical information etc.
A more sophisticated
and durable manifestation of this model is represented by the
various types of network markets that can be observed in virtually
all sectors. A 'network' may be defined "….as a closed
set of selected and explicit linkages with preferential partners
in a firm's space of complementary assets and market relationships,
having as major goal the reduction of static and dynamic uncertainty."
(Camagni, 1991:135). The distinction between strategic
and regional networks can also be found: A strategic network
is a "long-term, purposeful arrangement among distinct but
related for-profit organisations that allows those firms in them
to gain or sustain a competitive advantage vis-à-vis their
competitors outside the network" (Jarillo, 1988:32), while
a regional network "is made up of small and medium-sized
firms embedded in an industrial district." (Sydow, 1992:115).
These definitions are limited to the description of networks as
a form of dense inter-organisational relationships. But networks
can also evolve out of personal ties, or market relationships
among various parties (Powell, 1990).
A comparison between
the (neo-classical or "free") market, the hierarchical
and the network forms of organisation is summarised in Table 2,
while Table 3 presents an alternative classification of various
types of networks. Thus, the more sophisticated version of the
market model incorporates the characteristics of strategic networks
along with the characteristics of dynamic networks. In the case
of ports the other two types of networks, stable and internal
networks, can also apply.
4.1.3 The Interpersonal
World
The interpersonal world
is a framework of economic action that exhibits the following
characteristics:
- Production of dedicated-specialised
products as a direct response to individual demands;
- The production process
is characterised by specialisation utilising highly specialised,
even unique, resources and competencies;
- Inter-firm competition
is centred around product quality while the product's price directly
reflects its' assessment by the users in terms of quality;
- Production technology
involves the use of flexible and multi-use machinery and tools
with a view to reap the benefits of economies of variety;
- Labour is skilled
or even highly skilled, able to perform a wide variety of tasks;
- Both producers and
consumers face conditions of true market uncertainty since there
is no way to assess a priori a product's quality, this fact makes
the producer-user relationship the single most important element
of tackling uncertainty.
The organisational model
associated with the Interpersonal World (the Marshallian Market
Model) corresponds to firms or units that pursue a strategy of
diversified quality production, which is transactions- and information-intensive.
In this case the producer-user relation is of paramount importance.
Further, these firms are part of localised networks characterised
by dense interpersonal relationships. In other words the Marshallian
Market Model incorporates the characteristics of regional networks
and dynamic networks.
Table 2: Stylised
Comparison of Forms of Economic Organisation
| Forms
|
| Key features
| Market
| Hierarchy
| Network
|
| Normative basis
| Contract - Property rights
| Employment relationship
| Complementary strengths
|
| Means of communication
| Prices
| Routines
| Relational
|
| Means of conflict resolution
| Haggling - resort to courts for enforcement
| Administrative fiat-supervision
| Norm of reciprocity - reputational concerns
|
| Degree of flexibility
| High
| Low
| Medium
|
| Amount of commitment
| Low
| Medium to high
| Medium to high
|
| Tone or climate
| Precision and/or Suspicion
| Formal, bureaucratic
| Open-ended, mutual benefits
|
| Actor preferences or choices
| Independent
| Dependent
| Interdependent
|
| Mixing of forms
| Repeat transactions
| Informal organisation
| Status Hierarchies
|
| Contracts as hierarchical documents
| Market-like features: profit centres, transfer pricing
| Multiple partners
|
| | |
Formal rules
|
Source: Powell, 1990,
p. 269
Table 3: Types of
Networks
| Type of Network
| Stable
| Internal
| Dynamic
|
| Operating logic
| A large core firm creates market-based linkages to a limited set of upstream and/or downstream partners.
| Commonly owned business elements allocate resources along the value chain using market mechanisms.
| Independent business elements along the value chain form temporary alliances from among a large pool of potential partners.
|
| Primary Application
| Mature industries requiring large capital investments. Varied ownership limits risks and encourages full loading of all assets.
| Mature industries requiring large capital investments. Market-priced exchanges allow performance appraisal of internal units.
| Low tech industries with short product design cycles and evolving high tech industries (e.g. electronics, biotech, etc.)
|
Adapted from: Miles
and Snow, 1992, p. 64.
4.2 Potential Organisational
Patterns of the Port Industry
The theoretical concepts
that were presented in the previous section constitute the tools
of a new analytical framework that can be applied to the study
of a port industry that faces new and significant competitive
challenges. Under this prism it can be argued that the operational
and organisational logic of port activities during the conventional
era was conforming to the principles of the Industrial world.
Most major ports had adopted the Industrial model of port organisation,
which served efficiently the industry until the late 1970s. The
period after the late 1970's is characterised by fundamental changes
that cannot be addressed by ports solely operating according to
the principles of this model. The restructuring and reorganisation
of ports assumed various forms that reflected diverse strategic
choices. Nonetheless the main issues that a modern port must address
are the following: increased quality of services, high levels
of flexibility and adaptability, closer integration with other
transport modes, higher levels of product- and process-innovation,
better management and marketing strategies, more efficient labour
mobilisation and participation. The achievement of these goals
requires the existence of ports that exhibit hybrid organisational
structures that incorporate elements of all three possible Worlds
of Production and of their corresponding models of production.
Table 1 is the result
of an attempt to classify the characteristics of port products.
These characteristics indicate which model of production is better
suited to the production of the said product according to the
preceded "world of production" concept. Port products
can also be classified with reference to which world of production
they belong in (i.e. which framework of action is particularly
suited to the production of the said product). This classification
is illustrated in the following Diagram 1.
This diagram illustrates
the major transformation that has taken place: given their characteristics,
there are relatively few port products that are exclusively suited
to the industrial model of mass production. These include the
traffic management of vessels in the port, pilotage infrastructure,
traffic management in inland port area, Vessel Traffic Systems,
waste management & bunkering, the supply of utility services
to ships (such as electricity etc.), access to inland transport
networks. In other words the production of these services is more
efficient by a single firm using standardised production methods
and exploiting economies of scale that result in low prices.
There is a second category
of port products whose combinations of characteristics require
production either within the industrial model and/or within the
Marshallian market model. These are: towing of ships, loading/unloading
at the quay, and transportation to/from warehouses. The production
of these products is open to alternative organisational structures
that correspond to the Marshallian market model.
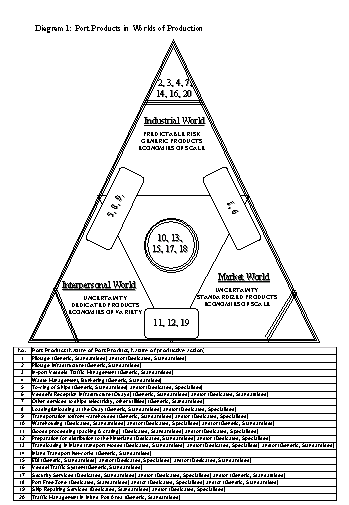
The characteristics
of a third category of port products, i.e. pilotage, vessel's
reception infrastructure, favour their production within organisational
models associated with the Industrial model and/or within the
Market model. A fourth category of port products, including goods
processing at the warehouse, preparation for distribution to the
hinterland, and ship repairing services, favour their production
within the Marshallian Market model and/or within the Market Model.
Finally, there are products, namely transloading in inland transport
modes, security services, activities in port free zones, EDI services,
and warehousing, whose characteristics allow any of the three
models of production.
The above conceptualisation
suggests that neither the industrial model of mass production,
which had been traditionally applied in the case of the port industry,
nor any other model alone can provide by definition an effective
pattern of port production. Within the new reality, modern ports
must provide a greater variety of services to port users than
in the past in order to be competitive. Many of these services
cannot be efficiently produced by a single port enterprise. The
provision of various port services can be more efficient when
regional or strategic networks operate under the logic of the
Interpersonal and the Market World respectively.
This fact opens the
possibility of intra-port competition - defined as the
competition between similar or complementary production units,
which provide the same services in the context of the same port
(Chlomoudis & Pallis, 1998) - and implicates the concept of
flexible specialisation. The demand for specialised as well as
new types of port services - which frequently represent only a
small component of the total of the services that a port supplies
- is profound. So, the introduction of specialised production
units focused on the production of specific services, and involving
decentralised management and various forms of employment and technologies,
creates the potential to match rapidly, innovatively and effectively
the demands of a port's current and potential users. These units
can provide services integrated within a wider cohesive programme
of port planning, whilst the responsibility for the effectively
supply of the services remain to the executives of these units.
Aiming to improve their competitive position they can act with
greater autonomy and demonstrate the essential entrepreneurship
and creativity.
In this context, the
role of the central port authority is to control the rules of
competition between production units offering the same but also
multiple port services. Once a process of restructuring that incorporates
elements of the interpersonal and market worlds is initiated,
the role of the port authority should be significantly reconsidered.
A system of many independent firms that are competing and co-operating
requires an institutional framework that prevents potentially
destructive ("cut-throat") price competition and favours
competition based on innovation and other non-price parameters.
When the port product
is offered within multiple frameworks of action, changes in the
patterns of employment become essential as well. The structural
modification of the qualitative characteristics of those employed
in ports becomes part of the restructuring process. Chains of
unqualified workers are replaced by skilled personnel, especially
as the implementation of new technologies modify the demand for
this production factor (Haralambidis & Veenstra, 1997; Chlomoudis
& Pallis, 1999). With regards to the administration of this
production process, the flexible co-operation of personnel along
with new type of employee relations and management practices become
essential, while the importance of the traditional hierarchical
administrative structure faces its limitations.
The diversity and complexity
of the contemporary port product require the application of multiple
organisational transformations incorporating elements of the different
possible worlds of production. The heterogeneity of the port industry
in terms of size, geographical location, management practices,
port operations - i.e. 'comprehensive ' 'service' and 'landlord'
ports - and employment patterns, is remarkable (Pallis, 1997).
This has several implications at the institutional and the operational
level along with other market developments (Langen, 1999). Therefore
the organisational strategy formulation for any particular port
has to be supplemented by a specific analysis for this port and
its competitive position. Each port attracts different users,
depends on markets that are structurally different and characterised
by divergent financial structure, hence each port might choose
to offer a different range of products aiming to expand towards
specific directions. There are many possible combinations of organisational
forms available and it is a matter of strategic choice to pick
the one that serves best the needs of a specific port.
5. Concluding Remarks
The substantial structural
changes in the world economy, the trading context and the port
industry itself, require the productive and organisational restructuring
of ports. Within the new reality, the traditional perceptions
of port activities have been widely expanded to include a variety
of new tasks and operations under a qualitatively new operational
logic. The new dimensions of the port production process observed
during the last decades are not irrespective of these developments.
Similarly to other industries, these developments can be interpreted
as attempts to overcome the limits of the conventional mass production
system, at least in so far as its application to the port industry
is concerned, and represent a break with it.
Utilising the theoretical
framework of the possible worlds of production, and an indicative
analysis of the contemporary port product, it is clear that several
of the products or services demanded by port users can be provided
effectively by organisational forms responding either to the Market
Model or the Interpersonal Model of production, The industrial
model of mass production might remain the more effective organisational
form for the production of another range of port services. Rather
than expecting the MPS to fail and ultimately be abandoned because
of its own endogenous problems, more complex and diverse forms
of port organisation might arise, involving the development of
concepts deriving from the implementation of the different frameworks
of action. These concepts include the introduction of intra-port
competition, the supply of services by several competing enterprises,
a new role for the port authority, and the restructuring of the
labour.
Any possible departure
from the conventional MPS involves the introduction of network-like
structures within a single port. Various port authorities may
still favour the operation of a single port enterprise. In this
case an organisational restructuring that introduces the principles
of internal networking to the operation of the port enterprise
is expected to result in significant competitive advantages (with
regards to the former mass production structure). When port authorities
favour the idea of allowing several independent enterprises to
operate within a single port there is a wide variety of possible
organisational forms. One might be the existence of few large
firms and many small and medium enterprises (SMEs) who act as
sub-contractors in a biding-out system. Other arrangements may
involve the operation of strategic or regional networks. Although
theoretically there is a wide spectrum of options available there
are also specific limitations as to what organisational forms
can be applied in a specific port. The most important limitation
is the entrepreneurial and industrial culture that shapes the
mentality of all those involved in production. When suspicion
and distrust prevail among entrepreneurs along with militant employee
relations then a strategic network (based on contractual relations)
is more likely to be created (a regional network is impossible
to develop under such conditions). On the other hand, when a port
society exhibits characteristics of mutual trust and consensual
employee relations the creation of a regional-type network within
a port is possible. These remarks are nothing but the tip of the
iceberg with regards to the importance of social, political, cultural,
ethical and other parameters that influence the creation and development
of any network-like organisational structure. They certainly require
further research in the context of the port industry.
As there are many possible
combinations of organisational forms available, and changes should
take into account the peculiarities of each port, variations should
be expected as the adjustment of the port industry to the new
reality progresses. Given the heterogeneity of ports around the
world, it is a matter of strategic choice to pick the one that
serves best the needs of a specific port.
References
Amin, A. (ed.) (1994). Post-Fordism:
A Reader. Oxford: Blackwell.
Best, M.H. (1990). The
New Competition: Institutions of Industrial Restructuring.
Polity Press.
Buck Consultants International
(BCI), (1996). Seaports and their Hinterland. Nijmegen,
The Netherlands: Buck Consultants International.
Camagni, R.P. (ed.)
(1991). Innovation Networks: Spatial Perspectives. London:
Belhaven Press.
Chlomoudis, C.I., and
Pallis, A.A., (1998). Ports, Flexible Specialisation, and Employment
Patterns. 8th World Conference on Transport Research. Antwerp,
Belgium.
Chlomoudis, C.I., and
Pallis, A.A., (1999). Adjusting Port Management and Organisation
to New Technologies. Proceedings of the Conference on Decision
Science and Info Systems. Athens, Greece.
Goss R. (1990). Economic
Policies and Seaports: 1. The economic functions of seaports.
Maritime Policy and Management 17(3), 207-219.
Haralambidis, H. and
Veenstra, A. (1997). World wide experiences of Port Reform. Meersman
H. and Van de Voorde E. (eds) (1997) Transforming the port
industry. Leuven: Amersfoort, 107-143.
Heaver, T.D. (1995).
The implications of increased competition among ports for port
policy. Maritime Policy and Management 22 (2), 125-133.
Jansson, J.O. and Shneerson,
D. (1982). Port Economics. Cambridge Massachusetts: The
MIT Press.
Jarillo, J.C. (1988).
On Strategic Networks. Strategic Management Journal 9,
31-41.
Langen, P.W. de (1999).
The future of small and medium sized ports. Maritime Engineering
and Ports, 263-279.
Miles, R.E. and Snow,
C.C. (1992). Causes of Failure in Network Organizations. California
Management Review, Summer 1992, 53-72.
Pallis, A.A. (1997),
Towards a Common Port Policy? EU-Proposals and the Industry's
Perceptions. Maritime Policy and Management, 24 (4), 365-380.
Pesquera, M.A. and De
La Hoz, L. (1992). EDI Key for shortsea shipping development:
the Arcantel platform. In: Winjnolst, Ir.N., Peeters, C., Liebman,
P. (eds.) (1993), European Shortsea Shipping. London: Lloyd's
of London Press.
Piore, M.J. and Sabel,
C.F. (1984). The Second Industrial Divide: Possibilities for
Prosperity. New York: Basic Books.
Powell, W.W. (1990).
Neither Market Nor Hierarchy: Network Forms of Organization. In
Thompson, G., Frances, J., Levacic, R. and Mitchell, J. (eds.)
(1991). Markets, Hierarchies and Networks: The Coordination
of Social Life. London: Sage Publications Ltd.
Salais, R. and Storper,
M. (1992). The Four 'Worlds' of Contemporary Industry. Cambridge
Journal of Economics 16, 169-193.
Storper, M. and Salais,
R. (1997). Worlds Of Production: The Action Frameworks of the
Economy. London: Harvard University Press.
Suykens, F. (1986).
Ports should be efficient (even when this means that some of them
are subsidised. Maritime Policy and Management 13(2), 105-126.
Suykens, F. and Van
de Voorde, E. (1998). A quarter of a century of port management
in Europe: Objectives and tools. Maritime Policy and Management
25(3), 251-262.
Sydow, J. (1992). On
the Management of Strategic Networks. In Ernste, H. and Meier,
V. (eds.) (1992). Regional Development and Contemporary Industrial
Response: Extending Flexible Specialisation. London: Belhaven
Press.