
|
The containership market in 2002
|
The freight market
Fleet growth versus demand
The operators
The fleet
The second-hand market
|
|
The year 2002 can be summed up as a year of convalescence,
after the 2001 traumas, while 2003 is hopefully to see full health recovered ' at least in the
absence of any unpredictable event.
Indeed, 2002 has been also a transitional year on another front, as new, stringent rules on
container content monitoring and cargo manifests have been elaborated by the U.S. administration to
prevent unwanted weapons entering the U.S. The year 2003 will see these rules coming into force.
During the implementation phase, hiccups will surely occur, resulting in ship delays. Carriers said
that they will have to pass the costs of these measures onto shippers, although it is not yet clear
if it will be through rate increases or through a 'U.S. cargo manifest' surcharge.
|
| The freight market |
|
|
2002 has been a mixed year, with varying fortunes
witnessed by operators. Some of them expected to close the year with comfortable profits while
others are deep in the red.
Charter rates for containerships have increased by around 75 % on average since the January 2002
lows. At least the rise lasted until November, when the winter season and its lower volumes of
cargoes started to take effect.
Rates eased slightly during the last weeks of 2002, but were expected to rise again in the first
quarter of 2003. Relatively strong rates can be anticipated for the next summer season, boosted by
traditional high seasonal volumes and a well-balanced supply / demand ratio.
The larger the ship, the more volatile the rates. This is well illustrated by the fluctuation in
rates for modern 3,500 teu ships, which plunged from $ 25 / 26,000 in the Summer 2000 to $ 10,000 in
January 2002. They have recovered month after month in the first part of 2002 to stagnate around $
17,500 in the second part of the year. Meanwhile, rates for 1,100 teu ships went down from $ 9,500
(summer 2000) to $ 5,250 (January 2002), and $ 7,000 / 7,500 during the last quarter 2002.
Having plunged under the $ 6,000 mark in January 2002, the rates for 1,700 teu ships -such as the
B-170s- have risen to reach $ 9,500 in October 2002 before easing just under $ 9,000 at the year
end. There is some way to go before flirting again with the $15,000 figure of the summer 2000.
The fleet of cellular ships over 1,000 teu identified
as idle (not including those which underwent routine general repairs) has decreased from 160,000 /
180,000 teu during the first four months of 2002 to around 60,000 teu during the summer. Is was
expected to increase slightly after the summer season, but it did not, thanks to the lock-out in the
USWC ports, which has prolonged artificially the demand for 1,000 to 2,500 teu ships in order to
scoop up the boxes left in Asia by delayed main-line ships. At the beginning of 2003, the idle fleet
stood at 65,000 teu. Interestingly, there were no large ships identified as mothballed. The
situation is indeed very different from one year ago.
Industrial production is rising again in most south east Asian countries while the export boom in
China seems endless. As this region of the world generates high containerised cargo volumes, it
governs the supply/demand balance in container transportation more than other regions.
In 2001, the world seaborne trade contracted by 1 %. It is now growing again. After a period of
stalling during the winter 2001-2002, the demand in container transportation has, surprisingly,
recovered above all expectations. The volume of containers carried at sea is expected to grow by 7
or 8 % in 2003, in line with growth rates observed in the 1990s.
The demand in container transportation may even surpass these figures. The cellular fleet has risen
by 10.8 % per annum over the past 7 years. The way the market has absorbed this extra capacity is
remarkable. So, with an expected cellular fleet growth of 'only' 7.5 % per annum for the years
2003 and 2004, the market will be on the owners side.
Another factor which may have a strong impact on rates is the trend of East Asian-U.S. cargoes
shifting from the U.S. West Coast ports to the U.S. East Coast, to the detriment of rail 'landbridges'.
The Panamax ships of 4,000+ teu are much sought after for the Far East-USEC services that have to
transit the Panama Canal.
The longer transportation distance means that eight or nine ships are needed on such services
instead of five or six for the Far East-USWC option. Assuming that, say, four new Far East-USEC
routes are launched, it means that a dozen supplementary Panamax ships are needed. This can be
sufficient to create a shortage of such ships, and could send the charter rates soaring for 4,000
teu ships.
|
| Fleet growth versus demand |
|
|
The fleet growth is expected to match the rise in
demand, at least during the years 2003 and 2004. A tight market may well even develop if the 10 to
11 % growth in containership demand observed since the mid-1990s is to continue.
This spectacular growth rate of the cellular fleet will not be repeated in the two years to come. It
will hover around 7.5 % (see accompanying table). This will lead to a fleet of 7 million teu in
January 2005, up from 6 million teu in January 2003 and 3 million teu in January 1996.
In fact, to keep up with the average yearly increases
of 7 % in the seaborne container trade observed during the past decade, the cellular fleet should
have grown from 3 million teu in 1996 to 4.8 million teu in early 2003 (notwithstanding the
increase in average ship speed and box handling productivity).
So, the extra 1.2 million teu of on board capacity added to reach the 6 million teu figure has been
filled with goods which were either already containerised, but were moved on general cargo vessels
or simply not containerised half a decade ago. Breakbulk liner services continue to fade away as the
cargoes they carry shift to the box (see inset).
This leads to think that, in the first instance, owners and operators were right to invest so
massively in container tonnage. However, the balance is fragile. Most operators are struggling in
trying to make profits, and economic accidents are catastrophic for the bottom line.
|
The dwindling breakbulk services
As the container continues to
make inroads into the breakbulk sector, the surviving regular conventional
services see their volumes dwindle year after year, vanishing like fading stars.
Each year brings it examples. In 2002, the U.S. Gulf-Brasil service operated by
Brasilian operator Global Transporte Oceanico (GBTO) was closed. This service
used to be run with up to five 17,000 dwt / 500 teu ships in the mid 1990s
(mostly Astrakhan tonnage), then lost progressively its grip on the market as
competitive container services were incessantly upgraded, up to the unavoidable
weekly frequency and with unbeatable transit times. High volumes of specific
cargoes (such as CKDs - Cars Knocked Down) and the boxes still carried on these
multipurpose ships were more and more siphoned off by full container ships,
while cheaper box rates helped to attract low value 'breakbulk' cargoes. And
as the cargoes flee the conventional ships, less and less sailings were offered.
Eventually, these services lost their remaining appeal with regular shippers.
| |
|
As for the non-cellular fleet deployed on liner
trades, it includes multipurpose cargo vessels, ro-ro ships and a few conbulkers. Some of these non-
cellular ships are currently deployed on liner trades, and as far as they can be identified they
total some 1,550 units of 100 teu and over, representing around 800,000 teu.
By comparison, in early 1996, the figure for these ships stood at around 2,600 units for almost 1.1
million teu. Thus, the non cellular component of the liner fleet has lost 1,050 ships for some 0.3
million teu in 6 or 7 years, which can be assumed to have shifted to cellular ships (and this is a
maximum figure as many general cargo ships and ro-ros do not make full use of their teu capacity).
This still leaves us with a differential of almost 1 million teu, which can be assumed as having
absorbed cargoes not yet containerised in the mid-1990s as well as empty boxes carried in larger
quantities than ever before.
In addition, it can be said that these massive investments spurred competition so that box rates
reached such low figures that the container sector now attracts low value cargoes or goods of a
certain value, which were until recently cheaper to carry in conventional or bulk carrying tonnage,
such as steel products, forest products or bagged sugar.
|
 |
 |
| No reversal expected in the box rates downtrend |
|
|
Should this trend continue, as there are still a lot
of goods that could be containerised, container tonnage could be ordered massively and yet be
filled. The question is of course the cost for carriers' It is a nonsense to carry waste paper on
ships plying at 25 knots but such low value cargoes make a few bucks when repositioning
otherwise empty boxes, which is better that nothing at all. Conversely, a lot of not so cheap
consumer goods are carried at a cost representing a tiny fraction of their prices as displayed on
the retail shelf.
The industry is still fragmented, with the 'Top 10 carriers' controlling roughly 50 % of the
market. So there is room for bitter rivalry. Intense competition between carriers and the race for
market share have driven rates down over the years, and there are no signs of a reversal of this
trend. Instead, the container shipping industry is under constant pressure not only from shippers
-which is natural- but also, more artificially, from regulators, which suspect every form of
alliance or sharing agreements to generate cartel-like behaviour.
And with 4,000+ teu ships starting to find their way on North-South trades, the box rates are
expected to plunge further in the long term on these trades, in corollary to the economies of scale
that these large ships allow.
Fragmentation, competition pressure and the race to market share are powerful incentives for mergers
and acquisitions. On the other hand, the destruction of value, which has followed large mergers in
the recent past (in sectors ranging from the automotive industry to the telecom and steel
industries) appears as a strong deterrent. There has been a lull in the consolidations since the
late 1990s. A new round of mergers is inevitable. But who can dare say when it will happen, and in
what context ?
|
The deadweight comes back in
vogue
The cargoes which have shifted to the
container over the recent years are generally significantly heavier than the cargoes
traditionally stuffed in boxes. The deadweight capacity of containerships now takes
on a greater significance than ever before. With most liner statistics focusing on
teu, the deadweight capacity has been forgotten. It is now time to reinstate it.
After all, the cellular fleet nom reaches 85 million dwt, which represents roughly 10
% of the deadweight tonnage of the world merchant fleet.
The traditional items carried by containers are light ones, both in their own nature
(think of the volume to weight ratio of a TV set) and because of the packing used
(think of the super light polyester pads which protect this same TV set in its bulky
cardboard box) ' not to mention boxes full of Christmas balls which flow
periodically out of China. Light boxes have now to share ship slots with boxes fully
laden in weight.
Modern cellular ships are designed in such a way that the average load of teu carried
stands at around 12 to 13 tons per teu, which leaves roughly 10 tons of cargo per teu
after subtraction of the box tares, and allowance for bunker supplies.
Most of the time, ships are today fully laden in weight well before deck cargoes are
complete. Fortunately, empty boxes have often to be repositioned on the legs where
the average loaded box weight is high. Thus, deck cargoes are topped up with these
empty boxes, provided that allowance has been planned to take their light weight into
account.
|
|
| The operators |
|
|
The liner shipping industry is not as concentrated as
other industrial sectors. It is scattered among some 300 operating groups operating 4,650 ships
deployed on liner trades worldwide, representing 6.3 million teu at the closure of the year 2002, of
which only 1 % were inactive, according to BRS-Alphaliner data.
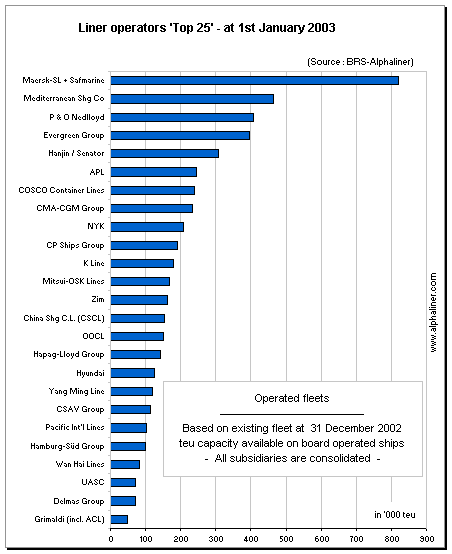
The largest of them, Maersk-SeaLand, operates a capacity of 825,000 teu, representing 12 % of the
global active capacity in teu terms. The next in size is MSC, with 6.8 % of the global capacity.
There have been only minor transactions in 2002. The most significant ones have been the sale by
Andrew Weir & Co of most of its services to Hamburg-S'd (which bought the Ellerman Line) and
CMA CGM (which bought MacAndrews and UBC), the sale by D'Amico di Navigazione of Italia Line to
C.P. Ships and the sale by CSX of its container shipping activities to US investors. Interestingly,
the ships owned by the sellers were not involved in the Andrew Weir and D'Amico deals, and were
merely chartered in. Other transactions are summed up in the accompanying table.
There are larger deals in the offing. P&O Nedlloyd could become a target when it will be
introduced on stock exchanges (which was postponed). APL, which suffers from heavy losses, is also
prone to accept an M&A deal (although APL parent company NOL is to raise cash from the planned
sale of its tanker subsidiary AET). The privatisations of Zim and S.C. India are still in the news,
although they have stalled for political reasons.
East-West niche carriers are also downsizing their operations as they cannot compete with global
organisations employing large, economic ships. In 2002, Trans Pacific Line (TPL) left the Asia-U.S.
trade while Sinotrans left its Asia-Europe trade. Senator Linie has also left all its U.S.-related
trades, which have been in fact shifted to its parent company Hanjin.
|
|
|
|
Operators : transactions and
significant moves in 2002
Straight sales
-
Hamburg-S'd bought the
Ellerman Line from Andrew Weir & Co.
-
CMA CGM bought
MacAndrews and UBC from Andrew Weir & Co.
-
C.P. Ships bought
Italia Line from D'Amico di Navigazione.
-
CSX Corp. (U.S.)
reached an agreement to convey its domestic container shipping unit
CSX Lines LLC to a venture formed with the Carlyle Group (effective
2003).
-
A.P. M'ller bought the
liner division of Copenhagen-based Torm A/S D/S.
-
Navalmar Transportes
Maritimo (Boggazzi Group) bought 50 % of the stock of Nordana Line A/S
from Dannebrog.
-
CSAV bought the Norsul
container shipping activities (Brasil), which were limited to its
participation in the 'Good Hope Express'.
-
Sea Star Line (U.S.)
bought Navieras de Puerto Rico (U.S.) from Holt (U.S.).
-
Tropical Shipping
(U.S.) bought certain assets of Tecmarine Lines and TMX Logistics
(U.S.).
-
Seaboard Marine (U.S.)
bought the remaining services of Tecmarine (U.S.).
-
Wan Hai took over the
customer base of Trans Pacific Line.
Transfers within operating groups
-
The Preussag Group
bought the remaining 0.4 % of Hapag-Lloyd shares, giving it the whole
control of the company.
-
Tschudi & Eitzen
(Norway) gained 100% ownership of the Estonian Shg Co.
-
NYK completed its stake
in TSK (its intra Asian arm), gaining 100% ownership.
-
Evergreen International
Storage and Transport Corp. bought Uniglory (intra Asian arm of
Evergreen) through a share swap.
Cessations of activity
-
International Shipping
Line (ISL) was terminated after Belgium - based MCL Shipping (Maritime
Chartering & Liner Shipping Company NV, which managed the ISL
service) filed for bankruptcy (ISL operated a North Europe - West
Africa breakbulk service).
-
Valuship ceased its
activities after the failure of its WCNA-Europe service.
Significant other moves
-
Senator Linie (Germany,
75 % Hanjin ownership) left all the services involving the U.S.
-
Sinotrans left the
China-Europe trade.
-
Fu Hai Line halted its
Far East-South Africa service.
-
Coral Container Line
(Cuba) closed its own Med-Cuba service and opted for slot buying.
-
Global Transporte
Oceanico (Brasil) closed it U.S. Gulf-Brazil multipurpose service.
-
Libyan carrier GNMTC
ran into difficulties.
|
|
| The fleet |
|
|
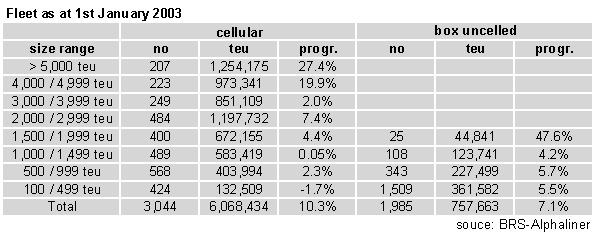
The cellular fleet stood at 6,068,000 teu on 1st January
2003, shared between 3,044 ships. It has doubled during the past seven years, in teu terms, meaning
that the average annual growth has been at roughly 10.5 %. In 2002, the growth reached 10.3 %.
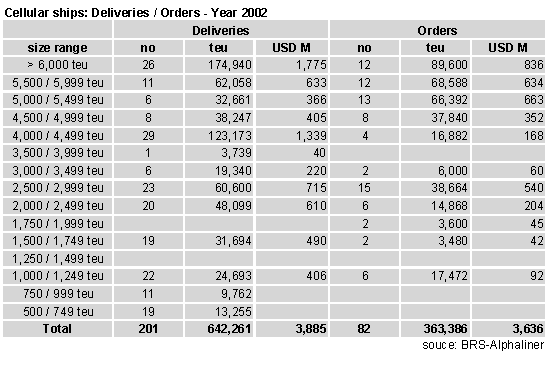
Two hundred and one cellular ships were delivered during the year 2002, for a total capacity of 642,261
teu. At the same time, 59 cellular ships were withdrawn for 74,001 teu, leaving a net fleet increase
of 568,260 teu.
Eighty two cellular ships were ordered for 363,000 teu, Their cumulated value is estimated at $3.6
billion. It is a far cry from the year 2000, when 1,038,000 teu were ordered for a total value of $11.5
billion (some of them were however cancelled in 2002, especially in Polish yards).
In 2003 and 2004, the annual growth should reach a relatively modest 7.5 %, based on the current
orderbook in January 2003 and taking into account a deletion rate of 50,000 teu per annum.
The largest ships in service remain the 19 'Sovereign' class series vessels of Maersk-SeaLand, the
capacity of which stands at around 8,000 teu (although advertised at 6,600 teu by A.P. M'ller).
Four of them were delivered in 2002. A.P. M'ller has six 'large' ships on order, for delivery
in 2003-2004. Their size is undisclosed and it is only when the first ship will be delivered that their
real capacity can be appreciated. Meanwhile, Seaspan has ordered five ships of 8,100 teu at Samsung on
behalf of a long term charter by China Shipping Container Lines (CSCL).
There are currently 28 ships of more than 7,000 teu in service, including 25 units owned by A.P. M'ller
and three by Hapag-Lloyd. There are 29 more on order : six for A.P. M'ller/Maersk-SeaLand, eight for
OOCL, five for Seaspan/CSCL, five for Rickmers Schiffahrts/Cosco, four for P&O Nedlloyd and the
remaining ship for Hapag-Lloyd. German owners have engaged discussions with Hyundai for a series of ships
of 8,450 teu.
With the exception of the six Maersk-SeaLand newbuildings, for which nothing is known, all the 7,000+ teu
ships offer a breadth of 42,80 m, allowing the stowage on deck of 17 rows of boxes. This is no
coincidence : most of the large terminals are fitted with gantry cranes with a 17-row or 18-row reach.
As for the six Maersk-SeaLand newbuildings for delivery this year and next, a breadth of 55 or 56 meters
cannot be ruled out. It corresponds to 22 rows on deck, in line with the gantry cranes in which
Maersk-SeaLand invested so much over the past three years for its own terminals. One can reasonably
speculate that such an investment will be matched with the construction of adequate ships. That means the
10,000 teu barrier could be broken.
|
| The containership second-hand
market in 2002
|
|
|
2002 as a vintage was relatively modest but nonetheless
respectable concerning the second-hand market activity, with some 135 containerships sold for a combined
value of $ 1.56 billion. The relative weakness of the market can be explained for the most part by the
quasi-non-existence of the German market (except the numerous orders of new ships), preoccupied by
placing the 150 ships already in her portfolio with local independent investors. On the other hand, this
year can be viewed as one of consolidation after several seasons rich in mergers and acquisitions.
The breakdown of the sales in 2002 quite accurately reflects the proportions of the existing fleet with
13 ships over 3,000 teu (of which 5 over 4,000 teu) sold, 30 ships between 2,000 and 3,000 teu, 50 ships
1,000 and 2,000 teu and 42 ships under 1,000 teu.
There were relatively few massive 'en bloc' sales this year, with the exception of the 11 ships built
in 1995-1996 of 650 teu for Elite Shipping sold to the Danish operator Clipper for a global price of $
110 million, and the 4 ships of 3,500 teu built in 1993-1994 of L+B sold to MSC following a bareboat
charter for about $ 20.7 million each.
The Greek owner Technomar was extremely active this year with 5 ships bought in 2002 to bring his total
to 13 (of which 4 GX-class, 4 G-class and 4 L-class) bought from Evergreen on a time charter back for 5
to 7 years.
The small number of ships scrapped this year is worth noting, 59 ships with a total containership
capacity of 74,001 teu roughly 1 % of the world capacity. This phenomenon can largely be explained by a
freight market, which on average was rising steadily throughout the year.
A large majority of business contracted in 2002 was combined with charter employments (longer or shorter
depending on investment sizes) to the liner operators, which has now become a recurring feature in this
sector's activity.
As to price variations over the year, it can be summarised by a rising curve, which saw all sectors
appreciate by some 10 to 20 % compared to 2001. Naturally this trend is more or less pronounced according
to the various type and size of ships. As to be expected the sale prices follow the tendency of the
market, with immediate effect in the case of a jump in daily rates (which happened this year), whereas
prices are bolstered up for a longer period in the case of falling freight rates. Consequently although
we have seen rates drop as from November 2002 after the prolonged strike in ports which blocked a large
number of ships on the U.S. West Coast, ship prices have nonetheless remained fairly stable over the last
two months.
|
|
Ships under 1,000 teu
As usual with this size, buyers are fairly heterogeneous. Given their poor
profit-earning capacity in terms of pure investment, it is rarely speculators but rather pure liner
operators who buy these ships. The market price has remained very steady. The improvement in rates has
helped reassure buyers as to the high prices being sought by sellers. It is in these conditions that we
have seen the following:
- 'Flemming Sif', 'Kathrin Sif' 9,750 dwt, 972 teu, 1990
Orskov, change hands at around $ 8.7 million each.
- 'Green Breeze', 'Green Better' and 'Green Bridge', 512
teu, 1984 Hakodate, sold to Bangladesh buyers at around $ 2.5 million each.
- 'Xin Hai Yi', 9,734 dwt, 612 teu, 1985 Japan, sold for $ 3
million in September 2002 to Chinese buyers.
|
|
Ships of 1,000 to 2,000 teu
The market took advantage of a favourable upsurge after having slumped in
the doldrums during the course of 2001. A large number of ships on order which can take the place of sold
units have been delivered or are on the point of being so. Sales have for the most part benefited from
time charters back, covering the interim period up until the delivery of new ships awaited by the
sellers. We can note for example :
- 'Sagittarius' 23,051 dwt, 2001 Szczecinska, 1,730 teu, 20 knots
on 50.5 t, sold by Costa Container Lines for $ 22 million in September to Lipsi
Navigation.
- 'Mapocho' 21,184 dwt, 1999 Hanjin, 1,620 teu, sold to CSAV for $
17.4 million in September.
- 'Iyo', 24,370 dwt, 1995 Shin Kurushima, 1,613 teu, 20 knots on
53 t, sold by Fair Wind Navigation to Tsakos for $ 13.3 million in December 2002.
- 'Box Wave', 'Gallant Wave', 24,083 dwt, 1995 and 1996, Shin
Kurushima, 1,510 teu, 19 knots on 45 t, sold in August to clients of Teo Shipping for $ 14
million each with a charter-party attached for 18 months at $ 8,000 per day.
- 'Kuo Lih', 18,050 dwt, 1995 Imabari, 1,471 teu, 17 knots on 31
t, sold in May to clients of Vroon for about $ 9.7 million, with a charter-party attached for
12 months at a level of $ 7,500 per day.
- 'Lisboa', 'Tavira' and 'Miden Agan', 21,370 dwt, 1982
Warnowwerft, 1,438 teu, 19 knots on 62 t, sold in October by Sarlis Container Line
for about $ 3 million each.
|
|
Ships of 2,000 to 3,000 teu
One can detect a certain hesitancy on the part of buyers in this market as
the future does not have the backing of a fair number of operators. Some fear that the units of 2,500 teu
will be replaced sooner or later by ships carrying more than 3,000 containers. This point of view is
supported by an orderbook which carries relatively few ships of this size. It is true that 1999, 2000,
and 2001 produced a large number of units between 2,000 and 2,800 teu. Operators have consequently been
prudent, in concluding several operations mainly secured against firm employment:
- 'P&O Nedlloyd Xiamen', 'Oriental Bay' and 'Grand
Vision', 44,006 dwt, 59,285 dwt and 44,005 dwt, built in 1991, 1989, and 1991 at Daewoo,
with a capacity of 2,797, 4,206, and 2,986 teu were sold en bloc on subjects to clients of
Zodiac for $ 61 million.
- 'MOL Victory' and 'MOL Independence', 40,638 dwt and 38,014
dwt, 1988 and 1986 Imabari, 2,890 and 2,571 teu, 22 knots, sold en bloc in October by Karakoram
Maritima to clients of Danaos for $ 24 million.
- 'MSC Europe', 45,647 dwt, 1986 Tsuneishi, 2,875 teu, 22.5 knots
on 89.5 t, sold in June by Acasia Shipping to clients of Danaos for $ 12 million.
- 'LT Glory', 'LT Grand', 'LT Globe', 43,310 dwt, 1984
Onomichi, 2,728 teu, 20.5 knots on 74 t, sold en bloc in December by Everglory Line to
clients of Technomar for $ 13 million each with a charter-party attached for 5 years at a rate
of $ 12,500 per day.
- 'CMA CGM Claudel', 34,622 dwt, 2002 STX, 2,602 teu, sold by
Efshipping to Schulte Group for $ 33.85 million, including a transfer of the charter-party to
CMA CGM until February 2007 at $ 16,600 per day.
- 'Christine Schulte', 33,871 dwt, 2001 Hyundai, 2,550 teu, sold
in December by B. Schulte to German investors for $ 33.5 million, including a transfer a 4-year
charter-party to CSAV at $ 16,750 per day.
- 'Ambassador Bridge', 45,643 dwt, 1986 Tsuneishi, 2,518 teu, 22.5
knots on 89.5 t, sold in May to clients of Danaos for $ 11 million with a 18 to 24 month
charter-party at $ 12,000 per day.
|
|
Ships over 3 000 teu
Only 13 sales were achieved out of more than 600 ships existing in this
category. None or very few sellers showed themselves. The market was extremely nervous on the selling
side, with owners reluctant to sell for fear of not finding a replacement unit and this, even if the sale
prices were attractive. Consequently outside of the 'straight' purchase by MSC of 4 ships from L+B,
already under charter to them, the others sales were all undertaken by operators / investors against
charters back. These operations are more and more sought after not only by the traditional German
investors, but also by owners such as Zodiac, Technomar, Danaos, Costamare'
- 'CMA CGM Normandie', 59,600 dwt, 1991 Samsung, 4,734 teu, 24
knots on 158 t sold in September by CMA CGM to clients of Zodiac for $ 31 million with a
3-year charter back at $ 21,775 per day.
- 'MSC Sarah', 'MSC Ingrid', and 'MSC Matilde', 67,795
dwt, 2000 Samsung, 4,400 teu, 25 knots, sold in March to Swiss buyers for $ 40 million each and
fixed for a long period with MSC.
- 'Peloponesian Pride', 53,240 dwt, 1986 Onomichi, 3,428 teu, 21
knots on 74.5 t, sold in August by Evergreen Marine to clients of Technomar for
$ 21 million with a 7-year charter back at $ 15,500 per day.
- 'MSC Martina', 'MSC Sophie', 'MSC Monica' and 'MSC
Rossela', 43,600 dwt, 1993, 1994, 1993 and 1994 at Samsung, 3,424 teu, 22.5 knots on 99
t, sold in February by Hansa Asia to MSC for $ 20.7 each, subjects lifted following a bareboat
charter with purchase option on the 4 ships.
|
|
* * * |
|
Nearly all analysts at the end of 2001 were predicting a
vintage 2002 somewhat depressed and a declining market. Once again as in 2000, the containership market
surprised everybody. In a stagnant world economy, shipping lines were able to re-distribute the cards to
be able to offer a service tailor-made to the situation. The specificity of containers allows such
flexibility. It is also this adaptability that reassures investors, who have found a means of investment
which insures regularity, safety (very few accidents), flexibility to market changes and - the icing on
the cake - tax relief.
At the time of writing, good news has been announced in France regarding the introduction of 'tonnage
tax' system. We can only hope that this tax incentive is as open and accessible as it has been in
Germany, which thanks to this opening, has experienced the shipping activity that we all know.
|
Shipping and Shipbuilding Markets in 2002
I N D E X
|